Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch51-Hip Dislocation and Femoral Head Fracture
Ch51-Hip Dislocation and Femoral Head Fracture
Uploaded by
陳韋傑0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesThe document provides guidelines for formatting document sections and subsections using titles, indentation, bolding and underlining. Sections should use size 14 title in Calibri font, while subsections use size 12 font. Borders can be adjusted for spacing. Key points in the content can be bolded and underlined. Subsections can have bullet points. The sample titles provided have up to 18 top-level sections with 2 subsections each to demonstrate the formatting structure.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ch51-hip dislocation and femoral head fracture
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides guidelines for formatting document sections and subsections using titles, indentation, bolding and underlining. Sections should use size 14 title in Calibri font, while subsections use size 12 font. Borders can be adjusted for spacing. Key points in the content can be bolded and underlined. Subsections can have bullet points. The sample titles provided have up to 18 top-level sections with 2 subsections each to demonstrate the formatting structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesCh51-Hip Dislocation and Femoral Head Fracture
Ch51-Hip Dislocation and Femoral Head Fracture
Uploaded by
陳韋傑The document provides guidelines for formatting document sections and subsections using titles, indentation, bolding and underlining. Sections should use size 14 title in Calibri font, while subsections use size 12 font. Borders can be adjusted for spacing. Key points in the content can be bolded and underlined. Subsections can have bullet points. The sample titles provided have up to 18 top-level sections with 2 subsections each to demonstrate the formatting structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
壱.
大標題(大小:14,中文:標楷體,英文:Calibri)
1. 大方向
A. 內文大小:12,中文一樣使用標楷體,英文使用 Calibri,標點符號使用全型
B. 邊界使用窄(可以節省空間,一頁塞下更多內容),位置再「版面配置」→「邊界」裡面可以
選擇邊界要哪種(見下圖)
1
2
C. 內容中如果覺得是重點處可以使用底線+粗
下面子項的符號大家可以隨意發揮
盡量子項到這層就好,再多建議直接換新的大標
弐. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
1. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
2. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
CH51 Hip Dislocations and Femoral Head Fractures
壱. Introduction to Hip Dislocations and Femoral Head Fractures
1. 好發年紀: early 30’s .
2. Event : 通常是 high energy trauma , ex: motor vehicle accidents
3. 看到 hip dislocation 需評估的 factor : The type of dislocation, direction, and the presence of a
fracture are all influenced by the amount of energy involved, the position the hip is in at the time of
injury, and the morphology of the hip
4. 看急診遇到 hip dislocation 需評估: standard trauma evaluation, a meticulous musculoskeletal and
neurologic examination, and detailed radiographic assessment to avoid missing injuries.
5. Hip dislocation outcome factor :
A. 不可改變的 factor : Cartilage damage, impacted femoral head fragments, and injury to medial
femoral circumflex artery (MFCA)
B. 可改變的 factor : timing and accuracy of the reduction
6. Poor outcome and complication : arthritis, avascular necrosis (AVN), neurologic injury, heterotopic
ossification , and re-dislocation
A. 後續產生 bad outcome 機會: 50%
弐. Assessment of Hip Dislocations
1. Evaluation of the entire patient!!!!(因為常常有 associated injuries)
2. 需考慮各種會影響 hip dislocation 的因子: the mechanism, the presence of any anatomic
characteristics that may predispose the patient to an unstable hip joint, and associated injuries that
will affect treatment plan.
