0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesSolar Energy Micro Project
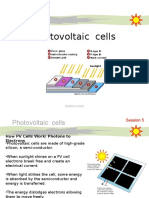
Solar power is a renewable energy source that converts sunlight into electricity or heat. There are two main technologies: photovoltaics (PV) which use solar panels to directly convert sunlight to electricity, and concentrated solar power (CSP) which uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight and make steam to power turbines. Solar power generation has grown exponentially in recent years and now accounts for 4% of global electricity, helping to limit climate change. However, more effort is still needed to integrate solar power into electrical grids and address policy and financing challenges.
Uploaded by
omkar chavanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesSolar Energy Micro Project
Solar power is a renewable energy source that converts sunlight into electricity or heat. There are two main technologies: photovoltaics (PV) which use solar panels to directly convert sunlight to electricity, and concentrated solar power (CSP) which uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight and make steam to power turbines. Solar power generation has grown exponentially in recent years and now accounts for 4% of global electricity, helping to limit climate change. However, more effort is still needed to integrate solar power into electrical grids and address policy and financing challenges.
Uploaded by
omkar chavanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd