0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views1 pagePythagorean Theorem
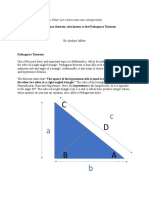
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides equals the square of the length of the hypotenuse. Named after the mathematician Pythagoras, this theorem is fundamental in mathematics and serves as a basis for more complex trigonometric theories. The formula is represented as AC² = AB² + BC², where AC is the hypotenuse, AB is one side, and BC is the other side.
Uploaded by
Debbie RiegoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views1 pagePythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two shorter sides equals the square of the length of the hypotenuse. Named after the mathematician Pythagoras, this theorem is fundamental in mathematics and serves as a basis for more complex trigonometric theories. The formula is represented as AC² = AB² + BC², where AC is the hypotenuse, AB is one side, and BC is the other side.
Uploaded by
Debbie RiegoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd