Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Andriod 3
Uploaded by
Mark Ghever PopuliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Andriod 3
Uploaded by
Mark Ghever PopuliCopyright:
Available Formats
Transaction No.2.
When the entity renders services on credit, it creates an entity’s normal operating cycle is not clearly identifiable, it is assumed to be
account receivable which is an asset account and a revenue account which twelve (12) months. The entity uses an accounting period that covers certain
increases owner’s equity. accounting functions which can be either a calendar or fiscal year.
Transaction No. 3. When an electric bill is received, an expense account Calendar year means the accounting operations of the business covers
is created, but it was not paid, therefore, the incurrence of an expense one year from January and ends in December.
decreases the owner’s equity account and increases the liability account due Fiscal year or period means any 12-month period covering the
to non – payment. accounting operations of the business.
Transaction No. 4. Borrowings increase the asset account Cash and the Example: May 2019 to May 2020 is one fiscal period.
Notes Payable due to issuance of promissory note which is a liability
account. Current Assets
Transaction No.5. The owner withdraws cash for personal use, therefore Cash. It refers to any medium of exchange that a bank will accept for
asset cash decreases and a withdrawal account is created which is a contra- deposit at face value including coins, currency, checks, money orders, bank
equity account. Owner’s equity account has a normal balance of “credit”, deposits and drafts.
the withdrawal account is a contra account and has a normal balance of Cash Equivalents. Per PAS No. 7, these are short-term , highly liquid
“debit”. investments that are readily convertible to known amount of cash and which
are subject to insignificant risk of changes in value
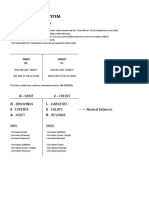
TYPICAL ACCOUNT TITLES USED Notes Receivable. A written pledge that the customer will pay the
Statement of Financial Position (briefly discuss) business a fixed amount of money on a certain date.
Assets. As per revised Philippine Accounting Standards (PAS) No. 1, Accounts Receivable. These are claims against customers arising from
assets should be classified only in two (2): Current and Non-Current Assets. sale of services or goods on credit. This type of receivable offers less
Assets are considered current when: security than a promissory note.
a. it expects to realize, consumes or intends to sell it within the normal Allowance for Uncollectible accounts /Bad debts. A contra-asst
operating cycle of the business account which provides for possible losses from uncollected accounts
b. it holds the asset primarily for the purpose of trading receivable. The amount provided for this is only an estimate.
c. it expects to realize the asset within twelve (12) months after the Inventories. Per PAS No. 2, these are assets (a) which are held for sale in
reporting period the ordinary course of business; (b) in the process of production for such
d. the asset is cash or cash equivalent (as defined in PAS No.7), unless sale; or (c) in the form of materials or supplies to be consumed in the
the asset is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at production process or in the rendering of services.
least twelve months after the reporting period.
Operating Cycle is the time between the acquisition of assets for
processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. When the
Prepaid Expenses. These are expenses paid for by the business in d. the entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement
advance. It is classified as an asset because the business avoids having to of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period.
pay cash in the future for a specific expense. Accounts Payable. It denotes obligations or debts of the business arising
from services received, merchandise, supplies or property, plant and
Noncurrent Assets equipment acquired on account. It is an “open account” obligation because it
Property, Plant & Equipment. Per PAS No. 16, these are tangible assets is not supported by a promissory note.
that are held by an enterprise for use in the production or supply of goods or Notes Payable. The treatment is similar to accounts payable however, this
services, or for rental to others, or for administrative purposes and which are account is supported with a promissory note executed by the debtor in favor
expected to be used during more than one period. of the creditor.
Examples: Land, Machinery, Equipment, furniture and fixtures. Accrued liabilities. Amounts owed to others for unpaid expenses. This
Accumulated Depreciation. It is a contra-account that contains the sum account includes salaries payable, utilities payable, interest payable and
of the periodic depreciation charges. The balance from this account is taxes payable.
deducted from the cost of the related asset – equipment or building – to Unearned Revenues. The business entity receives payment before
obtain book value. providing the customers with goods or services, the amount received is
Intangible Assets: Per PAS No. 38, these are identifiable non-monetary reorder to unearned revenue account. When the goods or services are
assets without physical substance held for use in the production or supply of provided to the customer, the unearned revenue account is reduced and
goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes. income is recognized.
Examples: Goodwill, patents, copyrights, licenses, franchises, Current Portion of Long-term Debt. These are portion of mortgage
trademarks, brand names, secret processes, subscription lists and on- notes, bonds and other long-term indebtedness which are to be paid within
competitive agreements. one year from the balance sheet date.
Liabilities Noncurrent liabilities
Current Liabilities. As per revised PAS No 1, an entity shall classify Mortgage Payable. This account is used to record long-term debt that is
liability as current when supported or backed up by a collateral or has pledged certain assets as
a. it expects to settle the liability in its normal operating cycle. security to the creditor.
b. it holds the liability primarily for the purpose of trading. Bonds Payable. Is a contract between the issuer and the lender specifying
c. the liability is due to be settled within twelve (12) months after the the terms and conditions of repayment and the amount of interest to be
reporting period. charged. It is a long-term obligation evidenced by certificate of
indebtedness. Business obtain funds to finance acquisition of equipment and
other needed assets by issuing bonds.
Equity. The equity represents what is left to the business after the liabilities are fully
paid.
Capital. This account is used to record the original and additional investments of the
owner of the business. It is increased by the amount of profit earned during the year or
decreased by a loss or by cash or other assets that the owner may withdraw from the
business. This account bears the name of the owner.
Example: if the owner of the business is Mr. Landicho, therefore, the capital account
of the business will be Landicho, Capital.
Withdrawals. When the owner of a business entity withdraws cash or other assets for
personal use, such is recorded in the withdrawal account rather than directly reducing the
owner’s equity account.
Income Summary. Is a temporary account used at the end of accounting period to close
income and expenses.This account shows the profit or loss for the period before closing to
the capital account.
Statement of Comprehensive Income
Income. Increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of
inflows and enhancement of assets. The definition of income encompasses both revenue
and gains. Though these terms are almost similar, however, there is a distinct technical
difference between them.
Service Income. Revenues earned by performing services for a customer or client.
Example: accounting services by a CPA, laundry services by a laundry shop.
Sales. Revenues earned as a result of sale of merchandise.
Example: sale of hardware materials by a hardware company sale of medicines by a
pharmaceutical company
Expenses. A decrease in economic benefits during the accounting period as a result of
outflows or depletion of assets.
Cost of Sales. The cost incurred to purchase or produce the products sold to the
customers during the period. It is also known as the cost of goods sold.
Salaries and Wages Expense. All payments that arise from services from workers/
employees in an employee-employer relationship. It includes salaries and wages, 13th
month pay, cost of living allowances and other related benefits.
Rent Expense. Expense
You might also like
- FABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument36 pagesFABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionVron Blatz100% (6)
- Accounts ReceivableDocument14 pagesAccounts Receivableaccesstariq100% (1)
- Accounting - : Basic Terms in Accounting - 1. TransactionDocument14 pagesAccounting - : Basic Terms in Accounting - 1. TransactionKaran Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Nationwide Bank StatementDocument1 pageNationwide Bank Statementwilliams edwards100% (1)
- Estmt - 2023 06 15Document14 pagesEstmt - 2023 06 15lorielys0909No ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting Notes 4051 by Regayitima ChinhutoDocument309 pagesPrinciples of Accounting Notes 4051 by Regayitima ChinhutoEMMANUEL GONESE100% (2)
- Mega Project Assurance: Volume One - The Terminological DictionaryFrom EverandMega Project Assurance: Volume One - The Terminological DictionaryNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 - EXERCISES3 - Working Capital Management - TheoriesDocument36 pagesTopic 3 & 4 - EXERCISES3 - Working Capital Management - TheoriesHazel Jane EsclamadaNo ratings yet
- Chart of AccountsDocument18 pagesChart of AccountsMargerie FrueldaNo ratings yet
- My Zone Credit Card Statement: Payment SummaryDocument2 pagesMy Zone Credit Card Statement: Payment Summarymohammad shamimNo ratings yet
- September 2020 Call RecordDocument9 pagesSeptember 2020 Call RecordIshwarya RajeshNo ratings yet
- Module 17 - ReceivablesDocument8 pagesModule 17 - ReceivablesLuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Elements of FsDocument53 pagesLesson 8 Elements of FsSoothing BlendNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument5 pagesThe Accounting EquationHuskyNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument31 pagesInternship Reportm qaiser75% (4)
- CMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleDocument12 pagesCMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleEunice AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- The Accounts and The Double-Entry SystemDocument14 pagesThe Accounts and The Double-Entry SystemLOURIE JANE GULLEMNo ratings yet
- 7 Stages in Loan OriginationDocument4 pages7 Stages in Loan OriginationFirdaus PanthakyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Loans and ReceivablesDocument55 pagesModule 4 Loans and Receivableschuchu tvNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - ReceivablesDocument15 pagesModule 2 - ReceivablesJehPoyNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument4 pagesHandoutZack CullenNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 - Module 7Document38 pagesAccounting 1 - Module 7CATHNo ratings yet
- BFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemDocument5 pagesBFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemSheryl cornelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)Document10 pagesLesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)yana jungNo ratings yet
- Typical Account Titles UsedDocument3 pagesTypical Account Titles Usedwenna janeNo ratings yet
- T.L.E. IV: Accounting Elements AssetsDocument5 pagesT.L.E. IV: Accounting Elements AssetsMavic Escuadro LaraNo ratings yet
- A. Under Statement of Financial Position: Typical Account Titles UsedDocument6 pagesA. Under Statement of Financial Position: Typical Account Titles UsedAshlyn MaeNo ratings yet
- Types and Effects Of: Transacti ONSDocument62 pagesTypes and Effects Of: Transacti ONSJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting 1 CDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Accounting 1 CAle EalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Statement of Financial PositionDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Statement of Financial PositionMartha Nicole MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terminology: Tangible AssetsDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting Terminology: Tangible Assetskavya guptaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II The Accounting Process Service and TradingDocument22 pagesUNIT II The Accounting Process Service and TradingAlezandra SantelicesNo ratings yet
- Actg 1 Module 3Document5 pagesActg 1 Module 3Mae BertilloNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument8 pagesBasic Accounting Termsjosephinemusopelo1No ratings yet
- Bsba Acctg 111Document2 pagesBsba Acctg 111Hansel UngartNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet and Financial StatementDocument3 pagesBalance Sheet and Financial StatementRochelle AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 Module 1Document7 pagesFABM 2 Module 1xernathanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Althea mary kate MorenoNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1Document7 pagesLearning Material 1salduaerossjacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Current Liabilities, Provisions, and Contingencies The Nature, Type and Valuation of Current LiabilitiesDocument12 pagesChapter One: Current Liabilities, Provisions, and Contingencies The Nature, Type and Valuation of Current LiabilitiesJuan KermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Financial Statement Analysis Balance SheetDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Financial Statement Analysis Balance SheetKhadija YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesCurrent LiabilitiesHimanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial StatementsDocument6 pagesElements of Financial StatementsAdelina AquinoNo ratings yet
- Updated Lecture Partnership and CorporationDocument10 pagesUpdated Lecture Partnership and CorporationAppleNo ratings yet
- FM 101 Chapter 3Document41 pagesFM 101 Chapter 3maryjoymayo494No ratings yet
- Types of Accounts and The Account TitlesDocument25 pagesTypes of Accounts and The Account TitlesSeung BatumbakalNo ratings yet
- Present ObligationDocument6 pagesPresent ObligationArgem Jay PorioNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Audit of Receivable and SalesDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Audit of Receivable and Salessolomon adamuNo ratings yet
- Session 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlDocument10 pagesSession 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlYamu HiadeenNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation and Double-Entry SystemDocument31 pagesAccounting Equation and Double-Entry SystemKendall JennerNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument5 pagesBalance Sheet114-CHE-TANMOY PATRANo ratings yet
- Fa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquityDocument6 pagesFa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquitycheskaNo ratings yet
- Accounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFDocument5 pagesAccounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFJake ShimNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of The Definition of AccountingDocument9 pagesEssential Elements of The Definition of AccountingPamela Diane Varilla AndalNo ratings yet
- Finance TermsDocument7 pagesFinance TermsTanveer HussainNo ratings yet
- Accounting Terns and DefitionDocument10 pagesAccounting Terns and DefitionReign MontejoNo ratings yet
- The Original Attachment: BasicsDocument32 pagesThe Original Attachment: BasicsVijayGogulaNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting Termskrishiv malkani100% (1)
- CCD - Bookeeping Module, Lesson 3 & 4Document6 pagesCCD - Bookeeping Module, Lesson 3 & 4Jessa Eve LitangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 AccountingDocument12 pagesLesson 3 AccountingDrin BaliteNo ratings yet
- Examples of LiabilitiesDocument11 pagesExamples of LiabilitiesSuzette MamangunNo ratings yet
- Ent M5Document5 pagesEnt M5Fransesca ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sebi Grade A 2020: Accounting and Its Terminology (PART 2)Document10 pagesSebi Grade A 2020: Accounting and Its Terminology (PART 2)Tarun SurjaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Dicționar de Termeni de BusinessDocument15 pages1.1 - Dicționar de Termeni de BusinessTeodora TudorNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Week 4Document7 pagesFABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Week 4Sheila Marie Ann Magcalas-GaluraNo ratings yet
- OpTransactionHistoryUX520 03 2022Document5 pagesOpTransactionHistoryUX520 03 2022Shakhir MohunNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate 30 January 2024Document2 pagesExchange Rate 30 January 2024mail.bdoaa2022No ratings yet
- Ontents: Appendixes 1 - 9Document24 pagesOntents: Appendixes 1 - 9Stevens ElevatorNo ratings yet
- Assignment September 2020 Semester: Subject Code MKM602 Subject Title Marketing Management Level Master'S DegreeDocument15 pagesAssignment September 2020 Semester: Subject Code MKM602 Subject Title Marketing Management Level Master'S Degreemahnoor arifNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector in IndiaDocument20 pagesBanking Sector in IndiaARSHITHA IRENE 2017117No ratings yet
- Aishwarya Precision Works GECLSDocument7 pagesAishwarya Precision Works GECLSchandan bhatiNo ratings yet
- Medical Invoice TemplateDocument2 pagesMedical Invoice TemplateDanielNo ratings yet
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesDocument2 pagesMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesJATIN GOYAL100% (1)
- BNK 601 - Tutorial 1 Solutions 2020Document5 pagesBNK 601 - Tutorial 1 Solutions 2020Inoke RawaigagaNo ratings yet
- 50-State Review of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Regulation - Stevens Center For Innovation in FinanceDocument30 pages50-State Review of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Regulation - Stevens Center For Innovation in FinanceellirafaeladvNo ratings yet
- 1180-Article Text-5977-1-10-20220928Document12 pages1180-Article Text-5977-1-10-20220928Putra YudaNo ratings yet
- SB Order 12-2020 - SBDocument4 pagesSB Order 12-2020 - SBBaskar ANgadeNo ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas BankDocument36 pagesAndhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas BankG MOTHYNo ratings yet
- 28 Dec 2022 - 28 Dec 2022Document2 pages28 Dec 2022 - 28 Dec 2022TAJ ENTRPRISESNo ratings yet
- Commerce Bank CaseDocument4 pagesCommerce Bank Casecrest_troughNo ratings yet
- Gazatt ChallanDocument2 pagesGazatt ChallanArshad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- MONEY AND CREDIT Worksheet - 1639023786Document11 pagesMONEY AND CREDIT Worksheet - 1639023786pratimaNo ratings yet
- SB / Ca / CC / Sb-Nre / Sb-Nro / Other: DdmmyyyyDocument2 pagesSB / Ca / CC / Sb-Nre / Sb-Nro / Other: DdmmyyyyDaleep RathoreNo ratings yet
- BDO Unibank, Inc. (Bangco de Oro)Document2 pagesBDO Unibank, Inc. (Bangco de Oro)Bevegel Sasan LlidoNo ratings yet
- NullDocument114 pagesNullapi-24920014No ratings yet
- BPI FAMILY SAVINGS BANK vs. FIRST METRO INVESTMENT CORP.Document6 pagesBPI FAMILY SAVINGS BANK vs. FIRST METRO INVESTMENT CORP.DANICA FLORESNo ratings yet
- Account Statement As of 07-08-2021 03:18:09 GMT +0530Document2 pagesAccount Statement As of 07-08-2021 03:18:09 GMT +0530brazil server0No ratings yet