Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics 1st Year Full Book
Uploaded by
Mukhtar Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Physics 1st year full book
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesPhysics 1st Year Full Book
Uploaded by
Mukhtar AhmedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
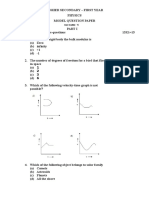
READER GROUP OF COLLEGES KUNDIAN
Subject: Physics 1st Year
Name: Marks: 17
Roll No: Time: 20 Mints
Objective Type
Q.1: Choose the correct answer. 17
i) Significant figures in 0.00876 are:
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6
ii) The percentage in radius of a sphere is 2%. The total percentage uncertainty in volume is:
(a) 2% (b) 4% (c) 6% (d) 8%
iii) Projection of B along A will be given as:
(a) A.B (b) A.B/B (c) A.B/cos 𝜃 (d) None
°
iv) If the angle between two vectors with magnitude 12 and 4 is 60 the their scalar product is
(a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 24 (d) None of these
v) A bullet is shoot straight up returns to its starting point in 10s.the initial speed
was:
(a) 9.8 m/s (b) 24.5 m/s (c) 49 m/s (d) 98 m/s
vi) The equation of motion are not useful for object moving with:
(a) Uniform velocity (b) Uniform acceleration
(c)Variable acceleration (d)Variable velocity
vii) As we move the body above the surface of earth, the change in potential energy will be:
(a) Negative (b) Positive (c) Zero (d) Infinity
viii) 100 radian is equal to
(a) 57.3° (b) 573° (c) 5730° (d) 5.73°
ix) All point on rigid body rotating about a fix axis do not have the same:
(a) Speed (b) Angular speed (c) Angular acceleration (d) angular displacement
x) When the body is falling under the action of gravity with terminal velocity the
acceleration is:
(a) Constant (b) Zero (c) Variable (d) 9.8 m/s2
xi) The wave form of SHM is:
(a) Sine wave (b) Square wave (c) Cosine Wave (d) None
xii) Speed of sound at 0° C is 332 m/s, the speed of sound at 2° C will be:
(a) 333.2m/s (b) 335m/s (c) 33m/s (d) 232 m/s
xiii) Star moving towards the earth shows:
(a) Blue shift (b) Red shift (c) No Shift (d) Longer wavelength
xiv) The wavelength of X-ray is of the order:
(a) 10 m (b) 10-10 m (c) 10-2 m (d) 10cm
xv) For glass air boundary the value of critical angle is
(a) 41.4° (b) 41.6° (c) 41.8° (d) 42.2°
st
xvi) In case of adiabatic process 1 law of thermodynamics is written as:
(a) W = ∆𝑈 ( b) W = Q (c) W =− ∆𝑈 (d) W =− ∆𝑄
xvii) Efficiency of petrol engine is:
(a) 25-30% (b) 45-50% (c) 34-67% (d) 49-60%
READER GROUP OF COLLEGES KUNDIAN
Paper code:4520
Subject: Physics 1st Year
Name: Marks: 68
Subjective Type
Roll No: Time: 2:40 hour
Section I
Q.2 Write short answer to any EIGHT (8) questions: (8×2 = 16)
i. What do you understand by the term precision and accuracy?
ii. Show that the famous “Einstein equation” E = mc2 is dimensionally consistent.
iii. Does dimensional analysis give any information on constant of proportionality that may appears in algebraic
expression? Explain.
iv. What are the dimensions of pressure and density?
v. Define impulse and show that how it is related to linear momentum?
vi. At what point or points in its path does a projectile have its minimum speed, its maximum speed?
vii. Find the relation for force due to water flow.
viii. Find the change in momentum for an object subjected to a given force for a given time and state law of motion in
terms of momentum?
ix. Derive Charle’s law from kinetic theory of gases.
x. Specific heat at constant pressure is greater than specific heat at constant volume. why?
xi. Give an example of a process in which no heat is transfer to or from the system, but temperature of the system
changes?
xii. What happens to the temperature of the room, when an air conditioner is left running on a table in the middle of
the room?
Q.3 Write short answer to any EIGHT (8) questions: (8×2 = 16)
i. Suppose the side of closed polygon represents vector arranged head to tail rule. What is the sum of these vectors?
ii. If all the components of the vector ⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴1 and ⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴2 are reversed, how would the alter ⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴1 × ⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴2 ?
iii. Show that sum and difference of two perpendicular vectors of equal length are also perpendicular and of the same
length?
iv. How much work is done by the upward force when a person holding the pail moving forward?
v. Calculate the work done in kilo joules in lifting a mass of 10 kg (at the steady velocity) through a vertical height
of 10 m?
vi. An object have 1 joule of potential energy. Explain what does it means?
vii. Prove that 1 rad = 57.3°
viii. ?why does diver changes his body position before and after diving in the pool?
ix. Why mud flies off the tyre of a moving bicycle, in what direction does it fly? Explain it.
x. An oil film spreading over a wet footpath shows colours? Explain how does it happen?
xi. Explain whether Young’s experiment is an experiment for studying interference or diffraction of light?
xii. How would you manage to get more orders of spectra using a grating?
Q.4 Write short answer to any SIX (6) questions: (6×2 = 12)
i. Why fog droplet appears to be suspended in air?
ii. What is meant by phase angle? Does it define the angle between maximum displacement and the driving force?
iii. What happens to the time period of the simple pendulum if its length is doubled? What happens if the suspended
mass is doubled?
iv. Describe some common phenomenon in which the resonance plays an important role?
v. Why does sound travels faster in solids than in gases?
vi. How beats are useful in tuning musical instrument?
vii. How should a sound source move with respect to an observer so that the frequency of its sound does not change?
viii. What do you understand by the linear magnification and angular magnification? Explain how a convex lens is
used as a magnifier?
ix. How the power is lost in optical fibre through dispersion? Explain.
READER GROUP OF COLLEGES KUNDIAN
SECTION II
Note: Attempt any Three from the following: (3×8 = 24)
Q.5 (a) Describe the method of addition of vectors by rectangular components. (5 + 3)
(b) Ten bricks, each 6.0 cm thick and mass 1.5 kg, lie flat on a table. How much work is required to stack them
one on the top of another?
Q.6 (a) Find the rotational K.E of the disc and hoop. Also derive the relations for the velocities of disc and hoop
moving down an inclined plane. (5 + 3)
(b) Two block of mass 2.0 kg and 0.5 kg are attached at two end of a compressed spring. The elastic potential
energy stored in the spring is 10J. Find the velocities of the block if the spring delivers its energy to the blocks when
released.
Q.7 (a) What is Doppler effect? Discuss its different cases. (5+3)
(b) What gauge pressure is required in the city mains for a stream from a fire hose connected to the mains to
reach a vertical height of 15.0 m.
Q.8 (a) What is simple pendulum? Show that the motion of pendulum is SHM. Also find relations for its time period and
frequency. (5+3)
(b) A second order spectrum is formed at an angle of 38° when light falls normally on a diffraction grating having
5400 lines per centimeter. Determine wavelength of light used.
Q.9 (a) What is Carnot’s Engine? Explain its working and calculate its efficiency. Also state Carnot’s Theorem.
(5 + 3)
(b) A simple astronomical telescope in normal adjustment has an objective of focal length 100 cm and an eye
piece of focal length 5.0 cm. (i) where is the final image formed? (ii) calculate the angular magnification.
You might also like
- Success Key Test Series Subject: Physics: Annual ExaminationDocument4 pagesSuccess Key Test Series Subject: Physics: Annual ExaminationBhavesh AsapureNo ratings yet
- Ops 1st YearDocument2 pagesOps 1st YearMuhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Half BookDocument4 pagesHalf BookMian Haroon SahilNo ratings yet
- Govt. Degree College For Boys, Jand Pre-Board Exams (Physics-I)Document4 pagesGovt. Degree College For Boys, Jand Pre-Board Exams (Physics-I)Ghulam FaridNo ratings yet
- Objective PhysicsDocument4 pagesObjective PhysicsleoyodapieNo ratings yet
- Xi-Physics-Half Yearly Exam (Sample Paper) - Set-Ii-2023-24Document5 pagesXi-Physics-Half Yearly Exam (Sample Paper) - Set-Ii-2023-24jaiswalswayam05No ratings yet
- 1st Half Book, PhysicsDocument3 pages1st Half Book, PhysicsFast ComputersNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPDocument8 pagesClass 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPSanjukta ChandaNo ratings yet
- Model Paper Physics Objective and SubjectiveDocument4 pagesModel Paper Physics Objective and SubjectiveAsifa AshrafNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Physics Public Exam Question Papers English Medium 221432Document24 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Physics Public Exam Question Papers English Medium 221432Real RemaNo ratings yet
- The Millennium School Annual Physics ExamDocument4 pagesThe Millennium School Annual Physics ExamCrackneet SuratNo ratings yet
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A ADocument37 pagesPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A AMamoon MashoriNo ratings yet
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A ADocument4 pagesPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A AAfzaal GhaziNo ratings yet
- Physics HSSC 1Document5 pagesPhysics HSSC 1Eman AliNo ratings yet
- Ch#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)Document2 pagesCh#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)QamarNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics Test ReviewDocument2 pagesPre Board Physics Test ReviewRana Hassan Tariq100% (1)
- 7 Models-I PU PhysicsDocument40 pages7 Models-I PU PhysicsMir RayyanNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QP I Puc 2023-24 PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Model QP I Puc 2023-24 PDFJayarajNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics Part 1 2023Document3 pagesPre Board Physics Part 1 2023Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics (Solved) - Set A - AglaSem SchoolsDocument6 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics (Solved) - Set A - AglaSem Schoolsamitaich1991No ratings yet
- TestDocument10 pagesTestSIMPINo ratings yet
- Physics 1stDocument4 pagesPhysics 1stAbdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- 11TH Physics Model QPDocument3 pages11TH Physics Model QPermaharajanNo ratings yet
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A ADocument2 pagesPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A AMansoor Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 11thDocument10 pagesPhysics Paper Class 11thMahiNo ratings yet
- Inter Part One Physics Old PaperDocument72 pagesInter Part One Physics Old PaperMian EjazNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneDocument2 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics QP Yly 06.03.2023Document4 pagesClass 11 Physics QP Yly 06.03.2023Kumaravelu PerumalNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics QP in ENglishDocument3 pages11 Physics QP in ENglishParam HeyNo ratings yet
- Time: 2 Hrs Max Marks: 70Document6 pagesTime: 2 Hrs Max Marks: 70Palanichamy MuthuNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFSilva scary svNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document7 pagesPhysics 2iitiansrd2025No ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics-1Document3 pagesClass 11 Physics-1Mask Man LifeNo ratings yet
- 11th Final PhysicsDocument5 pages11th Final Physicsanand tiwariNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Newtown SESSION 2021-202 Final Term ExaminationDocument5 pagesDelhi Public School Newtown SESSION 2021-202 Final Term ExaminationSAMPURNA GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Physics EngDocument6 pagesPhysics EngmuraliNo ratings yet
- Physics Mcqs Practice Test PDFDocument23 pagesPhysics Mcqs Practice Test PDF03145565327No ratings yet
- Class X Unit 1 AKDocument6 pagesClass X Unit 1 AKAshaNo ratings yet
- Cbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12Document8 pagesCbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12sciencepedia9No ratings yet
- Section - A (1×16 16 Marks) Objective Type QuestionsDocument4 pagesSection - A (1×16 16 Marks) Objective Type QuestionsPR LiveNo ratings yet
- Physics XI Sci Question Bank Second SemesterDocument9 pagesPhysics XI Sci Question Bank Second SemesterShriya RodeNo ratings yet
- Physics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyDocument4 pagesPhysics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyRAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Prajin MuruganNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneDocument3 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- Past 10 Years Paper SortDocument16 pagesPast 10 Years Paper Sortdanyalhaider222333No ratings yet
- Model Paper For Examinations 2024Document26 pagesModel Paper For Examinations 2024c4venom05No ratings yet
- St. Lawrance Govt. Girls' Degree College Physics Preliminary Exam 2021Document3 pagesSt. Lawrance Govt. Girls' Degree College Physics Preliminary Exam 2021MinalNo ratings yet
- XI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Document4 pagesXI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Muneeb AlamNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 HALF YEARLY (2023-24)Document4 pagesCLASS 11 HALF YEARLY (2023-24)shivkarnwal2No ratings yet
- Physics - XI - 5 SetDocument15 pagesPhysics - XI - 5 SetSambridhi NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Xi Hy Phy 2023-24Document2 pagesXi Hy Phy 2023-24Guru PrasathNo ratings yet
- 12th Board Physics Paper July 21 2023Document8 pages12th Board Physics Paper July 21 2023Jibin star50% (2)
- PRE BOARD EXAM (2021), PHYSICS XI (Chapter 7+9)Document3 pagesPRE BOARD EXAM (2021), PHYSICS XI (Chapter 7+9)Ghulam FaridNo ratings yet
- Set A QP Pre Annual XiDocument10 pagesSet A QP Pre Annual Xianish.chandrasekar.bloreNo ratings yet
- PhyDocument44 pagesPhyJaimin SentaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics 11thDocument2 pagesPre Board Physics 11thSyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 1Document4 pagesPhysics Set 1raha78056No ratings yet
- Instruction To Solve Physics PaperDocument7 pagesInstruction To Solve Physics PaperMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Solve Physics PaperDocument8 pagesInstructions To Solve Physics PaperMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 25 Teacher Interview Questions (And Answers!) - The MuseDocument11 pages25 Teacher Interview Questions (And Answers!) - The MuseMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Receive International Payments: Top 25 Teacher Interview Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesReceive International Payments: Top 25 Teacher Interview Questions and AnswersMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document98 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2van hoa nguyenNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Submitted By: Jovan Pierre C. Ouano Submitted To: Mark Gil T. DacutanDocument8 pagesThalassemia: Submitted By: Jovan Pierre C. Ouano Submitted To: Mark Gil T. DacutanJvnpierre AberricanNo ratings yet
- Memories of HomeDocument14 pagesMemories of HomeMary Francis Edmer SayconNo ratings yet
- IRRIGATION ENGINEERING MCQDocument40 pagesIRRIGATION ENGINEERING MCQpriya dharshini100% (1)
- Sampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesDocument11 pagesSampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Design & Operation of Clean Room-1Document39 pagesDesign & Operation of Clean Room-1Hafizur Rahman0% (1)
- Bio-Sil ULTRA 1050: Medically Pure Platinum-Cured Silicone Tubing With An Ultra-Smooth Inner SurfaceDocument2 pagesBio-Sil ULTRA 1050: Medically Pure Platinum-Cured Silicone Tubing With An Ultra-Smooth Inner SurfaceLari GrossiNo ratings yet
- Aquafina Marketing Strategy AnalysisDocument31 pagesAquafina Marketing Strategy AnalysisChintan Leo Patel0% (1)
- IQ 250/260 Transducer Quick Start GuideDocument2 pagesIQ 250/260 Transducer Quick Start GuideJoséEmmanuelCasasMunguíaNo ratings yet
- Preferred Drug ListDocument2 pagesPreferred Drug ListRamNo ratings yet
- Mother Teresa JerseyDocument2 pagesMother Teresa JerseyTanya van Zyl100% (1)
- Ras Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)Document4 pagesRas Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)tuan50% (2)
- HydrotherapyDocument7 pagesHydrotherapyGialys MoretaNo ratings yet
- Cheese Yoghurt and Ripening Cultures Reference Chart May 2020Document7 pagesCheese Yoghurt and Ripening Cultures Reference Chart May 2020AbitNo ratings yet
- Understanding of AVO and Its Use in InterpretationDocument35 pagesUnderstanding of AVO and Its Use in Interpretationbrian_schulte_esp803100% (1)
- G5 C11 TestDocument6 pagesG5 C11 TestvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Burford-Exam 3 Spring 2018Document6 pagesBurford-Exam 3 Spring 2018api-430812455No ratings yet
- Oxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopDocument12 pagesOxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopKanjaNo ratings yet
- Is There Bitcoin Atm Mexicali Baja California - Google SearchDocument1 pageIs There Bitcoin Atm Mexicali Baja California - Google Searchannejessica396No ratings yet
- 9709 s15 QP 12Document4 pages9709 s15 QP 12Abrar JahinNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios Tones y Staleks 01.04Document3 pagesLista de Precios Tones y Staleks 01.04Maria T. OliverosNo ratings yet
- Terpin Hydrate Oral SolutionDocument1 pageTerpin Hydrate Oral SolutionAbelard Maria EscrivaNo ratings yet
- Kapla ResumeDocument35 pagesKapla ResumeAbinashNo ratings yet
- Thyrotronic enDocument4 pagesThyrotronic enVladimirNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument3 pagesMidtermTrisha MondonedoNo ratings yet
- 30-300 MHZ Transmission Line Trainer Tla05Document1 page30-300 MHZ Transmission Line Trainer Tla05Kishor HandoreNo ratings yet
- Computational Models For Trunk Trajectory Planning and Load Distribution: A Test-Bed For Studying Various Clinical Adaptation and Motor Control Strategies of Low Back Pain PatientsDocument13 pagesComputational Models For Trunk Trajectory Planning and Load Distribution: A Test-Bed For Studying Various Clinical Adaptation and Motor Control Strategies of Low Back Pain PatientsOTorresGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Violet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceDocument16 pagesViolet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceMySecret Gardenmdp82% (11)
- NOISE ANALYSISDocument16 pagesNOISE ANALYSISDiana Rose TapelNo ratings yet