参. Mechanisms of Injury for Hip Dislocations
1. 最多的原因: high-energy motor vehicle trauma
2. 其他的原因: falls, pedestrians struck by motor vehicles, industrial accidents, and athletic injuries
3. 影響 dislocation 方向或是合併 fracture 的因子:
A. The position of the hip
B. the force vector applied
C. the individual's anatomy
<TABLE 51-1>Direction of Hip Versus Injury Pattern(跟轉腳差不多)
Flexion, adduction, IR Pure posterior dislocation
Partial flexion, less adduction, IR Posterior fracture–dislocation
Hyperabduction, extension, ER Anterior dislocation
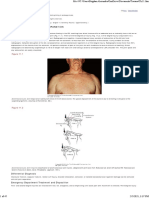
4. Posterior dislocation mechanism : dashboard injury=> hip flexion with axial loading
A. Letournel vector analysis( for force vector applied)
<figure51-1>The position of the hip during axial loading determines the type of injury
Increasing flexion, adduction, and IR pure dislocation
lesser degrees of flexion,adduction and IR fracture–dislocation. Ex: acetabulum posterior wall
fracture, pipkin femoral head fracture
B. the individual's anatomy(femoral head anatomy)
decrease in femoral anteversion , or retroversion pure dislocations 機會增加
greater anteversion and less internal rotation Fracture dislocation 機會增加
Ref: Biological factors predisposing to traumatic posterior dislocation of the hip: a selection process in the mechanism of injury. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985
5. anterior dislocation mechanism : hyperabduction and extension
A. degree of hip flexion determined the type of anterior dislocation
More Hip extension Leading to a superior pubic dislocation
More hip flexion resulting in an inferior obturator dislocation
6. 其他容易造成 hip dislocation 的運動: skiing and snowboarding injuries
A. snowboarding was five times higher than skiing (0.45 vs. 0.09/100,000)
B. snowboarding 造成的 posterior dislocation 有 30 趴機會造成 femoral head fractures
7. femoroacetabular impingement 可能也與這些 traumatic hip instability 有關,須待相關研究
A. Decreased femoral head-neck offset (CAM type) or a deep acetabulum (PINCER type) may exist in
these athletes who sustain a hip dislocation or even a subluxation
8. Fatigue fractures of the femoral head may also occur in patients with osteopenia(這邊突然神來一筆
在講 femoral head fracture~所以參考就好)
A. reported as “subchondral impaction” or “insufficiency ”fractures
四. Injuries Associated with Hip Dislocations
1. Hip Dislocations 要假設當作是 multiple trauma,常合併其他 trauma
A. Intra-abdominal, head, and chest trauma are common associated injuries
B. Thoracic aortic injury 也有被報導過
C. Common associated skeletal injuries: femoral head, neck, or shaft fractures; acetabular fractures;
pelvic ring fractures; knee injuries; ankle and foot injuries; and neurologic injuries
D. Knee injury 與 Posterior dislocation 常一起出現:
posterior dislocation, cruciate ligament injuries, and patellar fractures 合併出現機會有
25%
< Figure 51-2 > Photograph of a patient presenting after a dashboard injury.
2. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
伍. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
3. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
4. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
六. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
5. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
6. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
七. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
7. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
8. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
八. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
9. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
10. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
九. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
11. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
12. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
壱零. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
13. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
14. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
壱壱. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
15. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
16. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
壱弐. 我是範例標題 This is SAMPLE
17. 大標題 01
A. 子標題 01
子項
B. 子標題 02
18. 大標題 02
A. 子標題
子項 01
子項 02
You might also like
- Orthopedics Hyperguide MCQDocument1,445 pagesOrthopedics Hyperguide MCQAnonymous 43mqs5pElf100% (21)
- AAOS Basic Science (50 Soal)Document10 pagesAAOS Basic Science (50 Soal)Fasa RoshadaNo ratings yet
- Aaos 2015 TraumaDocument105 pagesAaos 2015 TraumaLuka Damjanovic100% (8)
- OSCE Short Case (PsA, As)Document2 pagesOSCE Short Case (PsA, As)Chaken ManiyanNo ratings yet
- Sports Medicine Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationDocument71 pagesSports Medicine Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 2017 OITE ReviewDocument105 pages2017 OITE ReviewJayNo ratings yet
- Dislocation of The Hip: A Review of Types, Causes, and TreatmentDocument12 pagesDislocation of The Hip: A Review of Types, Causes, and TreatmentTefera LeteboNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pelvic Fractures: Areview Article and A Case ReportDocument10 pagesPediatric Pelvic Fractures: Areview Article and A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- The Peel-Back Mechanism Its Role in Producing and Extending Posterior Type II SLAP Lesions and Its Effect On SLAP Repair RehabilitationDocument4 pagesThe Peel-Back Mechanism Its Role in Producing and Extending Posterior Type II SLAP Lesions and Its Effect On SLAP Repair RehabilitationSamuelNo ratings yet
- SC FractureDocument21 pagesSC FracturerynaldiandriansyaNo ratings yet
- Orthobullets Basic MODDocument172 pagesOrthobullets Basic MODNuno PaisNo ratings yet
- Reverse ShoulderreplacementDocument8 pagesReverse ShoulderreplacementagniosaiNo ratings yet
- Soal TraumaDocument10 pagesSoal TraumaYoga PribadiNo ratings yet
- SportDocument79 pagesSportMohamed Abdulgader MorganNo ratings yet
- Photography IIDocument12 pagesPhotography IIRosa Natalia Muente RojasNo ratings yet
- Shoulder and Elbow Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationDocument73 pagesShoulder and Elbow Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cause of An Implant Fracture Material - or Fabrication FailureDocument10 pagesCause of An Implant Fracture Material - or Fabrication Failurediegomez84No ratings yet
- نماذج اسئلة جراحة عظامDocument25 pagesنماذج اسئلة جراحة عظامMohammed AbuzayedNo ratings yet
- Jurding Fraktur Caput FemurDocument17 pagesJurding Fraktur Caput FemurWildan AfrNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb InjuriesDocument47 pagesLower Limb InjuriesDaisyyhyNo ratings yet
- Paid Orthobullet MCQs - SportsDocument144 pagesPaid Orthobullet MCQs - SportsShiKid COMIX-GAMENo ratings yet
- Braddom Upper Extremity DrillsDocument5 pagesBraddom Upper Extremity DrillsKennie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Specific Fractures and Joint Injuries in Children (Specific Fractures and Dislocations) The SpineDocument74 pagesSpecific Fractures and Joint Injuries in Children (Specific Fractures and Dislocations) The SpineokasyntaNo ratings yet
- Monteggia Type IV Fracture in A Child With Radial Head Dislocation Irreducible by Closed Means: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesMonteggia Type IV Fracture in A Child With Radial Head Dislocation Irreducible by Closed Means: A Case ReportAl AdvanceNo ratings yet
- In All The Slides Questions From 1 To 20 Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument22 pagesIn All The Slides Questions From 1 To 20 Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerABUBAKER ZANBOUZINo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome and Rotator Cuff Injuries: An Evidence-Based ReviewDocument10 pagesRehabilitation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome and Rotator Cuff Injuries: An Evidence-Based ReviewEduardo Santana SuárezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Elbow ComplexDocument24 pagesLecture 3 Elbow ComplexIbraheem MohdNo ratings yet
- Panfacial Trauma JCDocument47 pagesPanfacial Trauma JCx2t9wybt2wNo ratings yet
- Condylar Fracture - A Review: DR - Wasim Ahamed, Dr.S.Ishwarya, DR - Bhagya Mathivanan ADocument10 pagesCondylar Fracture - A Review: DR - Wasim Ahamed, Dr.S.Ishwarya, DR - Bhagya Mathivanan ASonali MishNo ratings yet
- Management of Orbital Floor Fractures: An Oculoplastic Surgeon's ViewDocument6 pagesManagement of Orbital Floor Fractures: An Oculoplastic Surgeon's ViewTejkiran ShettyNo ratings yet
- Hip Scope AnchorDocument9 pagesHip Scope AnchorMarcelo Wiltemburg AlvesNo ratings yet
- Morphopedics: Broken Neck (Hangman's Fracture)Document7 pagesMorphopedics: Broken Neck (Hangman's Fracture)Sulla FelixNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Slope & Def. (Virtual Work Method)Document8 pagesModule 6 - Slope & Def. (Virtual Work Method)John SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Prelab 4 Appendicular Skeleton and Joints Winter 2020Document4 pagesPrelab 4 Appendicular Skeleton and Joints Winter 2020Mareline MendietaNo ratings yet
- Misra 2019Document3 pagesMisra 2019Jawhar DhiafNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts of Posterolateral Corner Injuries of The Knee 2017Document13 pagesCurrent Concepts of Posterolateral Corner Injuries of The Knee 2017Mohan DesaiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0749806303001701 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0749806303001701 MainYoh ChenNo ratings yet
- The Disabled Throwing Shoulder Spectrum of Pathology Part II Evaluation and Treatment of SLAP Lesions in Throwers PDFDocument9 pagesThe Disabled Throwing Shoulder Spectrum of Pathology Part II Evaluation and Treatment of SLAP Lesions in Throwers PDFWallison LeaoNo ratings yet
- Broken Neck (Hangman's Fracture) : DescriptionDocument5 pagesBroken Neck (Hangman's Fracture) : DescriptionFatima RizwanNo ratings yet
- Orthobullets HANDDocument113 pagesOrthobullets HANDNuno PaisNo ratings yet
- HeadgearsDocument78 pagesHeadgearsMohammed bilal0% (1)
- Fracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarDocument69 pagesFracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarKaizar Ennis100% (1)
- Disorders of The HipDocument76 pagesDisorders of The HipMohamad RamadanNo ratings yet
- Aaos2007 Hip Knee PDFDocument61 pagesAaos2007 Hip Knee PDFHéctor Pando Sánchez100% (1)
- Trauma ExtremitatilorDocument45 pagesTrauma ExtremitatilorSavy RobynNo ratings yet
- Stemper2006 AnteriorDocument10 pagesStemper2006 AnteriorIsrael BlancoNo ratings yet
- Thediagnosisand Managementoffacial Bonefractures: Steve Chukwulebe,, Christopher HogrefeDocument15 pagesThediagnosisand Managementoffacial Bonefractures: Steve Chukwulebe,, Christopher HogrefeAna MariaNo ratings yet
- WCC Note Vol4 7Document7 pagesWCC Note Vol4 7Selma HasificNo ratings yet
- Mid Face Fractures#2 (NXPowerLite) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academy / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument37 pagesMid Face Fractures#2 (NXPowerLite) / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academy / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Reconstruction of The Umbilicus Using A Reverse Fan-Shaped FlapDocument5 pagesReconstruction of The Umbilicus Using A Reverse Fan-Shaped FlapfumblefumbleNo ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip-1Document44 pagesDislocation of Hip-1lionhearteagleNo ratings yet
- Review Questions: The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery Continuing Medical EducationDocument8 pagesReview Questions: The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery Continuing Medical EducationРоман ТерещенкоNo ratings yet
- Standards For Digital Photography in Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery - Part IIDocument12 pagesStandards For Digital Photography in Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery - Part IIYeny BelNo ratings yet
- 19-Chadha Et AlDocument4 pages19-Chadha Et AlAzmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Question OrthoDocument4 pagesQuestion OrthoMohammed AbuzayedNo ratings yet
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument4 pagesFemoral Neck Fractureehabede6445No ratings yet
- 0 2010 Rehabilitation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome AnDocument11 pages0 2010 Rehabilitation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome AnTheologos PardalidisNo ratings yet
- Soal Modul DR - LS SMT 3 SOF 2Document6 pagesSoal Modul DR - LS SMT 3 SOF 2ningshofieNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Anterior Shoulder Dislocation in An Epileptic PatientDocument4 pagesBilateral Anterior Shoulder Dislocation in An Epileptic PatientNick LasanianosNo ratings yet
- Joshi & Nagmani, 2019Document24 pagesJoshi & Nagmani, 2019Salsabila Kusuma JannatiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Clavicular Hook Plate With and Without Coracoclavicular Suture Fixation For Acute Acromioclavicular Joint DislocationDocument6 pagesComparison of Clavicular Hook Plate With and Without Coracoclavicular Suture Fixation For Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation陳韋傑No ratings yet
- Does Subacromial Osteolysis Affect Shoulder Function After Clavicle Hook Plating 2016Document5 pagesDoes Subacromial Osteolysis Affect Shoulder Function After Clavicle Hook Plating 2016陳韋傑No ratings yet
- How To Achieve An Optimal Alignment in Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy?Document11 pagesHow To Achieve An Optimal Alignment in Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy?陳韋傑No ratings yet
- tibia plateau 骨折Document8 pagestibia plateau 骨折陳韋傑No ratings yet
- Genu ValgumDocument2 pagesGenu ValgumBilly SangpengendaramerahNo ratings yet
- Test5 Congenital MalformationDocument7 pagesTest5 Congenital MalformationDera Uzoaku OkekeNo ratings yet
- Pe SubjectDocument3 pagesPe SubjectAkira EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Sports InjuriesDocument17 pages1.introduction To Sports InjuriesKhurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Hardware and Gadgets ExamDocument4 pagesHardware and Gadgets ExamLian rose Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Labiaplasty - Revision of The Large Labia MinoraDocument7 pagesLabiaplasty - Revision of The Large Labia Minoraufirst rejuvenationNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystrophyDocument55 pagesMuscular DystrophyElmutamim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Femoral Shaft FractureDocument5 pagesFemoral Shaft FracturePrimrose Gale ParingitNo ratings yet
- 5:2 Clinical Patterns in ShoulderDocument3 pages5:2 Clinical Patterns in Shoulder莉涵邱No ratings yet
- Causes of Knee TightnessDocument4 pagesCauses of Knee TightnessRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Proses Persalinan Normal Eb1Document43 pagesProses Persalinan Normal Eb1Cici RahmaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatDocument28 pagesAnterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatnurulNo ratings yet
- Bursitis and Tendonitis Power PointDocument24 pagesBursitis and Tendonitis Power PointnwaguguchinasamarthaNo ratings yet
- Congenital DeformitiesDocument102 pagesCongenital DeformitiesFahmi MujahidNo ratings yet
- 'Diamond On Quadriceps' Sign in DysferlinopathyDocument5 pages'Diamond On Quadriceps' Sign in Dysferlinopathyeseb666No ratings yet
- Bow LegsDocument6 pagesBow Legsdarkmatterangels3372No ratings yet
- Peh Module 5Document2 pagesPeh Module 5Hannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- Knee ProblemsDocument10 pagesKnee ProblemsXeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Discoid MeniscusDocument22 pagesDiscoid Meniscusonehipsa0% (1)
- NHL0035801 PDFDocument13 pagesNHL0035801 PDFCTV NewsNo ratings yet
- HOPEDocument3 pagesHOPEAndrea Venesse NaldaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis OsteoarthritisDocument33 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis OsteoarthritisTri Hastuti HendrayaniNo ratings yet
- Edukasi Kesehatan Tentang Pencegahan GoutDocument4 pagesEdukasi Kesehatan Tentang Pencegahan GoutuiNo ratings yet
- 18 - Elbow TraumaDocument42 pages18 - Elbow Traumadrcoolcat2000No ratings yet
- Hubungan Antara Usia Dengan Jenis Hernia Inguinalis Di Rs Pertamina Bintang Amin Lampung Tahun 2019-2020Document8 pagesHubungan Antara Usia Dengan Jenis Hernia Inguinalis Di Rs Pertamina Bintang Amin Lampung Tahun 2019-2020Gita AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Done-EDITED-HOPE1 q1 Mod5 ObservesPersonalSafetyProtocol-1Document18 pagesDone-EDITED-HOPE1 q1 Mod5 ObservesPersonalSafetyProtocol-1Mary Gloriscislle M. JoreNo ratings yet
- Knee Pain Knee Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamDocument1 pageKnee Pain Knee Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamKristine Joyce Quilang AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ergo MSD Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesErgo MSD Quiz AnswersOscar Jara-AlastueyNo ratings yet
- MSK Lab ManualDocument67 pagesMSK Lab ManualSyed Talha HussainNo ratings yet