Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integ-Reviewer ..
Uploaded by
Patricia Mae CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integ-Reviewer ..
Uploaded by
Patricia Mae CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
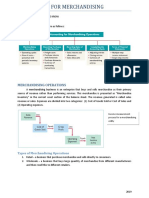
Accounting for Merchandising Purchasing Transactions
Operations
• Inventory account is • Inventory is always
Income Statements increased for the cost of recorded at the final cost
the merchandise to the buyer, purchase
• Single-step income • Gross Margin = Gross purchased plus the price less allowances
statement Profit = Net Sales – Cost freight cost necessary to received from the seller
• Multiple-step income of Goods Sold transport the inventory and any cash discounts
statement • Gross Margin ratio = to the buyer’s place of taken.
Gross Margin / Net business (FOB shipping
Sales point).
Operating Cycle • Trade discounts are deducted as part of the initial
purchase transaction; they are not a purchase
• Purchase merchandise • Pay cash to vendors discount.
from vendors for • Repeat again and again
inventory on account or • Note that these steps Purchase returns
for cash overlap so that the cash
• Sell inventory to collections from • Inventory account is decreased for the cost of the
customers on account customers may occur merchandise returned to the seller less any
• Collect cash from before and/or after the allowances or discounts already recorded in the
customers cash payments to ledger.
vendors.
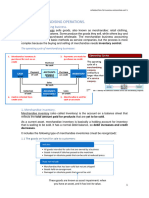
Sales Transactions
Merchandise Inventory
• Inventory account is • The selling price of the
• Merchandise Inventory • Inventory is a current decreased, and cost of merchandise sold
(Inventory or MI) refers asset since the company goods sold is increased represents revenue to the
to the goods the intends to sell it within for the cost of the seller and is recorded in
company has purchased one year. merchandise sold. a separate transaction.
and intends to sell to • The freight cost • Trade discounts are
others. necessary to transport deducted as part of the
the inventory to the initial sale transaction;
Cost of Goods Sold buyer’s place of they are not a sales
business is an expense discount nor a contra-
• Inventory that has been sold becomes an expense, in the period of sale revenue.
Cost of Goods Sold, in the period of sale. (FOB Destination).
Transportation Out or
Inventory Systems Freight Out are typical
accounts used to record
• Periodic Inventory • Perpetual Inventory the expense.
System records all System records all
inventory transactions as purchase-related Sales Returns
they occur in the inventory transactions as
Merchandise Inventory they occur in separate • Inventory account is • Sales returns and
account. accounts and records the increased, and cost of allowances is increased,
cost of goods sold only goods sold is decreased and cash or A/R is
at the end of the period. for the cost of the decreased for the selling
• Shrinkage is the cost of inventory not on hand and merchandise returned by price of the merchandise
not sold. It is part of cost of goods sold under either the buyer. returned by the buyer.
inventory system.
NOTE: ALWAYS KNOW WHETHER YOU ARE
THE BUYER OR THE SELLER IN THE
TRANSACTION. SOME OF THE ACCOUNTS
USED AND SOME OF THE DOLLAR AMOUNTS
RECORDED WILL DIFFER DEPENDING ON
WHETHER YOU ARE THE BUYER OR SELLER IN
THE TRANSACTION.
Transportation (Freight) Costs Merchandise Inventory 800
Cash 800
• FOB Shipping Point – • FOB Destination – Merchandise Inventory 100
Purchaser is responsible Seller is responsible for Cash 100
for paying the shipping paying the shipping $200 of merchandise purchased is returned prior to
charges. They are charges and they are payment:
usually prepaid by the recorded as the expense Cash 200
seller and added to the Transportation Out. Merchandise Inventory 200
invoice. Buyer adds the Buyer does not make an Example 2: $800 of inventory is purchased on
shipping costs to entry. account, FOB shipping point. The seller pays $100 to
inventory. If seller • Transportation the shipping company on behalf of the buyer, which is
prepays, seller has a (freight) costs are not added to the seller’s invoice. The credit terms offered
receivable from buyer. subject to a cash by the seller are 2/10, n/30. Therefore, the total cost
discount. of the inventory purchased is $800 purchase price +
$100 shipping charges:
Merchandise Inventory 900
Credit Terms
A/P 900
$200 of merchandise purchased is returned prior to
• Generally, take the • Only purchases are
payment.
form of 2/10, n/30 subject to the discount;
A/P 200 Merchandise Inventory 200
where transportation or freight
When the invoice is paid within the discount period
o 2 is the discount costs paid by the seller
$800 purchase - $200 return = $600
% on behalf of the buyer
merchandise * 2% = $12 discount
o 10 is the are not subject to a
$700 owed ($600 + $100 shipping) - $12
discount period discount.
discount = $688 paid
in days • Cash discounts reduce
o n is the net the cost of inventory for
A/P 700
(total) amount to the buyer (credit
Cash 688
pay merchandise inventory).
Merchandise Inventory 12
o 30 is the number • Cash discounts reduce
of days after the revenue for the seller
Example 3: $800 of inventory is purchased on
invoice date that (debit sales discounts, a
account, FOB destination. In a separate transaction,
the net amount is contra revenue account).
the seller pays $100 of shipping charges to the
due shipping company. The buyer records only the cost of
the merchandise. The credit terms offered by the
seller are 2/10, n/30. Therefore, the total cost of the
Purchase Transactions inventory purchased is $800 purchase price.
When companies purchase goods, they intend
to sell to customers, the transaction is recorded Merchandise Inventory 800
in the Merchandise Inventory account, a A/P 800
current asset. Inventory is recorded at cost, $200 of merchandise purchased is returned prior to
which includes the price paid for the goods payment.
plus all necessary costs of getting the A/P 200
inventory to the company’s place of business Merchandise Inventory 200
and ready to sell. The rules of FOB determine When the invoice is paid within the discount period
whether freight costs are included in the cost assuming credit terms of 2/10, n/30:
of inventory. $800 purchase - $200 return = $600
Example 1: $800 of inventory is purchased for cash, merchandise * 2% = $12 discount
FOB shipping point. In a separate transaction, the $600 owed - $12 discount = $588 paid
purchaser pays $100 of shipping charges to the A/P 500 Cash 490
shipping company, which are added to the cost of the Merchandise Inventory 10
inventory. Therefore, the total cost of the inventory Practice Problem #1
purchased is $800 purchase price + $100 shipping Journalize the following purchase related transactions:
charges:
a. Jingle Co. purchased $4,000 worth of merchandise shipping charges. The total cost of the inventory
on account, terms 2/10, n/30, FOB shipping point. when purchased was $640 (800 – (20% * 800)):
Prepaid transportation charges of $200 were added to A/R 900
the invoice. Sales 800
b. Returned $500 of merchandise purchased in (a). Cash 100
c. Paid on account for purchases in (a), less return (b) Cost of Goods Sold 640
and discount. Merchandise Inventory 640
Sales Transactions
When companies sell merchandise inventory, $200 of merchandise purchased is returned prior to
the transaction requires two journal entries: payment.
the first entry records the revenue from the Sales Returns and Allowances 200
sale at the selling price and the second entry A/R 200
decreases the inventory account and records Merchandise Inventory 160
the expense of the sale at cost. Cost of Goods Sold 160
Revenue (sales) is recorded at the time the When the invoice is paid within the discount period
transaction occurs, regardless of whether $800 purchase - $200 return = $600 merchandise *
payment is received from the buyer. Revenue 2% = $12 discount
is always greater the cost of the goods being $700 owed ($600 + $100 shipping) - $12 discount
sold. = $688 paid
Inventory is decreased for the cost of the Cash 688
inventory sold, which includes the price paid Sales Discounts 12
for the goods plus all necessary costs of A/R 700
getting the inventory to the company’s place Example 3: $800 of inventory is sold on account,
of business and ready to sell as noted above. FOB shipping point. In a separate transaction, the
The rules of FOB determine whether freight seller pays $100 to the shipping company. Therefore
costs are recorded as transportation out, a the total account receivable is $800 selling price. The
selling expense. total cost of the inventory when purchased was $640
The seller would record the examples in (800 – 20% * 800):
Purchase Transactions above as follows. Note
that the seller had a gross margin ratio of 20%. A/R 800
Example 1: Inventory is sold for $800 cash (FOB Sales 800
shipping point. In a separate transaction, the Cost of Goods Sold 640
purchaser pays $100 of shipping charges to the Merchandise Inventory 640
shipping company. The total cost of the inventory Transportation Out 100
when purchased was $640 (800 –(20% * 800)): Cash 100
Cash 800 $200 of merchandise purchased is returned prior to
Sales 800 Cost of Goods Sold 640 payment.
Sales Returns and Allowances 200
Merchandise Inventory 640 A/R 200
Merchandise Inventory 160
$200 of merchandise purchased is returned by the Cost of Goods Sold 160
customer prior to payment: When the invoice is paid within the discount period
$800 purchase - $200 return = $600 merchandise *
Sales returns and Allowances 200 2% = $12 discount
Cash 200 Merchandise Inventory 160 $600 owed - $12 discount = $588 paid
Cash 588 Sales Discounts 12
Cost of Goods Sold 160 A/R 600
Example 2: $800 of inventory is sold on account, Practice Problem #2
FOB shipping point. The seller pays $100 to the Journalize the following sales related transactions.
shipping company on behalf of the buyer, which is a) Sold merchandise on account to Jangle Co.,
added to the seller’s invoice. The credit terms offered $5,000, terms FOB Shipping Point, 2/10, n/30.
by the seller are 2/10, n/30. Therefore, the total The cost of the merchandise sold was $3,000.
account receivable is $900 selling price + $100
Paid transportation charges of $200, which separate inventory shrinkage expense account
were added to the invoice. reported within cost of goods sold.
b) Sold merchandise on account to Comet Co.,
$10,000, terms FOB Destination, 1/10, n/30. Example: The balance in the Merchandise Inventory
The cost of the merchandise was $6,000. account in the general ledger was $300,000 before
c) Paid transportation charges of $400 for adjustment. A Physical Inventory was taken and the
delivery of merchandise sold to Comet Co. value of the merchandise on hand was $294,000.
d) Issued credit memorandum for $2,000 to Adjusting entry required:
Comet Co. for merchandise returned from sale
in (b). The cost of the merchandise was Cost of Merchandise Sold 6,000
$1,200. Merchandise 6,00
e) Received amount due from Jangle Co. within Inventory 0
the discount period.
f) Received amount due, less return and discount Multi-Step Income Statement
from Comet Co. The Multi-Step Income statement provides a
g) Sold merchandise on account to Jangle Co., substantial amount of additional significant
$5,000, terms FOB Shipping Point, 2/10, n/30. information to the user of the financial
The cost of the merchandise sold was $3,000. statements. It also incorporates revenues and
Paid transportation charges of $200, which expenses unique to the merchandising
were added to the invoice. company versus a service provider.
h) Sold merchandise on account to Comet Co., Key changes compared to the single-step income
$10,000, terms FOB Destination, 1/10, n/30. statement include:
The cost of the merchandise was $6,000. • Gross-to-Net Sales to account for contra-revenue
i) Paid transportation charges of $400 for accounts
delivery of merchandise sold to Comet Co. • Gross Profit to report the margin or profit remaining
j) Issued credit memorandum for $2,000 to after covering the cost of merchandise sold that is
Comet Co. for merchandise returned from sale available to cover operating expenses
in (b). The cost of the merchandise was • Separating Operating Expenses into selling expenses
$1,200. and administrative expenses to provide an additional
k) Received amount due from Jangle Co. within level detail
the discount period. • Income from Operations to report the profitability of
l) Received amount due, less return and discount the company’s reason for being in business
from Comet Co. • Other Income and Other Expense to identify the
revenues and expenses not related to the company’s
Inventory Shrinkage reason for being in business
• In real life, income tax expense would be reported
When a company takes a physical count of its between net other revenues and expenses and Net
inventory, should it reasonably expect to find Income. It is excluded in this illustration and in the
all the inventory items present and accounted textbook for simplicity.
for? Unfortunately, this is not always the
case. Inventory could have been stolen (e.g., Gross Sales $500,00
shoplifting) or damaged, disposed of and not 0
reported as such (e.g., the inventory fell off - Sales Returns & $5,000
the shelf in the warehouse, was damaged by
allow.
the fall and was disposed of by the cleaning
crew). Although companies try to protect - Sales Discounts 3,00 8,000
their inventory through proper internal 0
controls, inventory losses or shrinkage still Net Sales 492,00
occur. Under the matching principle, these 0
losses are recorded as expenses in the period Cost of Merchandise 294,00
in which they occur to match them against the Sold 0
revenue earned. Although the text suggests Gross Profit 198,00
that they should be recorded as cost of goods 0
sold, in practice they may be recorded in a
Operating Expenses: g) Paid Cupid Co. on account for purchase in (b)
less return (d) and discount.
Selling Expenses 50,000 h) Received cash on account from Donner Co.
Admin Expense 45,000 for sale in (c) less return (f) and discount.
Total Operating 95,000 i) Perpetual inventory records indicate that
Expenses $85,000 of merchandise should be on hand.
Income from Operations 103,00 The physical inventory indicates that $81,350
0 of merchandise is on hand.
Other Income:
SAMPLE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
Interest Revenue 1,00
0 1. The difference between net sales and cost of
Other Expenses: merchandise sold for a merchandising business is:
a) Sales c) Gross Profit
Interest Expense 700 300 b) Net Sales d) Gross Sales
Net Income $102,70 2. When purchases of merchandise are made on
0 account, the transaction would be recorded with
Practice Problem #3 the following entry:
Using the format for the multi-step income statement, a) Debit Accounts Payable, c) Debit
compute the following: credit Merchandise Merchandise
a) Calculate Net Sales and Gross Profit if, Sales Inventory Inventory, credit
are $375,000, Sales Returns and Allowances b) Debit Merchandise Cash
are $32,000, Sales Discounts are $12,000 and Inventory, credit Accounts d) Debit Cash, credit
Cost of Merchandise Sold is $255,000. Payable Merchandise
b) Calculate Sales Returns and Allowances and Inventory
Cost of Merchandise Sold if, Sales are 3. When a corporation sells merchandise and the
$750,000, Sales Discounts are $9,000, Net terms are FOB shipping point and pays the
Sales are $736,000 and Gross Profit is shipping costs, the seller would record the
$310,000. transportation costs with the following entry:
c) Calculate Sales and Net Sales if, Sales Returns a) Debit Cash, credit c) Debit Accounts
and Allowances are $25,000, Sales Discounts Accounts Receivable Receivable, credit Cash
are $15,000, Cost of Merchandise Sold is b) Debit Accounts d) Debit Merchandise
$620,000 and Gross Profit is $185,000. Receivable, credit Sales Inventory, credit
Practice Problem #4 Accounts Payable
Journalize the following related transactions. 4. Multiple-step income statements:
a) Purchased mdse on account from Blitzen Co., a) Show gross profit but c) Show neither gross
list price $20,000, trade discount 25%, terms not income from profit nor income from
FOB shipping point, 2/10, n/30, with prepaid operations operations
transportation costs of $650 added to the b) Show both gross d) Show income from
invoice. profit and income from operations but not gross
b) Purchased merchandise on account from operations profit
Cupid Co., $8,000, terms FOB destination, 5. Which of the following would be reported on the
1/10, n/30. retained earnings statement for the current year?
c) Sold merchandise on account to Donner Co., a) Dividends for the c) Cost of merchandise
$9,800, terms 2/10, n/30. The cost of the current year sold
merchandise sold was $5,800. b) Sales d) Merchandise
d) Returned $2,000 of merchandise purchased inventory
from Cupid Co. (b) 6. A sales invoice included the following
e) Paid Blitzen Co. on account for purchase in information: merchandise price, $12,000;
(a) less discount. transportation, $500; terms 2/10, n/eom, FOB
f) Received merchandise returned by Donner Co. shipping point. Assuming that a credit for
from sale in (c), $1,800. The cost of the merchandise returned of $600 is granted prior to
merchandise returned was $1,080. payment, that the transportation is prepaid by the
seller, and that the invoice is paid within the
discount period, what is the amount of cash b) Debit Cash, $1,800; $26; credit A/R, $1,300
received by the seller? credit Sales Returns and d) Debit Cash, $1,800;
a) $11,662 c) $12,250 allowances, $500; credit credit Sales Discounts
b) $11,672 d) $11,172 A/R, $1,300 $36; credit A/R, $1,764
7. An acid-test ratio of 1.5 means 15. In a perpetual inventory system, what accounts
a) Quick assets are 1.15 c) That every $1.50 of are credited when a customer returns merchandise
times as large as sales. sales generates $1.00 of to the seller?
b) That every $1.50 of liabilities. a) Sales Returns and c) Merchandise
quick assets generates d) Quick assets are 1.5 Allowances and Inventory and Cost of
$1.00 in sales. times as large as total Accounts Receivable Merchandise Sold
liabilities. b) Accounts Receivable d) Sales Returns and
8. Merchandise with an invoice price of $7,000 is and Cost of Allowances and
purchased with terms of 2/10, n/30, FOB shipping Merchandise Sold Merchandise Inventory
point. Transportation costs paid by the seller were 16. Assume that sales are $450,000, sales discounts
$125. What is the cost of the merchandise are $10,000, net income is $35,000, and cost of
purchased if payment is made during the discount merchandise sold is $320,000. Gross profit and
period? operating expenses are, respectively
a) $6,860.00 c) $7,000.00 a) $130,000 and $95,000 c) $130,000 and $85,000
b) $6,982.50 d) $6,985.00 b) $120,000 and d) $120,000 and
9. Cost of Merchandise Sold would be classified as: $95,000 $85,000
a) Asset c) Liability 17. Which of the following accounts is credited by
b) Expense d) Revenue the seller when merchandise purchases are paid
10. The discount period for credit terms of 1/10, for within the discount period?
n/30 is: a) Merchandise c) Accounts Receivable
a) 1 day c) 20 days Inventory d) Sales Discounts
b) 10 days d) 30 days b) Accounts Payable
11. Freight costs incurred by the seller are 18. A classified balance sheet reports merchandise
recorded in the inventory as:
a) Sales account c) Transportation In a) Plant asset c) Current asset
b) Cost of merchandise account b) Long-term asset d) Current liability
sold account d) Transportation Out 19. Gross Margin is calculated as:
account a) Sales less cost of c) Sales less expenses
12. Which of the following would be classified in an merchandise sold d) Sales less operating
income statement as Other Income or Other b) Sales less expenses
Expense? merchandise inventory
a) Advertising Expense c) Transportation Out 20. Company A’s gross profit ratio has been
b) Interest Expense d) Cost of merchandise steadily declining for 5 years while the net profit
sold ratio has remained constant. The most likely
reason for this pattern is:
13. The sales discount is based on a) Cost of merchandise c) Cost of merchandise
a) Invoice price plus c) Invoice price plus sold and operating sold and operating
transportation costs transportation costs less expenses have both expenses have both
b) Invoice price less returns and allowances increased each year decreased each year
discount d) Invoice price less b) Selling price and d) Selling price
returns and allowances operating expenses have decreased and operating
14. Myers and Company sold $1,800 of both decreased each expenses increased each
merchandise on account to Oscar, Inc. on March 1 year year
with credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Oscar returned
$500 of the merchandise due to poor quality on SAMPLE TRUE/FALSE QUESTION
March 3. If Oscar pays for the purchase on March
11, what entry does Myers make to record receipt 1. Trade discounts represent a discount offered to the
of the payment? purchasers for quick payment.
a) Debit Cash, $1,764; c) Debit Cash, $1,274; 2. When a company sells a $100 service with a 20%
credit A/R, $1,764 debit Sales Discounts trade discount, $80 of revenue is recognized.
3. A sales discount represents a reduction, not in the 1. Pappy Corporation received cash of $18,000 on
selling price of a product or service, but in the September 1, 2012, for one year’s rent in advance
amount to be paid by a credit customer if payment and recorded the transaction with a credit to
is made within a specified period of time. Unearned Rent Revenue. The December 31, 2012,
4. A sale on account for $1,000 offered with terms adjusting entry is
2/10, n/30 means that the customers will get a $2 a. debit Rent Revenue and c. debit Unearned Rent
discount if payment is made within 10 days; credit Unearned RentRevenue and credit Rent
otherwise, full payment is due within 30 days. Revenue, $6,000 Revenue, $6,000
5. The Sales Discounts account is an expense b. debit Rent Revenue and d. debit Cash and credit
account. credit Unearned RentUnearned Rent Revenue,
6. A sales allowance is recorded as a debit to Revenue, $12,000 $12,000
Accounts Receivable and a credit to Sales 2. Panda Corporation paid cash of $30,000 on June
Allowances. 1, 2012, for one year’s rent in advance and
7. The Sales Returns account is an expense account. recorded the transaction with a debit to Prepaid
8. If a company has total revenues of $100,000, sales Rent. The December 31, 2012, adjusting entry is
discounts of $3,000, sales returns of $4,000, and a. debit Prepaid Rent andc. debit Rent Expense and
sales allowances of $2,000, the income statement credit Rent Expense,credit Prepaid Rent,
will report net revenues of $91,000. $12,500 $17,500
9. Cost of goods sold is an asset reported in the b. debit Prepaid Rent andd. debit Prepaid Rent and
balance sheet and inventory is an expense reported credit Rent Expense,credit Cash, $12,500
in the income statement. $17,500
10. If a company has beginning inventory of $15,000, 3. Tate Company purchased equipment on
purchases during the year of $75,000, and ending November 1, 2012, and gave a 3-month, 9% note
inventory of $20,000, cost of goods sold equals with a face value of $40,000. The December 31,
$70,000. 2012, adjusting entry is
11. For inventory that is shipped FOB destination, a. debit Interest Expense and c. debit Interest Expense and
title transfers from the seller to the buyer once the credit Interest Payable,credit Cash, $600
seller ships the inventory. $3,600 d. debit Interest Expense and
12. For inventory that is shipped FOB shipping point, b. debit Interest Expense andcredit Interest Payable, $600
title transfers from the seller to the buyer once the credit Interest Payable, $900
seller ships the inventory. 4. Starr Corporation loaned $150,000 to another
13. Freight-in is included in the cost of inventory. corporation on December 1, 2012, and received a
14. Gross profit equals net sales of inventory less cost 3-month, 8% interest-bearing note with a face
of goods sold. value of $150,000. What adjusting entry should
15. Sales revenue minus cost of goods sold is referred Starr make on December 31, 2012?
to as operating income. a. Debit Interest Receivablec. Debit Interest Receivable
16. When a company sells a $100 service with a 20% and credit Interest Revenue,and credit Interest Revenue,
trade discount, $80 of revenue is recognized. $3,000 $1,000
17. Sales returns and allowances occur when the b. Debit Cash and creditd. Debit Cash and credit
buyer returns the goods, or the seller reduces the Interest Revenue, $1,000 Interest Receivable, $3,000
customer's balance owed. 5. Murphy Company sublet a portion of its
18. Inventory is usually reported as a long-term asset warehouse for five years at an annual rental of
in the balance sheet. $30,000, beginning on May 1, 2012. The tenant,
19. Merchandising companies purchase inventories Sheri Charter, paid one year's rent in advance,
that are primarily in finished form for resale to which Murphy recorded as a credit to Unearned
customers. Rent Revenue. Murphy reports on a calendar-year
20. Sales revenue minus cost of goods sold is referred basis. The adjustment on December 31, 2012, for
to as operating income. Murphy should be
21. Income before income taxes equals operating a. No entry c. Rent Revenue
income plus nonoperating revenues less b. Unearned Rent Revenue 10,000
nonoperating expenses. 10,000 Unearned Rent
Rent Revenue Revenue 10,000
ADJUSTING ENTRIES MCQ 10,000 d. Unearned Rent Revenue
20,000
Revenue The following balances have been excerpted from
20,000 Dolan Corporation's balance sheets:
6. During the first year of Wilkinson Co.'s Accounts December Decembe
operations, all purchases were recorded as assets. 31, 2012 r 31,
Supplies in the amount of $25,800 were purchased. 2011
Actual year-end supplies amounted to $8,600. The Interest
adjusting entry for store supplies will receivable 18,200 15,000
a. increases net income byc. decrease supplies by Salaries and
$17,200 $8,600 wages payable 17,800 8,400
b. increases expenses byd. debit Accounts Payable Prepaid
$17,200 for $8,600 insurance 2,200 3,000
7. The income statement of Dolan Corporation for The cash paid for insurance premiums during 2012
2012 included the following items: was
Interest revenue $131,000 a. $13,000 b. $12,200
Salaries and wages expense 170,000 c. $16,000 d. $14,400
Insurance expense 15,200 10. The Supplies account had a balance at the
The following balances have been excerpted from beginning of year 3 of $8,000 (before the reversing
Dolan Corporation's balance sheets: entry). Payments for purchases of supplies during
Accounts December Decembe year 3 amounted to $50,000 and were recorded as
31, 2012 r 31, expense. A physical count at the end of year 3
2011 revealed supplies costing $9,500 were on hand.
Interest Reversing entries are used by this company.
receivable 18,200 15,000 The required adjusting entry at the end of year 3 will
Salaries and include a debit to:
wages payable 17,800 8,400 a. Supplies Expense for c. Supplies Expense for
Prepaid $1,500 $48,500
insurance 2,200 3,000 b. Supplies for $1,500 d. Supplies for $9,500
The cash received for interest during 2012 was 11. When an item of expense is paid and recorded
a. $112,800 b. $127,800 in advance, it is normally called a(n)
c. $131,000 d. $131,000 a. prepaid expense c. estimated expense
8. The income statement of Dolan Corporation for b. accrued expense d. cash expense
2012 included the following items: 12. When an item of revenue or expense has been
Interest revenue $131,000 earned or incurred but not yet collected or paid, it
Salaries and wages expense 170,000 is normally called a(n) ____________ revenue or
Insurance expense 15,200 expense.
