Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MC Kinsey 7 S
Uploaded by
Arfa AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MC Kinsey 7 S
Uploaded by
Arfa AliCopyright:
Available Formats
BUSINESS STRA TEGY
LESSON 28:
MC KINSEY‘S 7S FRAMEWORK
Learning Objectives versus global industries so on. Exhibit 9.2 presents CSFs for
some industries for the sake of clarification.
On completion of this chapter you should be able to:
Exhibit Critical success factors in different industries
• You should be able to undersatnd CSF’s referred to as a
strategic factors or key factors for success which are very Toothpaste industry. quality in terms of form, flavour, foam
crucial. and freshness, widearea distribution network, high level of
promotion, and brand loyalty.
• You should be able to understand that why companies
fail or succeed depending upon on whether CSF’s has Food processing industry. high quality product, packaging,
been identified or not. efficient distribution network, and sales promotion.
• You should be able to understand that CSF’s are based Shoe industry: high quality product, cost efficiency sophisti-
on practical logic, heuristic than an elaborate procedure. cated retailing, flexible product mix, and creation of product
image.
• You should be able to understand that CSF’s are result
of long years of managerial experience which leads to Automobile industry. styling, strong dealer network, manufac-
the development of intution, judgement and a hunch turing cost control, and ability to meet environmental
that can be used in strategic decision making. standards.
Courier service: speedy dispatch, reliability, and price.
Critical Success Factors Approach Managing these CSFs effectively generates competitive advan-
In order to understand how critical success factors (CSFs) tage. For example, Ohame states that:
approach is applied to generating competitive advantage and the “Key success factors (CSFs) in an industry and business need
concept of CSFs, let us take few examples. A good academician to be identified to inject a concentration of resources into a
can be successful in teaching and research and not necessarily, he particular area where the company sees an opportunity to gain
succeeds as a business man. A player having high competence in significant strategic advantage (competitive advantage) over its
a particular game, say lawn tennis, and is successful is unlikely to. competitors.
succeed in cricket. Even in the same game, a player cannot
succeed in all positions, for example, a good, wicket keeper Identifying Industry CSFs
cannot be a good bowler too. The question is: why does this In order to generate competitive advantage along CSFs, it is
happen? The answer is: each activity has unique requirement, necessary to identify these. Based on a study related to identify-
and a single person cannot meet the requirement of all activities. ing strategic factors which are important to different businesses,
He can be successful only in that for which he has competence Steiner views that “there are indeed strategic factors needed for a
to meet its requirement. (Success is defined in terms of business and they can be identified. However, the question is :
objective achievement.) This social phenomenon can be if CSFs differ from industry to industry, how can these be
replicated in business situation where the question may be identified? In order to find out the answer of this question,
asked: why does a successful business organisation in one managers can put another question: what do we need to do in
industry fails in another industry? The answer of this question order to be successful in a particular business? It is just like an
lies in the opening part of this chapter: an organisation’s core individual putting a question: what does he/she need to do to
competence does not necessarily lead to competitive advantage be successful in studies, in career, etc. However, the answer of
because it may not have any relevance to the industry hi which the question ‘what needs to be done for success in a business’ is
the organisation fails. It appears, then, that requirement of an not as simple as it prima facies appears. Therefore, managers
industry differs from those of other industries. This require- need to generate as much information as possible by going
ment is expressed in terms of critical success factors. through following ways:
1. CSFs can be identified based on logic, heuristics, or even a
Concept of Critical Success factors
rule of thumb rather than through any theoretical model.
Critical success factors, also referred to as strategic factors or key
These are based on long years of managerial experience
factors for success, are those characteristics, conditions, or
which leads to the development of intuition, judgement,
variables which when maintained and sustained can have
and hunch.
significant impact on the success of an organisation competing
in a particual industry. A CSF may be a characteristic such as 2. CSFs can also be identified internally in the organisation by
product features, a condition such as high capital investment, or using creative techniques like brainstorming.
any other variable. A basic nature of CSFs is that they differ 3. CSFs can be deduced from other companies’ statements,
from Industry to industry: consumer goods versus industrial expert opinions, organisational success stories, etc.
goods, differentiated versus undifferentiated industries, local
© Copy Right: Rai University
108 11.351
Using CSF Approach consultant, has prescribed seven factors which lead to success as
BUSINESS STRA TEGY
CSF approach can be used in a number of ways to generate shown in Figure
competitive advantage. Rockart has identified three steps in 1. Strategy a means to achieve objectives.
using CSF approach: generate the critical success factors, refine 2. Structurebasic framework to designate responsibilities and
CSFs into objectives, and identify measures of performance. 17 functions.
While the first step is related to identification of CSFs, other
3. Systemsmanagement tools for planning, decision making,
two are related to using these CSFs. A company can generate
communication, and control.
competitive advantage based on CSFs in the following ways:
4. Staffshuman resources of the organisation.
1. The company can identify key result areas based on CSFs. A
key result area is an aspect of an organisation or its unit that 5. Skillsorganisational and individual capabilities. S. Stylehow
must function effectively for the entire organisation to managers lead and motivate.
succeed. If a key result area has been defined in terms of 6. Shared valuesorganisational values which govern behaviour
CSFs, its focus is more relevant. A key result area may be any of its members.
type, for example, aftersales service In automobile or Based the McKinsey 7S framework, Peter and Waterman have
equipment industry. identified eight characteristics of successful companies (called as
2. The company can allocate its resources, both physical and excellent companies):
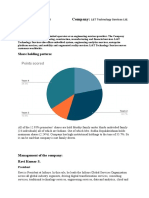
human, on the basis of CSFs. For example, in fastmoving CSF ‘s diagram
consumer goods, there are two critical success factors:
product innovation and efficient distribution system.
Hindustan, Lever has focused on both by deploying its
critical resources in both these areas.
3. A company can generate new CSFs as these are not static but
dynamic. Thus, the new CSF may be more important than
the existing ones. This is based on the maxim of doing
things differently. For example, when Reliance entered textile
fabrics, it introduced the concept of branding which was not
a critical concept in textile at that time. In order to promote
its brand, it went for huge advertising. With the result,
Reliance became number one in textile business very soon.
On the basis of CSFs, a company can differentiate itself from
others by doing the same thing differently or by doing different
thing. However, CSF approach is not free from its limitation
which are in two forms. First, existing or potential competitors
can emulate the strategy through benchmarking and other tools
and a company cannot remain as competitive as it used to be.
Second, if one company can generate a new CSF, others can also
do. Inthis case also, the company may not remain highly
competitive. Thus,allocating huge resources based on CSFs runs
a risk. However, the risk is a 1. Bias for action,
prime element of any strategy. It does not mean that CSF 2. Close to customers
approach is not meaningful because of its limitations. In fact, it
has, What an organisaiton needs to do is that it takes continu- 3. Autonomy and entrepreneurship
ous realigning of CSFs into its operations 4. Productivity through people
Organisational Critical Success Factors 5. Handson, value driven
The above discussion of CSFs is externally focused in the sense 6. Stick to knitting
that it concentrates on what an organisation should do to be 7. Simple form, lean staff, and
successful in a particular industry. Researchers, both academi-
8. Simultaneous loosetight control.
cians and consultants, have made attempt to find out the
answer of the question: what are the characteristics of an However, these characteristics should not be taken on static
organisation which make it successful in different industries or basis for generating competitive advantage. For example, some
meeting the requirements of CSFs of these industries? Though of the companies such as Delta Airlines, Digital Equipment,
the answer of this question is not, precise because of interplay IBM, Included in the list of excellent companies started
of different variables in determining success of an showing declining performance soon after the publication of
organisation, some clues can be derived from various prescrip- the book.
tions and research studies. McKinsey & Company, a USbased AT Kearney, another USbased consultancy firm, conducted a
study which included 1100 companies in Europe. American
© Copy Right: Rai University
11.351 109
continent, and AsiaPacific region to identify organisational performance standards set by the personnel themselves, and
BUSINESS STRA TEGY
growth drivers. In association with Economic Intellegent Unit, sharing of outcomes of performance by all. The company has
the researchers also surveyed 57 CEOs of Indian and set a culture in which no stakeholder aspires to take more than
MNCcontrolled companies. They identified five organisational what it contributes. Work culture is quite friendly and emphasis
growth driversleadership, strategy, competencies and resources, is placed on teamwork.
organisational design, and organisational culture and climate. Organisation Structure. The company has adopted a free
The external factors affecting growth were macro environment, form organisation devoid of hierarchies. Everyone is known as
competitive pressure, customer satisfaction, shareholder associates irrespective of his position in the company. Software
pressure, and technological change in that order. development is undertaken through teams and the constitution
Finance Asia has adjudged Infosys Technologies and Reliance of teams is based on the principle of flexibility. A member who
Industries as the two bestmanaged companies of Asia for the might have been team leader in one project,. may be replaced by
year 2000. While a case on Reliance has been given In Part V of another member of the same team for another project. This
the text, Exhibit 9.3 traces the success factors of Infosys system not only helps in creating the feeling of equality but also
Lets take an example helps in developing project leaders.
Critical Success Factors of Infosys
Infosys Technologies Limited is engaged in development of
application software mostly for business. Software develop-
ment is highly knowledgebased industry in which quality of
human resources is a key determinant of competitive advantage.
Infosys derives most of its revenues from overseas operations.
For achieving excellence, it has concentrated on five key
elementsleadership, human resources, strategy, organisational
culture, and organisation structure.
Leadership. Infosys believes that leadership is one of the most
essential ingredients of organisational success which is provided
by its Chairman, N R Narayanmurthy (affectionately called as
NRN by Infocionsthose who work for the company call
themselves). Leadership is based on high business vision and
predominently supportive styles. There is emphasis on
developing leadership qualities among employees
Throughout the organisation so that there is no role vacuum.
Top management emphasises on opendoor policy, continuous
sharing of information, takes inputs from ernployees in
decision making, and builds personal rapport with employees.
Human Resources. Since Infosys is in knowledgebased
industry, it focuses on the quality of the human resources. Out
of total personnel, about 90 per cent are computer profession-
als. At the entry level, it emphasises on selecting candidates who
find the company’s middleclass culture satisfying, superior
academic records, technical skills, and high level of learnability.
The company emphasises on training and development of its
employees on continuous basis and spends about 2.65 per cent
of its revenues on upgradation of employees’ skills. In an era
when personnel turnover is very high in IT industry, Infosys
has offered stock options to every employee with the result that
not only personnel turnover is negligible but employees are
highly motivated to work.
Strategy. Infosys has adopted a clientfocused strategy to achieve
growth. Rather than focusing on numerous small
organisations, it focuses on limited number of large
organisations throughout world. In order to cater its clients, the
company emphasises on custombuilt softwares.
Organisational Culture. Organisational culture is one of the
strongest features of Infosys. It emphasises on high ethical
values in all operations, equality among all personnel irrespective
of their organisational positions, encouragement of high
© Copy Right: Rai University
110 11.351
You might also like
- EVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESFrom EverandEVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESNo ratings yet
- S#2 Strategic Management Unit-1 by Prof. Vivek V. WankhedeDocument16 pagesS#2 Strategic Management Unit-1 by Prof. Vivek V. WankhedeProf. Vivek V. WankhedeNo ratings yet
- SM ChalisaDocument84 pagesSM ChalisaKartikeya SinghNo ratings yet
- S#4 Strategic Management Unit-1 by Prof. Vivek V. WankhedeDocument23 pagesS#4 Strategic Management Unit-1 by Prof. Vivek V. WankhedeProf. Vivek V. WankhedeNo ratings yet
- MBA 8 Year 2 Managerial Finance January 2020Document269 pagesMBA 8 Year 2 Managerial Finance January 2020weedforlifeNo ratings yet
- Satya Nadella OCD CaseDocument21 pagesSatya Nadella OCD CaseNamrata RanaNo ratings yet
- Hush Puppies ProjectDocument21 pagesHush Puppies Projectjoel joyNo ratings yet
- All 34 501 0 73016232 20221230015333820000000 Iy5yjS PDFDocument25 pagesAll 34 501 0 73016232 20221230015333820000000 Iy5yjS PDFAdilet ZhakengerNo ratings yet
- Strategic FormulationDocument79 pagesStrategic FormulationVartika NagarNo ratings yet
- 7 Powerful Turnaround Strategies To Revive A Dying BusinessDocument20 pages7 Powerful Turnaround Strategies To Revive A Dying Businessheyihov407No ratings yet
- PHARMA 2 Sir RafDocument1 pagePHARMA 2 Sir Rafshirlenedel cariñoNo ratings yet
- Money and Rewards: Your Guide To Earn MoreDocument24 pagesMoney and Rewards: Your Guide To Earn MoreadriancheeNo ratings yet
- Working of Stock Market and Depository ServicesDocument59 pagesWorking of Stock Market and Depository ServicesSweta Singh0% (1)
- F9最新版基础讲义Document158 pagesF9最新版基础讲义Kevin Ch LiNo ratings yet
- CRACKING THE CODE Viz DaggerDocument110 pagesCRACKING THE CODE Viz DaggerSam's WarehouseNo ratings yet
- 360degree Brand ManagementDocument229 pages360degree Brand ManagementLeslie HeNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking GuidelinesDocument2 pagesPublic Speaking GuidelinesSterling GuessNo ratings yet
- 2 What Makes Dialogue UniqueDocument7 pages2 What Makes Dialogue UniqueJoshua Custodio100% (1)
- Summary BRM PidiliteDocument2 pagesSummary BRM PidiliteNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Kalra: Professional SynopsisDocument5 pagesJyoti Kalra: Professional SynopsisJyoti Sanjay KalraNo ratings yet
- Aurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Famotidine Tablets (OTC) (Company Update)Document2 pagesAurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Famotidine Tablets (OTC) (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- SGMT PPT Group 13Document8 pagesSGMT PPT Group 13prachi singhNo ratings yet
- NewgasDocument71 pagesNewgasRishab GargNo ratings yet
- Mini Cases CSRDocument4 pagesMini Cases CSRseemakatariaNo ratings yet
- Email and Other Traditional Tools For Business CommunicationDocument42 pagesEmail and Other Traditional Tools For Business CommunicationHang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 3 - Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning 2020Document82 pages3 - Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning 2020Azmii BelimNo ratings yet
- Hindustan TimesDocument46 pagesHindustan TimesRavindra Varma PvsNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Hero-Motocorp-Ltd-55844bb02b8ee (Repaired)Document66 pagesFdocuments - in - Hero-Motocorp-Ltd-55844bb02b8ee (Repaired)HIMANSHU KUMAR TIWARINo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5-Budgetary PlanningDocument73 pagesTOPIC 5-Budgetary PlanningDashania GregoryNo ratings yet
- Managerial CommunicationDocument24 pagesManagerial CommunicationSai KiranNo ratings yet
- Rags To RichesDocument77 pagesRags To RichesIshan MishraNo ratings yet
- BCOM HONS SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT - Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesBCOM HONS SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT - Operations ManagementYOLANDANo ratings yet
- MSDS - HelizymeDocument10 pagesMSDS - HelizymeNurhari OgiNo ratings yet
- SSC ALL PREVIOUS YEAR ASKED IDIOM & PHRASE PDF (For More Book - WWW - Gktrickhindi.com)Document30 pagesSSC ALL PREVIOUS YEAR ASKED IDIOM & PHRASE PDF (For More Book - WWW - Gktrickhindi.com)ֆαnjєєp ᎡαíNo ratings yet
- A Content Analysis Study of P&G'Document18 pagesA Content Analysis Study of P&G'tran huyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Notes - 18ME734Document10 pagesModule 2 Notes - 18ME734SANTOSHNo ratings yet
- FoW Skills and Learning OnlineDocument44 pagesFoW Skills and Learning Onlinesantiago pachecoNo ratings yet
- DBDocument133 pagesDBфывйцйцNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets Day 2020: December 10th, 2020Document90 pagesCapital Markets Day 2020: December 10th, 2020PirvuNo ratings yet
- 12-Week Plan ModuleDocument35 pages12-Week Plan Moduleapi-639237714No ratings yet
- National Open University of Nigeria Faculty of Agricultural SciencesDocument76 pagesNational Open University of Nigeria Faculty of Agricultural SciencesDurotoye ToheebNo ratings yet
- How To Make Aromatherapy Roll-Ons HelloGlow - CoDocument20 pagesHow To Make Aromatherapy Roll-Ons HelloGlow - CojoNo ratings yet
- Google Talk - The Prejudices of Mr. MarketDocument19 pagesGoogle Talk - The Prejudices of Mr. MarketPrinceSadhotraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Procrastination Among The StudentsDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Procrastination Among The StudentsEDUARDO lll NADATENo ratings yet
- Article 7 - Drivers of The Use and Facilitators, and Obstacles of The Evolution of Big Data by The Audit ProfessionDocument12 pagesArticle 7 - Drivers of The Use and Facilitators, and Obstacles of The Evolution of Big Data by The Audit ProfessionFakhmol RisepdoNo ratings yet
- Title IX FinalDocument18 pagesTitle IX FinalKathryn RyanNo ratings yet
- Your First 100 Million - Dan Peña - Compressed-5Document10 pagesYour First 100 Million - Dan Peña - Compressed-5Hair Queens RDNo ratings yet
- 2024 Year-Ahead Outlook: The Last Leg On The Long Road To NormalDocument14 pages2024 Year-Ahead Outlook: The Last Leg On The Long Road To NormaljeanmarcpuechNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning March 2020Document18 pagesFinancial Planning March 2020rajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- 02 Anwar Ul Tanzeel W Asrul TaveelDocument16 pages02 Anwar Ul Tanzeel W Asrul TaveelAnabiya Ch ChNo ratings yet
- Mental Health First Aid Training Information Flyer FinalDocument1 pageMental Health First Aid Training Information Flyer FinalT RNo ratings yet
- Does Luck Play Important Role in SuccessDocument2 pagesDoes Luck Play Important Role in Successshivam singhNo ratings yet
- Mohit Sharma Zonal HeadDocument4 pagesMohit Sharma Zonal HeadKriday SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thesies On PepperDocument268 pagesThesies On PepperKadamba MarketingNo ratings yet
- Koforidua Technical University: Faculty of Applied Science and TechnologyDocument9 pagesKoforidua Technical University: Faculty of Applied Science and TechnologyGabriel AgyemangNo ratings yet
- Kitab Un NahwaDocument180 pagesKitab Un NahwaShafiq Ahmed AamiriNo ratings yet
- Consumer Goods RetailDocument2 pagesConsumer Goods RetailSanam TNo ratings yet
- Looking at The No Child Left Behind Policy: The Implementers' PerspectivesDocument4 pagesLooking at The No Child Left Behind Policy: The Implementers' PerspectivesAriel E SJ100% (1)
- CBM121 3rd ExamDocument4 pagesCBM121 3rd ExamArafe MayangaNo ratings yet
- GEntrep Chapter 5-8Document165 pagesGEntrep Chapter 5-8Xyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- Infosys - Competitor AnalysisDocument2 pagesInfosys - Competitor AnalysisAkhilM100% (1)
- InfosysDocument2 pagesInfosystejumola250% (1)
- InfosysDocument24 pagesInfosysHIGGSBOSON304100% (2)
- Case StudyDocument18 pagesCase StudyUrvika MathurNo ratings yet
- Infosys LimitedDocument24 pagesInfosys LimitedShivanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- N Ot Co Py: ICMR Case CollectionDocument4 pagesN Ot Co Py: ICMR Case CollectionSreenivasan LNo ratings yet
- Infosys Technologies-International Strategy and Global MeltdownDocument30 pagesInfosys Technologies-International Strategy and Global Meltdownvipulk7975% (4)
- Employer Branding: A Case of Infosys: Kirti Makwana, Dr. Govind DaveDocument8 pagesEmployer Branding: A Case of Infosys: Kirti Makwana, Dr. Govind DaveinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Report On Performance Management System at InfosysDocument12 pagesReport On Performance Management System at InfosysDiksha Singla100% (2)
- Infosys Sales StrategyDocument9 pagesInfosys Sales StrategyPrasad Ganti100% (1)
- Training and Development - Issues in Indian ContextDocument10 pagesTraining and Development - Issues in Indian ContextDanish Ahmed AlviNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis SapmDocument13 pagesTechnical Analysis SapmambikagmetiNo ratings yet
- Infosys Case StudyDocument7 pagesInfosys Case Studypaacho100% (4)
- Building Brand: InfosysDocument3 pagesBuilding Brand: InfosyschanshahNo ratings yet
- Infosys: Strategic Human Resource Management: Presented byDocument14 pagesInfosys: Strategic Human Resource Management: Presented bytanyaNo ratings yet
- Infosys Technologies LTD Growing Share of A Customer'S BusinessDocument8 pagesInfosys Technologies LTD Growing Share of A Customer'S BusinessSaurabh YadavNo ratings yet
- Infosys Technologies - The Best Among Indian CorporationsDocument14 pagesInfosys Technologies - The Best Among Indian CorporationsPriNcess AsmaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Report On InfosysDocument14 pagesIndustrial Report On InfosysMitesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- VG Som BrochureDocument16 pagesVG Som BrochureAzam HassanNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument28 pagesCompensationSomalKantNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesManagement Information Systems: Case Analysismahtaabk100% (1)
- Claims Not Having Pre & Post Hospitalization Expenses Must Be Lodged WithinDocument3 pagesClaims Not Having Pre & Post Hospitalization Expenses Must Be Lodged WithinsrikanthNo ratings yet
- Project Senior PDFDocument89 pagesProject Senior PDFPavani SimhadriNo ratings yet
- Infosys OverviewvkoovfdkDocument86 pagesInfosys OverviewvkoovfdkRahul GabaNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Infosys CSRDocument13 pagesCase 2 Infosys CSRsuryajeet patilNo ratings yet
- Infosys, by Guru PriyaDocument19 pagesInfosys, by Guru PriyaGuru priyaNo ratings yet
- Infosys Analysis For Finlatics FMEPDocument5 pagesInfosys Analysis For Finlatics FMEPyogeshNo ratings yet
- Will RBI Move To Settle Trade Deals in Rupees Work?: No Need For AlarmDocument16 pagesWill RBI Move To Settle Trade Deals in Rupees Work?: No Need For AlarmDeep kardaniNo ratings yet
- Infosys: Group MembersDocument10 pagesInfosys: Group MembersunnatiusbNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Infosys & TCSDocument17 pagesGroup 2 - Infosys & TCSDeepa AroraNo ratings yet
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinFrom EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Summary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyFrom EverandSummary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyFrom EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingFrom EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- Jim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryFrom EverandJim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Small Business For Dummies: 5th EditionFrom EverandSmall Business For Dummies: 5th EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeFrom EverandThe Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeFrom EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdFrom EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessFrom EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesFrom Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 1-Page Strategic Plan: A step-by-step guide to building a profitable and sustainable farm businessFrom Everand1-Page Strategic Plan: A step-by-step guide to building a profitable and sustainable farm businessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Your Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesFrom EverandYour Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureFrom EverandThe 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (289)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)