Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uranium Is A Silvery
Uploaded by
IAN2130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
Uranium is a silvery
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageUranium Is A Silvery
Uploaded by
IAN213Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Uranium
is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the
periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the
chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92
electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium has the
highest atomic weight of all naturally occurring elements.
Uranium occurs naturally in low concentrations in soil, rock
and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-
bearing minerals such as uraninite. Uranium ore can be
mined from open pits or underground excavations. The ore
can then be crushed and treated at a mill to separate the
valuable uranium from the ore. Uranium may also be
dissolved directly from the ore deposits in the ground (in-
situ leaching) and pumped to the surface. Uranium mined
from the earth is stored, handled, and sold as uranium oxide
concentrate (U3O8).
Uranium was discovered in 1789 by Martin Klaproth, a
German chemist, who isolated an oxide of uranium while
analyzing pitchblende samples from the Joachimsthal silver
mines in the former Kingdom of Bohemia, located in
present-day Czechia. He named his discovery “uran” after
the planet Uranus.
For many years, uranium was used primarily as a colorant
for ceramic glazes and for tinting in early photography. Its
radioactive properties were not recognized until 1866, and
its potential for use as an energy source was not manifested
until the mid-20th century. Uranium is now used to power
commercial nuclear reactors that produce electricity and to
produce isotopes used for medical, industrial, and defense
purposes around the world.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EinstienniumDocument4 pagesEinstienniumIAN213No ratings yet
- Oxygen O2: 1structuresDocument3 pagesOxygen O2: 1structuresIAN213No ratings yet
- CobaltDocument4 pagesCobaltIAN213No ratings yet
- Unit 2: MeiosisDocument38 pagesUnit 2: MeiosisIAN213No ratings yet
- Different Types of MediaDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of MediaIAN213No ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Resistors in Direct Circuits ObjectivesDocument5 pagesSeries and Parallel Resistors in Direct Circuits ObjectivesIAN213No ratings yet
- Arsenal Football Club Is A Professional: ForbesDocument1 pageArsenal Football Club Is A Professional: ForbesIAN213No ratings yet
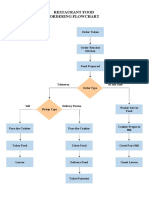
- Restaurant Food Ordering FlowchartDocument1 pageRestaurant Food Ordering FlowchartIAN213No ratings yet