Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics Formulas
Uploaded by
Shivam Pathak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document lists key thermodynamics formulas including:
1) The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in energy of the universe is equal to the change in energy of the system plus the change in energy of the surroundings.
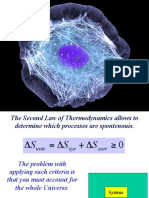
2) The second law states that the entropy of the universe is always increasing, and the entropy change of the universe must be greater than or equal to zero.
3) The third law states that the entropy of a pure crystal at absolute zero is equal to zero.
4) Standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is made from its elements in standard conditions.
Original Description:
thermodynamics formulas
Original Title
thermodynamics-formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document lists key thermodynamics formulas including:
1) The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in energy of the universe is equal to the change in energy of the system plus the change in energy of the surroundings.
2) The second law states that the entropy of the universe is always increasing, and the entropy change of the universe must be greater than or equal to zero.
3) The third law states that the entropy of a pure crystal at absolute zero is equal to zero.
4) Standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is made from its elements in standard conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThermodynamics Formulas
Uploaded by
Shivam PathakThis document lists key thermodynamics formulas including:
1) The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in energy of the universe is equal to the change in energy of the system plus the change in energy of the surroundings.
2) The second law states that the entropy of the universe is always increasing, and the entropy change of the universe must be greater than or equal to zero.
3) The third law states that the entropy of a pure crystal at absolute zero is equal to zero.
4) Standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is made from its elements in standard conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Thermodynamics Formulas
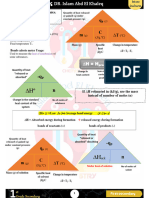
Name Formula
1st Law of Δ Euniverse = Δ Esystem + ΔE surroundings Energy cannot be created nor
Thermodynamics destroyed – only change forms.
2nd Law of Δ Suniverse = Δ Ssys + ΔS surr ≥ 0 Entropy of the universe is always
Thermodynamics increasing.
3rd Law of S = KB lnW = K B ln(1) = 0 S of a pure crystal at 0K is
Thermodynamics 0 J/mol·K
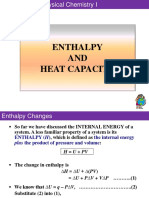
Enthalpy ΔH= q Enthalpy, ΔH, is the measure of
heat energy in a system at constant
pressure.
Standard Enthalpy Δ H ° = ∑ Δ H° f ,products + ∑ Δ H° f , reactants Enthalpy change when one mole of
a substance is made from its
elements in standard conditions.
(Enthalpy Change of Formation)
Entropy q reversible Entropy, ΔS, is the measure of
ΔS= disorder in a system.
T A higher entropy = A greater
amount of disorder.
Solids < Liquids < Gases.
Δ H system
Δ Ssurroundings = −
T
Standard Entropy Δ S ° = ∑ Δ S °products + ∑ Δ S°reactants (Standard Molar Entropies)
Gibb's Free Energy Δ G = ∑ Δ Gproducts + ∑ Δ Greactants Used to to predict whether a
process will occur spontaneously
at a constant temperature and
pressure.
Δ G = ΔH − T Δ S
Δ G = ΔG° + RT ⋅ln(Q) Q = Reaction Quotient
R = 8.3145 J/mol·K
Standard Free Energy Δ G ° = ∑ ΔG° f ,products + ∑ Δ G°f , reactants
Specific Heat q = mc Δ T The amount of heat energy needed
Capacity, to raise the temperature of 1 gram
c of a substance by 1℃.
Used in "coffee-cup" calorimetry.
m = mass in grams.
(Specific Heat Capacities)
Heat Capacity, q = CΔT The amount of energy required to
C raise the temperature of a
substance by 1℃.
Used in "bomb" calorimetry.
You might also like
- Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry GC2Document44 pagesChapter 5 - Thermochemistry GC2helalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - THERMOCHEMISTRY (Handout)Document6 pagesChapter II - THERMOCHEMISTRY (Handout)anon_40967343No ratings yet
- Chapter 20 (Entropy & Free Energy)Document7 pagesChapter 20 (Entropy & Free Energy)Richard KimNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem 2 ReviewerAthen Chelsea DuranNo ratings yet
- Laws of 1st Chemistry 2nd TermDocument3 pagesLaws of 1st Chemistry 2nd TermUnicorn KittyNo ratings yet
- 40 Minutes ThermodynamicsDocument20 pages40 Minutes ThermodynamicsDheeraj dixitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHM476 (Part 3 and 4)Document25 pagesChapter 1 CHM476 (Part 3 and 4)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Part 2Document6 pagesThermochemistry Part 2GeraldNo ratings yet
- Chemistry From BBDocument8 pagesChemistry From BBLorenz lingaoNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Two Page Summary 4.13.2022-1Document2 pagesThermochemistry Two Page Summary 4.13.2022-1GREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics HandoutDocument8 pagesThermodynamics HandoutAmartya NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 S10 WebDocument7 pagesChapter 8 S10 WebRobo KnapNo ratings yet
- Energy-Changes-And-Rates-Of-Reaction CheatsheetDocument4 pagesEnergy-Changes-And-Rates-Of-Reaction CheatsheetMaryam SameerNo ratings yet
- Measuring E For Chemical Reactions: Constant-Volume CalorimetryDocument35 pagesMeasuring E For Chemical Reactions: Constant-Volume CalorimetryMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Energy RelationshipsDocument28 pagesChapter 6 Energy RelationshipsRidhaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Study of Heat Change in Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesThermochemistry: Study of Heat Change in Chemical ReactionsAllen SiaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Revision 2021 Part 1Document70 pagesThermodynamic Revision 2021 Part 1Rawda AliNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsManish SainiNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergiesDocument24 pagesChemical EnergiessaraNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Pres StudentDocument12 pagesCH 6 Pres StudentReyzhel Mae MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 - Thermochemistry PlusPortalDocument15 pagesChapter - 6 - Thermochemistry PlusPortalYunNo ratings yet
- Closed System: Isolated System:: ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesClosed System: Isolated System:: ThermodynamicsMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- 6 - Gibbs Free Energy PDFDocument12 pages6 - Gibbs Free Energy PDFJey BlaQNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument8 pagesThermo ChemistryANGELA JOIE BAIZASNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Activity SheetDocument15 pagesEnthalpy Activity SheetPrincess Fenix Sabio100% (1)
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument45 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsGlecie RasNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynaics PDFDocument24 pagesNEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynaics PDFGajendran PandiNo ratings yet
- AP Chem ThermodynamicsDocument58 pagesAP Chem ThermodynamicsLynda BkrNo ratings yet
- Cet-Iv - MCQDocument6 pagesCet-Iv - MCQRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument34 pagesThermoNez ArdenioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemical Energetics: ChemistryMuneeb MunawarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics: 1 Semester-Module 5Document8 pagesChemical Thermodynamics: 1 Semester-Module 5Irish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document37 pagesModule 5Marklynnard BautistaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesThermodynamicsAssdfNo ratings yet
- Part 1. - Chem - ThermodynamicsDocument64 pagesPart 1. - Chem - ThermodynamicsTaymeng LyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - Entropy - 2022 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 5 - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - Entropy - 2022 PDFJey BlaQNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument38 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- 9 Thermochemistry EditedDocument108 pages9 Thermochemistry EditedNur AleyaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry 2 - Entropy and EnthalpyDocument18 pagesThermochemistry 2 - Entropy and Enthalpyx seyiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: 222 PHYSDocument24 pagesThermodynamics: 222 PHYSAdhanom G.100% (1)
- Pertemuan 9 Termodinamika KimiaDocument44 pagesPertemuan 9 Termodinamika KimiaVemas SatriaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageChemical ThermodynamicsYukiko HachiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Biophysics Free EnergyDocument12 pagesLecture 06 Biophysics Free EnergyBelaliaNo ratings yet
- 3 ThermodynamicsDocument23 pages3 Thermodynamicsizabellacorreia68No ratings yet
- 7 - ThermochemistryDocument31 pages7 - ThermochemistryLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Chem2 Q3 Week 5 6Document6 pagesChem2 Q3 Week 5 6Gwyneth CataneNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument48 pagesThermochemistryNurfarhanah KNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Spontaneity: Entropy and Free Energy: What Drives A Reaction To Be Spontaneous? Enthalpy (Entropy (Document9 pagesAP Chemistry Spontaneity: Entropy and Free Energy: What Drives A Reaction To Be Spontaneous? Enthalpy (Entropy (KahfiantoroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Enthalpy and Heat CapacityDocument46 pagesLecture 3 Enthalpy and Heat CapacitylisaNo ratings yet
- 3 +thermochemistryDocument33 pages3 +thermochemistryAustin LipnicaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Group 1 NebresDocument35 pages2nd Law of Thermodynamics Group 1 NebresrbxwmnNo ratings yet
- Free EnergyDocument24 pagesFree EnergyVivek PattanashettiNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Spontaneity: Universitas Negeri SemarangDocument19 pagesEquilibrium and Spontaneity: Universitas Negeri SemarangMuhammad Sultan Al-hafizhNo ratings yet
- PHY - CHEM - Reviewer - Lecture 11Document5 pagesPHY - CHEM - Reviewer - Lecture 11Ori SeinNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument63 pagesThermo ChemistryTony OkunsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Chemical Thermodynamics: 17.1 When Is A Process Spontaneous?Document4 pagesChapter 17: Chemical Thermodynamics: 17.1 When Is A Process Spontaneous?Carlos Mella-RijoNo ratings yet
- Week 011-012 Presentation Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesWeek 011-012 Presentation Chemical ThermodynamicsFigh terNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Crib SheetDocument5 pagesPhysical Chemistry Crib SheetMuhammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet