0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views1 pageFluid Resuscitation for Sepsis Management
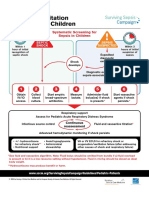
This document outlines a fluid resuscitation algorithm for adults presenting with sepsis. It recommends giving patients presenting with hypotension a minimum of 30mls/kg of isotonic crystalloid intravenously in the first hour, unless they are fluid intolerant. It provides guidance on assessing for signs of hypovolaemia or fluid overload and monitoring lactate levels to guide further fluid administration and treatment. The algorithm emphasizes continuous monitoring, reassessment, and exercising clinical judgement tailored to individual patient comorbidities.
Uploaded by
Sorina BiliutaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views1 pageFluid Resuscitation for Sepsis Management
This document outlines a fluid resuscitation algorithm for adults presenting with sepsis. It recommends giving patients presenting with hypotension a minimum of 30mls/kg of isotonic crystalloid intravenously in the first hour, unless they are fluid intolerant. It provides guidance on assessing for signs of hypovolaemia or fluid overload and monitoring lactate levels to guide further fluid administration and treatment. The algorithm emphasizes continuous monitoring, reassessment, and exercising clinical judgement tailored to individual patient comorbidities.
Uploaded by
Sorina BiliutaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd