Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syndromes and Manifestations
Uploaded by
Leila Supetran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSyndromes and Manifestations
Uploaded by
Leila SupetranCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Genetic Mutation
Syndrome/Disease Type of Mutation Symptoms/Manifestations
Beta thalassemia Insertion They do not gain weight and grow at the
- a blood disorder that reduces the expected rate (failure to thrive) and may
production of hemoglobin develop yellowing of the skin and whites of
the eyes (jaundice).
Cystic Fibrosis Deletion sinus infections, poor growth, fatty
- The most common genetic stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes,
abnormality causing cystic and infertility in most males.
fibrosis involves the deletion of just
three DNA bases (a codon) from the
CFTR gene.
Sickle cell anemia Substitution Anemia, pain, swelling of hands and feet,
- an inherited red blood cell disorder frequent infections, delayed growth or
in which there aren't enough healthy puberty, vision problems
red blood cells to carry oxygen
throughout your body.
Chromosomal Mutation
Syndrome/Disease Type of Symptoms/Manifestations
Mutation
Opitz-Kaveggia syndrome Inversion dysmorphic features, including
- is a rare cause of X-linked relative macrocephaly, hypertelorism,
intellectual disability and downslanted palpebral fissures, prominent
associated anomalies in males due forehead with frontal hair upsweep, and broad
to a mutation in the MED12 gene thumbs and halluces.
located at chromosome Xq13.
Cri du chat syndrome Deletion high-pitched cat-like cry, mental retardation,
- rare genetic disorder caused by delayed development, distinctive facial features,
missing pieces on a particular small head size (microcephaly), widely-
chromosome. spaced eyes (hypertelorism), low birth
weight and weak muscle tone (hypotonia) in
infancy.
Pallister-Killian mosaic syndrome Duplication severe intellectual disability, poor muscle tone,
- usually caused by the presence of an "coarse" facial features, and a prominent
abnormal extra chromosome forehead. They tend to have a very thin upper lip,
12 called isochromosome 12p.
with a thicker lower lip and a short nose.
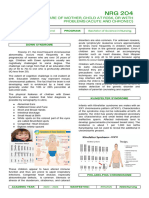
Down Syndrome Trinomy 21 flattened face, almond shape eyes that slant up,
- babies with Down syndrome have short neck, small ears, a tongue that tends to
an extra copy of one of these stick out, tiny white spots on the iris, small hands
chromosomes, chromosome 21. and feet
Klinefelter Syndrome Klinefelter Taller than average stature, longer legs, shorter
- is a genetic condition that results torso and broader hips, absent, delayed or
when a boy is born with an extra incomplete puberty, small firm testicles, small
copy of the X chromosome. penis, enlarged breast tissue
Turner Syndrome Turner Short stature and non-functioning ovaries which
- a condition that affects only causes infertility, some may also have extra skin
females, results when one of the X on the neck, puffiness or swelling of hands and
chromosomes (sex chromosomes) feet, skeletal abnormalities, heart defects, high
is missing or partially missing. blood pressure, kidney problems
You might also like
- Developmental Delays and Aging ChangesDocument231 pagesDevelopmental Delays and Aging ChangesAbedDabaja100% (1)
- XI.C. Common Chromosomal Disorders Resulting in Physical or Cognitive Developmental DisordersDocument2 pagesXI.C. Common Chromosomal Disorders Resulting in Physical or Cognitive Developmental DisordersErvina Luisa Delias CampusNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot DR - Pete Peterson, Part 2 - David Wilcock TranscriptDocument22 pagesProject Camelot DR - Pete Peterson, Part 2 - David Wilcock TranscriptChristian UFO Illuminati100% (1)
- NBME Quests ActualDocument66 pagesNBME Quests ActualDeborah Peters100% (3)
- Rapid Fire FactsDocument10 pagesRapid Fire FactsMichael LinebargerNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Disorders: Causes and CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesChromosomal Disorders: Causes and CharacteristicsYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics For Biologists PDFDocument396 pagesBioinformatics For Biologists PDFHannibal BarkaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument61 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitiesManisanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Table of Genetic DisordersDocument14 pagesTable of Genetic DisordersMuqaddam Ahmed Salim0% (1)
- Human Genetic Disorders: A Visual GuideDocument49 pagesHuman Genetic Disorders: A Visual GuideJessie AzarragaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations LectureDocument30 pagesCongenital Malformations LecturemulaewolloNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders PDFDocument38 pagesGenetic Disorders PDFEllen Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Abnormalities in Humans and AnimalsDocument15 pagesChromosomal Abnormalities in Humans and AnimalsGautam ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnostic in DysmorphologyDocument74 pagesPhysical Diagnostic in Dysmorphologynendaayuwandari100% (1)
- Abnormalities Involving Sex ChromosomesDocument5 pagesAbnormalities Involving Sex ChromosomesManveth DawnAnne Narvaez BahunsuaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Syndromes NotesDocument58 pagesPediatric Syndromes NotesLGK maoreNo ratings yet
- Deletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoDocument55 pagesDeletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- IlluminaDocument68 pagesIlluminaAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders and Chromosome AbnormalitiesDocument8 pagesGenetic Disorders and Chromosome AbnormalitiesSource NatoNo ratings yet
- Incomplete DominanceDocument53 pagesIncomplete Dominancemarian buenafeNo ratings yet
- DNA Programming Kit Manual PDFDocument65 pagesDNA Programming Kit Manual PDFavrajamohamedNo ratings yet
- CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES (40 charactersDocument21 pagesCHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES (40 charactersKenneth Sapnu50% (2)
- High School Genetics Lesson on Heredity and VariationDocument4 pagesHigh School Genetics Lesson on Heredity and VariationPablo Ragay JrNo ratings yet
- Dys Morphis MDocument27 pagesDys Morphis MdrmindhackerNo ratings yet
- Birth DefectDocument35 pagesBirth DefectAdvocate subhan abbasiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders in Humans PresentationDocument16 pagesGenetic Disorders in Humans PresentationKaty W. IvesNo ratings yet
- Thea Brigette Vergara: Name: Date SubmittedDocument9 pagesThea Brigette Vergara: Name: Date SubmittedMj YuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Chromosomal DiseasesDocument60 pagesLecture 2 Chromosomal DiseasesПарул КатіярNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument32 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitieszahraaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling ExplainedDocument7 pagesGenetic Counseling ExplainedfdgrgNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities in Chromosomal StructureDocument19 pagesAbnormalities in Chromosomal StructureMarry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Disorder ProjectDocument23 pagesChromosomal Disorder ProjectUmair RizwanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Assessment and CounselingDocument23 pagesGenetic Assessment and CounselingNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project ChromosomaDocument20 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Chromosomaashishkumar140806No ratings yet
- Genetic Diseases in HumansDocument3 pagesGenetic Diseases in Humansjosh chavezNo ratings yet
- Mutations and Genetic Disorders 4Document28 pagesMutations and Genetic Disorders 4MaleehaNo ratings yet
- VitiligoDocument42 pagesVitiligoabdi40113No ratings yet
- Introduction To Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Chromosomal DisordersKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentRona MaeNo ratings yet
- Genetic Abnormalities Explained: Down Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Patau Syndrome, Edward’s SyndromeDocument11 pagesGenetic Abnormalities Explained: Down Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Patau Syndrome, Edward’s SyndromeCarmsNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument6 pagesGenetic DisordersaireishcNo ratings yet
- NRG 204 - Genetics and TestingDocument2 pagesNRG 204 - Genetics and TestingkeishyaaacarlosNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic Disorders: Biology By: Dr. Sandhya GodsheDocument55 pagesHuman Genetic Disorders: Biology By: Dr. Sandhya GodshevishalukeyNo ratings yet
- Noonan Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment NORDDocument24 pagesNoonan Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment NORDSerik AdaiNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomal DisordersMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Types of Chromosome Abnormalities by Pura VitiDocument23 pagesTypes of Chromosome Abnormalities by Pura VitipurerclintonsNo ratings yet
- Syndromes Aarskog Syndrome (9p)Document10 pagesSyndromes Aarskog Syndrome (9p)M BeirutiNo ratings yet
- cOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSDocument11 pagescOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSChari RivoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diseases Types & CausesDocument34 pagesGenetic Diseases Types & CausesNeo RealyouNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetic AbnormalitiesDocument48 pagesCytogenetic AbnormalitiesGlomelyn Rose Ortiz TañedoNo ratings yet
- Path SummaryDocument30 pagesPath SummaryFranklinSappNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument2 pagesDiseasesMikaela EuniceNo ratings yet
- FINALLLDocument58 pagesFINALLLImie AldoyesaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 3Document32 pagesGenetics 3Dipesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- SyndromesDocument19 pagesSyndromesapi-26826496No ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument20 pagesGenetic Disorderszaryabali771No ratings yet
- DISORDERS: 10 Conditions SummarizedDocument4 pagesDISORDERS: 10 Conditions SummarizedJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- 10 15 07 1100 Birth Defects ERFDocument2 pages10 15 07 1100 Birth Defects ERFGodwillingNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeDocument27 pagesChromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- Kaycee LorescaDocument6 pagesKaycee LorescaKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Kaycee LorescaDocument6 pagesKaycee LorescaKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Coffin-Lowry SyndromeDocument3 pagesCoffin-Lowry SyndromeTamo JanNo ratings yet
- Presidency School Mangalore: Chromosomal DisordersDocument28 pagesPresidency School Mangalore: Chromosomal DisordersAiman SyedNo ratings yet
- Sex Chromosome Aberration: By: Moncera, Miguel Gabriel R. Dela Rosa, Hannah ShaneDocument14 pagesSex Chromosome Aberration: By: Moncera, Miguel Gabriel R. Dela Rosa, Hannah ShaneKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document2 pagesScience 2Vinz RegenciaNo ratings yet
- Syndromes (Bio)Document1 pageSyndromes (Bio)Leila SupetranNo ratings yet
- Social Media (MIL)Document1 pageSocial Media (MIL)Leila SupetranNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Expression (MIL)Document1 pageFreedom of Expression (MIL)Leila SupetranNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory SystemLeila SupetranNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Biotechnology SyllabusDocument2 pagesAgricultural Biotechnology SyllabusKamlesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Transcripción Alberts 2014 PDFDocument240 pagesTranscripción Alberts 2014 PDFLaliito LeNo ratings yet
- MCB 110 Study GuideDocument10 pagesMCB 110 Study GuideAlexPowersNo ratings yet
- Potential of CRISPR Cas System in The Diagnosis of COVID 19 InfectionDocument12 pagesPotential of CRISPR Cas System in The Diagnosis of COVID 19 InfectionHillaryNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HealthDocument31 pagesGenetics and HealthSagiraju SrinuNo ratings yet
- Rachel Wilson - Research Paper - 2960536Document11 pagesRachel Wilson - Research Paper - 2960536api-538867842No ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1riyashreeNo ratings yet
- X-Gal Manual - 5prime - 1044374 - 032007Document8 pagesX-Gal Manual - 5prime - 1044374 - 032007Miguel Montero VazquezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanDocument37 pagesForm 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Portfolio 2019 - 2020 Ashrika DudejaDocument44 pagesAp Biology Portfolio 2019 - 2020 Ashrika Dudejaapi-520142437No ratings yet
- 11 OperonDocument24 pages11 OperonSanghaviNo ratings yet
- Make A Difference EssayDocument9 pagesMake A Difference Essayapi-285563924No ratings yet
- Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Document36 pagesAmplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Muhammad Achin YasinNo ratings yet
- Module in EnglishDocument28 pagesModule in EnglishIannNo ratings yet
- Blood 2015 05 646240 1 PDFDocument97 pagesBlood 2015 05 646240 1 PDFSpinu LiliaNo ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis Restriction Enzymes and PCRDocument8 pagesGel Electrophoresis Restriction Enzymes and PCRAshley ClarkNo ratings yet
- Genetics Foldable Task CardsDocument9 pagesGenetics Foldable Task CardsshasagailNo ratings yet
- Chloetroulan - Essential Biology 3.3 DNA Structure SLDocument3 pagesChloetroulan - Essential Biology 3.3 DNA Structure SLChloe TroulanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Module 4Document19 pagesEarth and Life Module 4Nicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Students Topic 1 and 2 NotesDocument25 pagesUNIT 5 Students Topic 1 and 2 Noteskayecec996No ratings yet
- Evolution CreationistDocument152 pagesEvolution CreationistdanielsctNo ratings yet
- Biotech Apps Conserve BiodiversityDocument4 pagesBiotech Apps Conserve BiodiversitysaranyaNo ratings yet
- Jaleisha Joan Vélez VelázquezDocument1 pageJaleisha Joan Vélez Velázquezapi-550244804No ratings yet
- BIOA01 Lec 3Document3 pagesBIOA01 Lec 3Brendan L.No ratings yet