Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ashley Zuniega Me Lab2
Ashley Zuniega Me Lab2
Uploaded by
Ashley ZuniegaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ashley Zuniega Me Lab2
Ashley Zuniega Me Lab2
Uploaded by
Ashley ZuniegaCopyright:
Available Formats
FRANCIS FUENTES
BSME 4B
ME LAB
Physical Study of the Steam Generating Unit
Different types of Steam-generating unit:
Fire tube These are most often used in processes that need anywhere from 15 to 2,200 horsepower (1hp =
746 watts, or W). This type of boiler is cylindrical, with the flame in the furnace cavity itself and the
combustion gases themselves kept inside a series of tubes. These come in two basic designs: dry back and wet
back.
Water tube. In this arrangement, tubes contain steam, water or both, while the products of combustion pass
around the outside of tubes. These often have multiple sets of drums, and because they use relatively little
water, these boilers offer unusually fast steaming capabilities.
Commercial. These usually feature combinations of watertube, firetube and electric-resistance designs. They
are popular in large buildings requiring a mostly constant temperature, such as schools and libraries, office
and government buildings, airports, apartment complexes, college and other research laboratories hospitals,
and so on.
Condensing. Condensing boilers can reach thermal efficiency levels of to 98 percent, compared to 70 to 80
percent attainable using standard boiler designs. Typical efficiency levels reach about 90 percent when the
return water temperature is at 110 F or lower, and rise with decreasing water-return temperature thereafter.
Flexible water tube (flex tube). This construction is particularly resistant to "heat shock," making it a natural
option for heating uses. Flexible water tube boilers come in a wide range of fuel inputs and are well-suited for
low-pressure applications using either steam or hot water. (Not all "boilers" actually boil water!) These are
also quite easy to maintain, with easy access to their working parts from the outside.
Electric. These boilers are famously low-impact: clean, quiet, easy to install, and small in relation to their
utility. Because nothing is actually burned (that is, there is no flame to worry about), electric boilers are
marvelously simple. There are no fuels or fuel handling equipment in the mix, and hence no exhaust and no
need for associated pipes and ports. In addition, these have heating elements that are easy to replace.
Heat recovery steam generator (HRSG). This is an innovative energy-recovery "heat exchanger" that
recovers heat from a stream of hot gas passing by. These create steam that can be used to drive a particular a
process or used to drive a steam turbine to power electricity generation using an electromagnet. HRSGs are
built on a foundation of three primary components – an evaporator, a superheater and an economizer.
RELATED RESEARCH
Steam generators
1. James Charles Smith, in Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors, 2022
2. J.C. Smith, in Steam Generators for Nuclear Power Plants, 2017
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 03 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument2 pages03 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5808)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- MD Coaching Discussion 1Document2 pagesMD Coaching Discussion 1Ashley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Exp. 1 Centrifugal FanDocument3 pagesExp. 1 Centrifugal FanAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Ashley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Completion Me LabDocument2 pagesCompletion Me LabAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- File For ScrewDocument22 pagesFile For ScrewAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Delos Reyes 2 StoreyDocument8 pagesDelos Reyes 2 StoreyAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Capsu Logo Word Docs 1Document4 pagesCapsu Logo Word Docs 1Ashley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report (Ojt)Document4 pagesAccomplishment Report (Ojt)Ashley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
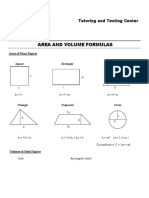
- Area and Volume FormulasDocument3 pagesArea and Volume FormulasAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Area and Volume FormulasDocument3 pagesArea and Volume FormulasAshley ZuniegaNo ratings yet