The following balances have been excerpted from a. Prepaid c. estimated
Dolan Corporation's balance sheets: b. Adjusted d. accrued
Accounts December Decembe 13. If, during an accounting period, an expense
31, 2012 r 31, item has been incurred and consumed but not yet
2011 paid for or recorded, then the end-of-period
Interest adjusting entry would involve
receivable 18,200 15,000 a. a liability account and c. a liability account and
Salaries and an asset account an expense account
wages payable 17,800 8,400 b. an asset or contra- d. a receivable account
Prepaid asset and an expense and a revenue account
insurance 2,200 3,000 account.
The cash paid for salaries during 2012 was 14. Which of the following would not be a correct
a. $179,400 b. $160,600 form for an adjusting entry?
c. $161,600 d. $187,800 a. A debit to a revenue c. A debit to a liability
9. The income statement of Dolan Corporation for and a credit to a liability and a credit to a revenue
2012 included the following items: b. A debit to an expense d. A debit to an asset
Interest revenue $131,000 and a credit to a liability and a credit to a liability
Salaries and wages expense 170,000 15. Gomez Company received $7,200 on April 1,
Insurance expense 15,200 2001, for one year's rent in advance and recorded
the transaction with a credit to a nominal account. Accrued
The December 31, 2001, adjusting entry is Salaries 8,900 4,200
a. debit Rent Revenue c. debit Unearned Rent Payable
and credit Unearned and credit Rent Prepaid
Rent, $1,800 Revenue, $1,800 insurance 1,100 1,500
b. debit Rent Revenue d. debit Unearned Rent 19. The cash received for interest during 2001 was
and credit Unearned and credit Rent a. 66,400 c. 75,500
Rent, $5,400 Revenue, $5,400 b. 73,900 77,100
16. Forbes Company paid $4,800 on June 1, 2001, 20. The cash paid for salaries during 2001 was
for a two-year insurance policy and recorded the a. 69,700 c. 60,800
entire amount as Insurance Expense. The b. 60,300 d. 73,900
December 31, 2001, adjusting entry is 21. The cash paid for insurance premiums during
a. debit Insurance c. debit Prepaid 2001 was
Expense and credit Insurance and credit a. 8,500 c. 10,000
Prepaid Insurance, Insurance Expense, b. 8,100 d. 9,200
$1,400 $1,400 Poole Company paid or collected during 2001 the
b. debit Insurance d. debit Prepaid following items:
Expense and credit Insurance and credit Insurance premiums paid $ 12,400
Prepaid Insurance, Insurance Expense, Interest collected 25,900
$3,400 $3,400 Salaries paid 125,200
17. Lane Company purchased equipment on The following balances have been excerpted from
November 1, 2001, and gave a 3-month, 9% note Poole's balance sheets:
with a face value of $30,000. The December 31, Accounts December Decembe
2001, adjusting entry is 31, 2012 r 31,
a. debit Interest Expense c. debit Interest Expense 2011
and credit Interest and credit Cash, $450
Payable, $2,700 d. debit Interest Expense Prepaid 1,200 1,500
b. debit Interest Expense and credit Interest Insurance
and credit Interest Payable, $450 Interest
Payable, $675 Receivable 3,700 2,900
18. Perez Corporation received cash of $6,000 on
August 1, 2001, for one year's rent in advance and Salaries 12,300 10,600
recorded the transaction with a credit to Rent Payable
Revenue. The December 31, 2001, adjusting entry 22. The insurance expense on the income statement
is for 2001 was
a. debit Rent Revenue c. debit Unearned Rent a. $9,700 c. $12,700
and credit Unearned and credit Rent b. $12,100 d. $15,100
Rent, $2,500 Revenue, $2,500 23. The interest revenue on the income statement
b. debit Rent Revenue d. debit Cash and credit for 2001 was
and credit Unearned Unearned Rent, $3,500 a. $19,300 c. $26,700
Rent, $3,500 b. $25,100 d. $32,500
The income statement of Carsen Corporation for 2001
included the following items: 24. The salary expense on the income statement
Interest revenue $75,500 for 2001 was
Salaries expense 65,000 a. $102,300 c. $126,900
Insurance expense 9,600 b. $123,500 d. $148,100
The following balances have been excerpted from 25. Rice Corporation loaned $45,000 to another
Carsen Corporation's balance sheets: corporation on December 1, 2001, and received a
Accounts December Decembe 3-month, 8% interest-bearing note with a face
31, 2012 r 31, value of $45,000. What adjusting entry should Rice
2011 make on December 31, 2001?
Accrued a. Debit Interest c. Debit Interest
Interest 9,100 7,500 Receivable and credit Receivable and credit
receivable Interest Revenue, $900 Interest Revenue, $300
b. Debit Cash and credit d. Debit Cash and credit 32. Timothy Corporation received cash of $18,000
Interest Revenue, $300 Interest Receivable, on September 1, 2012, for one year’s rent in
$900 advance and recorded the transaction with a credit
26. Live Nation sells concerts tickets for Blackpink to Unearned Rent Revenue. The December 31,
concert on September 16, 2022, which are sold out 2012, adjusting entry is
on the same date. Live Nation follows calendar a. debit Rent Revenue c. debit Unearned Rent
year for its financial statements. The concert will and credit Unearned Revenue and credit Rent
take place on March 26, 2023. Applying revenue Rent Revenue, $6,000 Revenue, $6,000
recognition principle when Live Nation will b. debit Rent Revenue d. debit Cash and credit
recognize revenue? and credit Unearned Unearned Rent
a. September 16, 2022 c. January 1, 2023 Rent Revenue, $12,000 Revenue, $12,000
b. December 31, 2022 d. March 26, 2023 33. Tyco Corporation paid cash of $30,000 on June
27. If a resource has been consumed but a bill has 1, 2012, for one year’s rent in advance and
not been received at the end of the accounting recorded the transaction with a debit to Prepaid
period, then Rent. The December 31, 2012, adjusting entry is
a. an expense should be c. an adjusting entry a. debit Prepaid Rent c. debit Rent Expense
recorded when the bill is should be made and credit Rent and credit Prepaid Rent,
received recognizing the expense Expense, $12,500 $17,500
b. an expense should be d. it is optional whether b. debit Prepaid Rent d. debit Prepaid Rent
recorded when the cash to record the expense and credit Rent and credit Cash, $12,500
is paid out. before the bill is Expense, $17,500
received 34. Joe is a lawyer who requires that his clients pay
28. Accrued revenues are him in advance of legal services rendered. Joe
a. received and recorded c. earned but not yet routinely credits Legal Service Revenue when his
as liabilities before they received or recorded clients pay him in advance. In June Joe collected
are earned d. earned and already P8,000 in advance fees and completed 75% of the
b. earned and recorded received and recorded work related to these fees. What adjusting entry is
as liabilities before they required by Joe's firm at the end of June?
are received a. Debit, Unearned c. Debit, Cash, P8,000;
29. Prepaid expenses are Revenue, P6,000; Credit, Legal Service
a. paid and recorded in c. incurred but not yet Credit, Legal Service Revenue, P8,000
an asset account before paid or recorded Revenue, P6,000 d. Debit, Legal Service
they are used or d. incurred and already b. Debit, Unearned Revenue, P2,000;
consumed paid or recorded Revenue, P2,000; Credit, Unearned
b. paid and recorded in Credit, Legal Service Revenue, P2,000
an asset account after Revenue, P2,000
they are used or 35. Al is a barber who does his own accounting for
consumed his shop. When he buys supplies, he routinely
30. Accrued expenses are debits Supplies Expense. Al purchased P1,500 of
a. paid and recorded in c. incurred but not yet supplies in January and his inventory at the end of
an asset account before paid or recorded January shows P600 of supplies remaining. What
they are used or d. incurred and already adjusting entry should Al make on January 31?
consumed paid or recorded a. Debit, Supplies c. Debit, Supplies, P600;
b. paid and recorded in Expense, P600; Credit, Credit, Supplies
an asset account after Supplies, P600 Expense, P600
they are used or b. Debit, Supplies d. Debit, Supplies
consumed Expense, P1,500; Credit, Expense, P900; Credit,
31. Unearned revenues are Cash, P1,500 Supplies, P900
a. received and recorded c. earned but not yet
as liabilities before they received or recorded ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
are earned d. earned and already
b. earned and recorded received and recorded 1. Mrs. A is an owner of a dry goods store located
as liabilities before they in Divisoria. The business operations can be
are received
handled by herself and get all the profits of the 12. These are resources owned by the business and
business. Her business is a are expected to benefit the business over a number
a. sole proprietorship c. corporation of years
b. partnership d. joint venture a. assets c. equity
2. A form of business organization where it is b. liabilities d. contingencies
managed by board of directors is 13. The consumption of asset or using up of service
a. sole proprietorship c. corporation to generate revenue is called a/an __________.
b. partnership d. joint venture a. assets c. income
3. ABC Dental Clinic provides for dental need of b. equity d. expense
its patients. Its type of business operation is 14. Which of the following is an asset account?
a. service c. manufacturing a. Insurance Exp. c. Office supplies
b. merchandising d. profession b. Supplies exp d. Sales
4. An external user of accounting information, 15. Which of the following accounts is classified
which assesses the ability of the business to pay differently from the others listed?
the principal debt and additional charge, called a. Prepaid rent c. acc. receivable
interest. b. cash d. owner’s capital
a. Investor c. lender 16. Entries recorded on the right side of any
b. manager d. customer account are called
5. It uses the accounting reports to determine a. debit c. increases
whether the business is paying the right taxes b. credit d. decreases
and mandatory contributions to its employees 17. A debit may signify a decrease in
a. Investor c. manager a. liability acc c. revenue acc
b. customer d. government b. asset acc d. liabilities & revenue
6. Financial statement that reports the financial acc
performance of the business by determining its 18. When collections are made on Accounts
profit or loss for a period Receivable
a. Financial position c. Cash flow a. OE increase c. Asset decrease
b. Changes in equity d. Income b. Asset increase d. Total assets remains
statement the same
7. Financial statement that shows the resources of 19. The owner of the business withdraws cash from
the business and its corresponding obligations business for personal use. This
owed by the business a. Is not a business c. Decrease assets
a. Financial position c. Cash flow transaction and OE
b. Changes in equity d. Income b. Decrease asset d. Increase assets
statement and OE
8. This accounting principle refers to expectation 20. Which of the following transactions decreases
that the business will continue to exist indefinitely both assets and owner’s equity?
a. Business entity c. Assumption a. Payment of a c. Receipt of a
b. Principle accrual d. Going concern liability phone bill, to be
9. It is a business document used when cash is paid b. Owner withdrawal paid at a later
or a check is issued. of cash time
a. Invoice official c. voucher d. Advance payment
b. receipt d. check made for
insurance
10.This business document is issued when cash is 21. What is the effect of settlement of debt to a
received by the business supplier in a business transaction
a. Invoice official c. voucher a. Increase in assets; c. Increase in assets;
b. receipt d. check Increase in liabilities Decrease in liabilities
11. The debits and the credits of each account are b. Decrease in assets; d. Decrease in assets;
recorded for every transaction in _________. Increase in liabilities Decrease in liabilities
a. journal c. worksheet
b. ledger d. trial balance
22. Area of accounting practice where the
accountant works as an external auditor or tax Special Non-working 130% of the basic
consultant Holiday daily rate
a. Public practice c. Government
b. Industry d. Education Regular Holidays Special Non-Working
23. Identify the incorrect statement Holidays
a. Assets – Liabilities = c. Assets = Equity + • New Year’s Day • Lunar New Year
Equity Liabilities • Araw ng Kagitingan • EDSA People Power
b. Equity – Liabilities = d. Assets – Equity = • Maundy Thursday Revolution Anniversary
Assets Liabilities • Good Friday • Black Saturday
24. A business has total assets of P 381,000 and • Labor Day • Ninoy Aquino Day
owner’s equity of P 264,000. How much were the • Independence Day • All Saints’ Day
liabilities? • Eid’l Fitr • Day after All Saints’
a. Cannot be c. P117,000 • Eid’l Adha Day
determined d. P264,000 • National Heroes Day • Feast of the
b. P381,000 • Bonifacio Day Immaculate Conception
25. Suppose your business has cash of P50,000, • Christmas Day of Mary
receivables of P60,000 and furniture totaling • Rizal Day • Christmas Eve
P200,000. The store owes P80,000 on account and • Last Day of the Year
has a P100,000 note payable. How much is your
equity? B. NIGHT SHIFT DIFFERENTIALS
a. 20,000 c. P180,000 Night Shift Differentials (NSD) occurs from 10pm
b. P130,000 d. P310,000 to 6am and is 10% of the basic pay.
C. OVERTIME PREMIUM
Overtime premium just like holiday pay is
classified into three categories:
Regular Day - 25% of the basic pay.
Payroll in the Philippines
Rest Day, Special Non-Working Day -
30% of the basic pay.
Legal Holiday - 100% of the salary/wage.
Probationary, Regular - paid semi-monthly D. EMPLOYEE BENEFITS
(15 and 30) and was compensated by an 13th Month Pay – a government-
amount referred to as salary.
mandated form of compensation in the
Casual, Contractual - workers were usually
Philippines given to employees at the end
paid hourly, daily, and weekly. Their
of the year. The computation is as follows:
compensation is known as wages.
o 13th month pay = (monthly
Taxable income is the employee’s gross income after
salary / 12) x months worked
making relevant salary adjustments.
The basic formula for calculating taxable income is: Vacation Leave
Net Pay = Gross Pay - Deductions Sick Leave
Additional pay can refer to additional income because
of holiday pay or overtime and night shift DEDUCTIONS TO GROSS PAY
differential rates. Deductions include mandatory
government contributions and salary deductions In the Philippines, employees make mandatory
due to attendance or internal policies. government contributions of which employers also
pay a share.
ADDITIONS TO GROSS PAY
A. SOCIAL SECURITY SYSTEM (SSS) -
A. HOLIDAY PAY Contributions made to the SSS depend on the
employee’s salary. However, there is a fixed ceiling
Type of Holiday Special Hourly Rate amount for employees with a monthly salary of PHP
20,000 or more. Employers also pay a share for the
Regular Holiday 200% of the basic employee’s SSS contributions.
daily
B. PHILIPPINE HEALTH INSURANCE
CORPORATION (PhilHealth) - PhilHealth
provides a national health insurance program in the
Philippines. PhilHealth contribution is 3% of the
employee’s salary each month. The employee and
employer pay an equal share for PhilHealth.
C. HOME DEVELOPMENT MUTUAL FUND
(Pag-IBIG) - The Pag-IBIG fund is responsible for a
national savings program and also offers loans and
housing programs. The employer and employee each
pay a fixed amount of PHP 100 per month for PAG-
IBIG.
You might also like
- Business Takeover AgreementDocument4 pagesBusiness Takeover AgreementAlankar NarulaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Inventories and Cost of Goods SoldDocument84 pagesChapter 3 Inventories and Cost of Goods SoldSampanna Shrestha100% (1)
- Merchandising Operations - CRDocument21 pagesMerchandising Operations - CRNicole CagasNo ratings yet
- Merchandising BusinessDocument26 pagesMerchandising BusinessPatricia Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- Merchandising Operations - CRDocument21 pagesMerchandising Operations - CRHabte AbeNo ratings yet
- MerchandisingDocument17 pagesMerchandisingFelipe DologNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - 6 - Inventory Accounting and ValuationDocument61 pagesChapter 5 - 6 - Inventory Accounting and ValuationNaeemullah baig100% (1)
- Accounting For Merchandising Business (Report)Document37 pagesAccounting For Merchandising Business (Report)Garet Julia Marie T.100% (1)
- ACC101 Chapter4new PDFDocument25 pagesACC101 Chapter4new PDFJonnafe Almendralejo IntanoNo ratings yet
- 10 Accounting Cycle of A Merchandizing BusinessDocument21 pages10 Accounting Cycle of A Merchandizing BusinessJames CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Inventory Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesInventory Lecture NotesMinh ThưNo ratings yet
- Accounting PrinciplesDocument36 pagesAccounting PrinciplesEshetieNo ratings yet
- Merchandising CompaniesDocument7 pagesMerchandising CompaniesGoogle UserNo ratings yet
- 2 - FSA1 Handout (Topic 4 Reading 25, 28) - InventoryDocument51 pages2 - FSA1 Handout (Topic 4 Reading 25, 28) - InventoryGuyu PanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For A Merchandising Business Week 3Document35 pagesAccounting For A Merchandising Business Week 3kayeNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles: Second Canadian EditionDocument36 pagesAccounting Principles: Second Canadian EditionMelody YayongNo ratings yet
- ch05 Accounting For Merchandising OperationDocument59 pagesch05 Accounting For Merchandising OperationJawad Arko100% (1)
- Accounting Principles: Second Canadian EditionDocument36 pagesAccounting Principles: Second Canadian EditionKerby Gail RulonaNo ratings yet
- Lect 11TVDocument25 pagesLect 11TVsalman siddiqui100% (1)
- INVENTORIESDocument28 pagesINVENTORIESLourdios EdullantesNo ratings yet
- P2 Notes MerchandisingDocument14 pagesP2 Notes Merchandisingchen.abellar.swuNo ratings yet
- M2.3C-1 Inventories PDFDocument70 pagesM2.3C-1 Inventories PDFLiandrew MadronioNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument12 pagesInventoriesRIAN MAE DOROMPILINo ratings yet
- MerchandisingDocument7 pagesMerchandisingtwice onceNo ratings yet
- 05 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsDocument33 pages05 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsoriboiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Accounting For Merchandising TransactionsDocument30 pagesChapter 6-Accounting For Merchandising Transactions05 Phạm Hồng Diệp12.11No ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivableDocument6 pagesAccounts Receivablejustinenakpil09No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Second Year Financial Accounting: Merchandising Operation 1Document40 pagesLecture 2 Second Year Financial Accounting: Merchandising Operation 1sara100% (1)
- Accounting For A Merchandising Business Week 2Document31 pagesAccounting For A Merchandising Business Week 2kayeNo ratings yet
- ACCT1111 Chapter 6 Lecture (Revised)Document63 pagesACCT1111 Chapter 6 Lecture (Revised)Wky JimNo ratings yet
- ACTBAS 2 - Lecture 1 Merchandising Business and Inventory SystemDocument7 pagesACTBAS 2 - Lecture 1 Merchandising Business and Inventory SystemJason Robert MendozaNo ratings yet
- Merchandising SummaryDocument15 pagesMerchandising SummaryKang ChulNo ratings yet
- Merchandising - AccountingDocument9 pagesMerchandising - AccountingKen AggabaoNo ratings yet
- March 10,2023-Exam Study GuideDocument4 pagesMarch 10,2023-Exam Study GuideReneeby SombilonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Merchandising Operations: Weygandt - Kieso - KimmelDocument62 pagesAccounting For Merchandising Operations: Weygandt - Kieso - KimmelMaidah NaeemNo ratings yet
- Purchases With Cash DiscountsDocument3 pagesPurchases With Cash Discountsgnzg.belaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Inventories InventoriesDocument24 pagesChapter 7 Inventories InventoriesharumanNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Inventories - Rev (Students)Document42 pagesTopic 9 - Inventories - Rev (Students)RomziNo ratings yet
- A Merchandising Business Is One That Buys and Sells Goods in Order To Make A Profit Nature of Merchandising BusinessesDocument6 pagesA Merchandising Business Is One That Buys and Sells Goods in Order To Make A Profit Nature of Merchandising BusinessesCyrra BalignasayNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Apuntes Unit 5 Gulag FreeDocument12 pagesWuolah Free Apuntes Unit 5 Gulag FreeNOA PEREZ FERRERNo ratings yet
- Akuntansi Perusahaan DagangDocument25 pagesAkuntansi Perusahaan DagangCholis LatteNo ratings yet
- Acc117-Chapter 5Document51 pagesAcc117-Chapter 5Fadilah JefriNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle of A Merchandising BusinessDocument53 pagesAccounting Cycle of A Merchandising Businessalfabeth rariza100% (1)
- Inventories: Inventories Net Sales FormulaDocument6 pagesInventories: Inventories Net Sales Formulagab camonNo ratings yet
- Inventories NotesDocument7 pagesInventories NotesJessel Ann MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Book1 PDFDocument9 pagesBook1 PDFyelzNo ratings yet
- Merchandising BusinessDocument10 pagesMerchandising BusinessMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 101: Merchandising OperationsDocument14 pagesAccounting 101: Merchandising OperationsLove AmorNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Quarter 2 - Week 2Document7 pagesFABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Quarter 2 - Week 2Sheila Marie Ann Magcalas-GaluraNo ratings yet
- Exam Revision - 5 & 6Document10 pagesExam Revision - 5 & 6Minh Tran Huu NgocNo ratings yet
- Tle 3rd Monthly Test Reviewer FinalDocument18 pagesTle 3rd Monthly Test Reviewer Finalallen c.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - InventoriesDocument49 pagesChapter 2 - Inventorieszein lopezNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Merchandising CompaniesDocument40 pagesAccounting For Merchandising CompaniesAnonymous mnAAXLkYQC100% (1)
- Accounting For Merchandising CompaniesDocument40 pagesAccounting For Merchandising CompaniesAnonymous mnAAXLkYQCNo ratings yet
- Less: ExpensesDocument6 pagesLess: ExpensessohaibqayyumNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesCheat SheetJason wonwonNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles 1: Accounting For Merchandising Operations InventoriesDocument41 pagesAccounting Principles 1: Accounting For Merchandising Operations InventoriesKevin Chandra100% (1)
- Module 8 - Inventories Part IIDocument14 pagesModule 8 - Inventories Part IIMark Christian BrlNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Prepared By: Michael G. AuditorDocument49 pagesInventories: Prepared By: Michael G. AuditorMARRY ANN JOY FERRERNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesFrom EverandFinancial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Festivals978 1 888822 46 5.webDocument434 pagesFestivals978 1 888822 46 5.webJuve HV0% (1)
- People v. Mallari (GR No L-58886, Dec 13, 1998)Document1 pagePeople v. Mallari (GR No L-58886, Dec 13, 1998)d100% (1)
- Republic Vs de Guzman - DEL ROSARIODocument1 pageRepublic Vs de Guzman - DEL ROSARIOJohn L.No ratings yet
- Fernandez vs. NoveroDocument5 pagesFernandez vs. NoveroAdrianne BenignoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical v. DOHDocument1 pagePharmaceutical v. DOHSean Hinolan100% (1)
- Third Division G.R. No. 204659, September 19, 2016 JESTER MABUNOT, Petitioner, v. PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Respondent. Resolution Reyes, J.Document6 pagesThird Division G.R. No. 204659, September 19, 2016 JESTER MABUNOT, Petitioner, v. PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Respondent. Resolution Reyes, J.Jomar TenezaNo ratings yet
- Simplifying It Security For DummiesDocument76 pagesSimplifying It Security For DummiesAnonymous 1eZNBWqpB100% (2)
- G.R. No. 180245 Case DigestDocument3 pagesG.R. No. 180245 Case DigestMaricel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Identity Theft Unit: Annual Id Theft & Scams ReportDocument8 pagesIdentity Theft Unit: Annual Id Theft & Scams ReportABC15 NewsNo ratings yet
- 4 Security of Data OnlineDocument5 pages4 Security of Data OnlineJedediah PhiriNo ratings yet
- Profiles in Diversity Journal - Sep/Oct 2007Document201 pagesProfiles in Diversity Journal - Sep/Oct 2007Profiles in Diversity JournalNo ratings yet
- 26 So Ping Bun v. Court of Appeals PDFDocument5 pages26 So Ping Bun v. Court of Appeals PDFAbegail GaledoNo ratings yet
- Common GoodDocument13 pagesCommon GoodXyzzielleNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts DWG 384jet 128-9003-01H PDFDocument1 pageSpare Parts DWG 384jet 128-9003-01H PDFjoaopedrolorNo ratings yet
- SMEs (Students Guide)Document11 pagesSMEs (Students Guide)Erica CaliuagNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Must or Mustn't Andres Franco y Luis SolorzanoDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Must or Mustn't Andres Franco y Luis SolorzanoCRISTIAN ANDRES RODRIGUEZ FRANCONo ratings yet
- Union Performance Railways Dual Freight Policy Transportation 14 2015Document106 pagesUnion Performance Railways Dual Freight Policy Transportation 14 2015gautamNo ratings yet
- El ActsDocument4 pagesEl ActsSonia LawsonNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument2 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelAsad SyedNo ratings yet
- The 100 Best Non-Fiction Books of The CenturyDocument8 pagesThe 100 Best Non-Fiction Books of The Centurydinh son myNo ratings yet
- Ginger AddressDocument3 pagesGinger AddressRaj Kothari MNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: 8.223, Classical Mechanics II Exercises 1Document4 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: 8.223, Classical Mechanics II Exercises 1Uriel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Terms and ConditionsDocument2 pagesTerms and Conditionsackyard MotoworksNo ratings yet
- 22 Beware of Banking Fees (B) - 703063Document3 pages22 Beware of Banking Fees (B) - 703063tryguy088No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Dynamics of Structures 4 e Anil K ChopraDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Dynamics of Structures 4 e Anil K Chopracrantspremieramxpiz100% (43)
- DEL MONTE V Sunshine Sauce - DigestDocument5 pagesDEL MONTE V Sunshine Sauce - DigestAdmin DivisionNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Statistics For Social Workers 8th Edition Weinbach Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Statistics For Social Workers 8th Edition Weinbach Test Bank PDFmasonh7dswebb100% (11)
- 1929 - The Crash ExplainedDocument3 pages1929 - The Crash Explainedfrederic9866No ratings yet
- Firms With Negative EarningsDocument10 pagesFirms With Negative Earningsakhil reddy kalvaNo ratings yet