Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light and Shadows: P3/4 Science
Uploaded by
dotdotDOT000Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light and Shadows: P3/4 Science
Uploaded by
dotdotDOT000Copyright:
Available Formats
P3/4 science
Light and Shadows
1. (a) How is a shadow formed? [1m]
(b) List two factors that affect the size of a shadow formed on a screen. [2m]
Look at the list of objects and materials below.
torchlight cellophane paper chiffon cardboard
frosted glass oil lamp firefly tracing paper
aluminium foil car windscreen magnifying glass lens star
cling wrap wooden door mirror moon
(c) Using a suitable classification table, classify the above objects/materials into separate
groups. Label each group accurately. [4m]
moon
cardboard tracing paper star
mirror chiffon magnifying glass lens firefly
wooden door cellophane paper car windscreen oil lamp
aluminium foil frosted glass cling wrap torchlight
• The distance between the object and the screen
Opaque Translucent Transparent Light source
1. (b) • The distance between the light source and the object
Objects / Materials an opaque object or partially blocked by a translucent object.
1. (c) Answers: 1. (a) A shadow is formed when light is completely blocked by
Taken from Science Process Skills Lower Block 3/4
© Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd SAPSCSP3&4_W36
Website: www.sapgrp.com | Facebook: Singapore-Asia-Publishers Page 1/4
P3/4 science
Light and Shadows
1. When light enters the camera lens, it comes into contact with the photographic film, causing
an image to be captured on the film. A pin-hole camera works on the same principle.
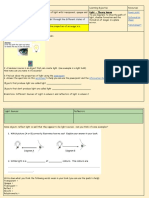
Sally made a toy pin-hole camera as shown below.
cardboard box with a small
hole cut out in front to allow
object light to enter
the back of the box has been
replaced with a sheet of tracing
hole paper to act as a screen
(a) Based on the rays of light from the object to the screen, draw in the space below the
image seen on the screen. (Hint: Look carefully at where the rays of light from the top
and bottom of the object end up on the screen.) [2m]
(b) Describe the image formed on the screen. [1m]
(c) How will the image be affected if the object is moved further away from the pin-hole
camera? [1m]
1. (b) It is upside down (inverted) and smaller in size than the actual object. 1. (c) The image formed will be even smaller in size. Answers: 1. (a)
Taken from Science Process Skills Lower Block 3/4
© Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd SAPSCSP3&4_W36
Website: www.sapgrp.com | Facebook: Singapore-Asia-Publishers Page 2/4
P3/4 science
Light and Shadows
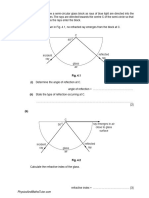
1. (a) A ray of light is shone from a torch and it hits a polished metallic surface.
Draw a clearly labelled diagram in the space below to illustrate this. [2m]
(b) The polished metallic surface is replaced by a sheet of paper.
Draw a clearly labelled diagram to show how the rays of light hitting the paper are
reflected. [2m]
(c) Account for the different observations in (a) and (b). [2m]
sheet of paper
1. (b)
results in having no clear reflection formed.
of light hitting the paper is reflected at a different angle. This polished metallic surface
rough and uneven when viewed under a microscope. Each ray
results in a clear reflection. However, a sheet of paper is quite
reflected at the same angle as the incident ray of light. This
reflected ray incident ray Answers: 1. (a)
1. (c) When light shines on a smooth, polished surface, it is
Taken from Science Process Skills Lower Block 3/4
© Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd SAPSCSP3&4_W36
Website: www.sapgrp.com | Facebook: Singapore-Asia-Publishers Page 3/4
P3/4 science
Light and Shadows
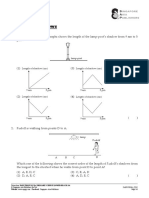
1. The incomplete graph below shows the changes in the length of a shadow of a tree throughout
a sunny day.
Length of tree/m
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 Time of day
9 am
(a) Complete the graph above with [2m]
(i) a line to indicate how the height of the shadow continues to change throughout the
day.
(ii) the missing times on the horizontal ‘Time of day’ axis.
(b) Why does the length of the shadow change throughout the day? [1m]
(c) At what time of the day is the shadow the shortest and why? [1m]
(ii)
9 am 10am 11am 12pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm
Time of day 0
1
2
3
4
overhead in the sky. 5
1. (c) The shadow is shortest at 12 noon when the sun is directly 6
it moves from the east to the west in the sky. 7
1. (b) This is due to the apparent change in position of the sun as (i) 8
Length of tree/m Answers: 1. (a)
Taken from Science Process Skills Lower Block 3/4
© Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd SAPSCSP3&4_W36
Website: www.sapgrp.com | Facebook: Singapore-Asia-Publishers Page 4/4
You might also like
- Power Point Information Sheet Worksheet : Light - Theory LessonDocument11 pagesPower Point Information Sheet Worksheet : Light - Theory Lessonapi-351722096No ratings yet
- S10 Q2 Week-6Document5 pagesS10 Q2 Week-6Aiphrell Anne D. MoradaNo ratings yet
- Light and Shadows: Lamp-PostDocument6 pagesLight and Shadows: Lamp-PostdotdotDOT000No ratings yet
- Lelm 313Document17 pagesLelm 313meenakshi guptaNo ratings yet
- Light and Shadows: P3/4 ScienceDocument5 pagesLight and Shadows: P3/4 SciencedotdotDOT000No ratings yet
- 32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2Document10 pages32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2LiliNo ratings yet
- CBSE XChapterwise (PreviousYears) Qs Science&MathsDocument158 pagesCBSE XChapterwise (PreviousYears) Qs Science&MathsHarshit SalujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lithography - IDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Lithography - Isatyam singhalNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Science Workbook Primary 4 (Chapter 02)Document9 pagesHands-On Science Workbook Primary 4 (Chapter 02)Sheila YongNo ratings yet
- 26 - Ray Optics - Master Slides (06-05-2022)Document16 pages26 - Ray Optics - Master Slides (06-05-2022)Zafar AhmadNo ratings yet
- MC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C05Document7 pagesMC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C05Camille HugoNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For OpticsDocument19 pagesHand Out For OpticsnidharshanNo ratings yet
- 7TH Week LensesDocument7 pages7TH Week LensesMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Workshops and Investigations: Make A DVD Smartphone SpectrometerDocument19 pagesChemistry Workshops and Investigations: Make A DVD Smartphone SpectrometerAli BretNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Paper 1: Section B: Question-Answer BookDocument12 pagesF4 Physics Paper 1: Section B: Question-Answer BooksagiriNo ratings yet
- 9272304-Class 6 - Science - Light, Shadows and Reflections - WS With Ans. - SumaDocument6 pages9272304-Class 6 - Science - Light, Shadows and Reflections - WS With Ans. - SumaPushmeetNo ratings yet
- Rendering Glass and Metal 3dmaxDocument17 pagesRendering Glass and Metal 3dmaxRicardoVoladorNo ratings yet
- 5277685-Class 6 - Science - Light, Shadows and Reflections - WS With Ans. - ShrutiDocument6 pages5277685-Class 6 - Science - Light, Shadows and Reflections - WS With Ans. - Shrutimagicsanctuary79No ratings yet
- Academic Year 2020-2021 Light and Shadow AssessmentDocument10 pagesAcademic Year 2020-2021 Light and Shadow AssessmentLael Christoval WibisanaNo ratings yet
- Question/Answers: Class - Vi Subject - Science LESSON - 12 - (Light, Shadows and Reflection)Document8 pagesQuestion/Answers: Class - Vi Subject - Science LESSON - 12 - (Light, Shadows and Reflection)yashicaNo ratings yet
- SS2 Physics 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument22 pagesSS2 Physics 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFAloysius EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Microscope Sturcture & Essay - AnswerDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - Microscope Sturcture & Essay - AnswerChow Zi JianNo ratings yet
- Homemade PolarimeterDocument5 pagesHomemade PolarimetercsandrasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lithography - I From WaterlooDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Lithography - I From WaterlooAdhi Cahyo WijayaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Act 5Document8 pagesCH 4 Act 5Chemistry courseNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Cloud Chamber: Background InformationDocument3 pagesDiffusion Cloud Chamber: Background Informationraydio 4No ratings yet
- CH-11 Light PPT-2Document33 pagesCH-11 Light PPT-2SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Documentation CompressedDocument11 pagesDocumentation Compressedapi-621966181No ratings yet
- Group 3 Matt Bergson Scott Miller Alec Cowarz Nicole Scott Hemanshu Agnahotri Josh Permaul Mayra VianiDocument7 pagesGroup 3 Matt Bergson Scott Miller Alec Cowarz Nicole Scott Hemanshu Agnahotri Josh Permaul Mayra VianiMayra VianiNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own ProjectorDocument9 pagesMake Your Own ProjectorswapnasridharanNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Teaching TipsDocument5 pagesX-Ray Teaching TipsgbsubbuNo ratings yet
- 2015 Phillip Reu All About Speckles - Edge SharpnessDocument3 pages2015 Phillip Reu All About Speckles - Edge SharpnessGilberto LovatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan LightDocument12 pagesLesson Plan LightRhisia RaborNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class6 Science-Light Shadows-And-Reflection 1Document4 pagesAssignment Class6 Science-Light Shadows-And-Reflection 1Varun kumarNo ratings yet
- Rendering Smoke & Clouds - PaperDocument8 pagesRendering Smoke & Clouds - PaperjuergentremlNo ratings yet
- 87-038Document25 pages87-038sosokad485No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan LightDocument9 pagesLesson Plan LightMarielle CuestaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Anti-Copying Method Based On Average Grayscale DifferenceDocument7 pagesA Novel Anti-Copying Method Based On Average Grayscale DifferenceNam PhanNo ratings yet
- Revision Charts Chapter 4 Light PDFDocument1 pageRevision Charts Chapter 4 Light PDFivanaNo ratings yet
- Lasercut 1Document26 pagesLasercut 1Pedro VítorNo ratings yet
- Lighting Camera MaterialsDocument47 pagesLighting Camera MaterialsNermeen ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Science Extra Question (Ch-8)Document3 pagesScience Extra Question (Ch-8)Divya ChettiyarNo ratings yet
- Class VI-Science- Light,shadows and reflection - Work Sheet-محولDocument2 pagesClass VI-Science- Light,shadows and reflection - Work Sheet-محولdodoNo ratings yet
- Gcse Astronomy Coursework Shadow StickDocument7 pagesGcse Astronomy Coursework Shadow Stickf5dct2q8100% (2)
- Reflection & RefractionDocument24 pagesReflection & RefractionNihar ParijaNo ratings yet
- Light Part 1 AssignmentDocument6 pagesLight Part 1 AssignmentSumit WNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Worksheet 3.1 and 3.2Document4 pagesUnsolved Worksheet 3.1 and 3.2samerafurqan2019No ratings yet
- Optics-Image Formation - Student WorksheetDocument19 pagesOptics-Image Formation - Student WorksheetDanikaNo ratings yet
- Light 4 QP_240314_053608Document10 pagesLight 4 QP_240314_053608diyanooooooorNo ratings yet
- Light 4 QPDocument9 pagesLight 4 QPahmedNo ratings yet
- Optics Refraction Index Glass BlockDocument9 pagesOptics Refraction Index Glass BlockHabibullah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Light and Shadows: W X Y ZDocument5 pagesLight and Shadows: W X Y ZdotdotDOT000No ratings yet
- Optics-Exam Paper-2009Document3 pagesOptics-Exam Paper-2009shadowosNo ratings yet
- General Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)Document2 pagesGeneral Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)exploreharyanaNo ratings yet
- 10 PhysicsDocument3 pages10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- MC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C04Document7 pagesMC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C04Camille HugoNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction in Mirrors and LensesDocument9 pagesReflection and Refraction in Mirrors and LensesEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Budget Astrophotography: Imaging with Your DSLR or WebcamFrom EverandBudget Astrophotography: Imaging with Your DSLR or WebcamNo ratings yet
- Hand Shadows - The Complete Art Of ShadowgraphyFrom EverandHand Shadows - The Complete Art Of ShadowgraphyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GMS175CSDocument4 pagesGMS175CScorsini999No ratings yet
- Major Project Report - Template 2021Document18 pagesMajor Project Report - Template 2021vamkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption and Elimination DisordersDocument120 pagesMalabsorption and Elimination DisordersBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- A Primer On Financial Time Series AnalysisDocument93 pagesA Primer On Financial Time Series AnalysisKM AgritechNo ratings yet
- 4) April 2023 Current AffairsDocument24 pages4) April 2023 Current AffairsPicturesque vibrant shadesNo ratings yet
- Reporte Corporativo de Louis Dreyfus Company (LDC)Document21 pagesReporte Corporativo de Louis Dreyfus Company (LDC)OjoPúblico Periodismo de InvestigaciónNo ratings yet
- Qcs 2010 Section 13 Part 3 Accessories PDFDocument3 pagesQcs 2010 Section 13 Part 3 Accessories PDFbryanpastor106No ratings yet
- Thesis Hakonen Petri - Detecting Insider ThreatsDocument72 pagesThesis Hakonen Petri - Detecting Insider ThreatsalexandreppinheiroNo ratings yet
- B.Ed Syllabus NEW 2015-16 PDFDocument170 pagesB.Ed Syllabus NEW 2015-16 PDFVikas KuthadiNo ratings yet
- 2iccas2005 Paper 377Document5 pages2iccas2005 Paper 377Cristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- Unit Rates and Cost Per ItemDocument213 pagesUnit Rates and Cost Per ItemDesiree Vera GrauelNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issue in StrategyDocument13 pagesContemporary Issue in Strategypatrick wafulaNo ratings yet
- 7 - NIBL - G.R. No. L-15380 Wan V Kim - DigestDocument1 page7 - NIBL - G.R. No. L-15380 Wan V Kim - DigestOjie SantillanNo ratings yet
- REMOVE CLASS 2024 SOW Peralihan MajuDocument4 pagesREMOVE CLASS 2024 SOW Peralihan MajuMohd FarezNo ratings yet
- Arduino Programming Step by Step Guide To Mastering Arduino Hardware and SoftwareDocument109 pagesArduino Programming Step by Step Guide To Mastering Arduino Hardware and SoftwareMohan100% (3)
- Satisfaction ExtraDocument2 pagesSatisfaction ExtraFazir AzlanNo ratings yet
- 0520 Int OTG P4 MSDocument12 pages0520 Int OTG P4 MSTrévina JosephNo ratings yet
- ArchimedesDocument22 pagesArchimedessharfexNo ratings yet
- RTR Piping Inspection GuideDocument17 pagesRTR Piping Inspection GuideFlorante NoblezaNo ratings yet
- IT-02 Residential StatusDocument26 pagesIT-02 Residential StatusAkshat GoyalNo ratings yet
- Mercury Poisoning Symptoms and TreatmentsDocument1 pageMercury Poisoning Symptoms and TreatmentsRakheeb BashaNo ratings yet
- Grab E-Receipt for 15,000 RP Ride on March 30Document1 pageGrab E-Receipt for 15,000 RP Ride on March 30WellyNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingBalasubramanian AnanthNo ratings yet
- Tax1 Course Syllabus BreakdownDocument15 pagesTax1 Course Syllabus BreakdownnayhrbNo ratings yet
- What Is Robotic Process Automation?: ERP SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is Robotic Process Automation?: ERP SystemAna BoboceaNo ratings yet
- Bareos Manual Main ReferenceDocument491 pagesBareos Manual Main ReferenceAlejandro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 EstándarDocument2 pagesUnit 5 EstándardechillbroNo ratings yet
- 24.ratios, Rates and Proportions PDFDocument9 pages24.ratios, Rates and Proportions PDFMilsonNo ratings yet
- Nelson Climate Change Plan UpdateDocument37 pagesNelson Climate Change Plan UpdateBillMetcalfeNo ratings yet
- Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide: IV CalculationsDocument2 pagesMedication Calculation Examination Study Guide: IV Calculationswaqas_xsNo ratings yet