Professional Documents
Culture Documents
40-Publication Peer Reviewing
Uploaded by
nagi zomrawiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
40-Publication Peer Reviewing
Uploaded by
nagi zomrawiCopyright:
Available Formats
wjert, 2021, Vol. 7, Issue 2, 175-184.
Review Article ISSN 2454-695X
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
WJERT
www.wjert.org Impact Factor Value: 5.924
PUBLICATION PEER REVIEWING
Dr. Nagi Zomrawi Mohammed*
Sudan University of Science and Technology, College of Engineering, Khartoum, Sudan
Albaha University, Albaha, Saudi Arabia.
Article Received on 08/02/2021 Article Revised on 28/02/2021 Article Accepted on 18/03/2021
ABSTRACT
*Corresponding Author
Dr. Nagi Zomrawi
Publication and scientific research are some interests of schooler
Mohammed community. Many of them, especially beginners and those, who are
Sudan University of Science interesting to know more about this matter and its circulation from
and Technology, College of submission up to publication. Peer review is a framework used to
Engineering, Khartoum,
assess the quality of research article prior to publication and gives
Sudan Albaha University,
Albaha, Saudi Arabia.
authors feedback. It judges the validity, significance and originality of
the work. This review article tried to provide a general concept of
scientific publications and their types, peer review and peer review models, and publication
route. Moreover, it highlighted some relevant topics such as plagiarism, data fabrication and
publication ethics. From literature review and topics discussed, it can be noted that, scientific
publication starts with correct writing of the article i.e., knowing how to write an article
considering the type of the article to be written. Knowing peer review process and common
types of peer review models is also necessary. Committing to research ethics leads to avoid
plagiarism and altering research materials. Moreover, it is also necessary to know how article
is evaluated and how review report is written and submitted.
KEYWORDS: Article, Citation, Fabrication, Falsification, Manuscript Transfer Program
(MTP), Peer reviewing, Plagiarism, Publication, Research integrity, Reviewer, Scientific
research, and Single blind reviewing.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific paper or sometimes known as journal article is a special type of written work. This
work can be a production of laboratory, field, social or even self-experience. It always
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 175
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
subjects to peer reviewing process.[7] It is usually written to meet especial characteristics,
such as:
Published in a periodical (journal) oriented to publish this kind of work.
Peer reviewed.
Citable.
Include citations i.e., the paper frequently refers to previous publications that are relevant
to the work topic. All cited works are listed in a reference section at the end of the paper.
Written in specific structure. This structure should include:
Title: reflecting the contents of the article.
Author(s): who contributed to the work.
Abstract: brief synopsis of paper.
Introduction: context and purpose of study.
Materials and methods: how did the study executed.
Results: objective presentation of what found out.
Discussion: debates what do results mean.
Acknowledgments (optional): who helped and support to complete the work.
References/Literature cited: whose work did publication refer to.
Appendices (optional): extra Information.[7]
Each periodical usually has its own template. This template follows a special style of writing
and data presentation to layout the work.
TYPES OF JOURNAL ARTICLES
Publications or journal articles can be assorted in different types. The most common types
are; original, short, case study and methodologies article.[8] The following are some of
publication types.
a. Original research article
This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from
research. It may be called an original article, research article, research, or just article.
b. Short article
Known also as report article or brief communication. This type of paper communicates brief
report of data from original research.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 176
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
c. Review Article
Review article provides a comprehensive summary of research on a certain topic, and a
perspective on the state of the field and where it is heading.
d. Case Study
This article reports specific instance of interesting phenomena. A goal of case study is to
make other researchers aware of the possibility that a specific phenomenon might occur.
e. Methods
Methods or Methodologies presents a new experimental method, test, or procedure. The
method described may either be completely new or may offer a better version of an existing
method. The article should describe a demonstrable advance on what is currently available [8].
Fig. 1: Types of journal articles.
RESEARCH INTEGRITY AND ETHICS
Research integrity means directing research to make others to have confidence and trust in
the methods and the results of the research.[7] It principally based on honesty, responsibility,
fairness, and accountability for all author, reviewer and the journal represented by the editor.
Author should be honor enough to submit original and not previously published research.
And not submit the research to more than one journal at the same time.
Author ethics also concerned with source of finding i.e., reliability of the collected data and
the correctness of the results.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 177
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
When, the article has more than one author, it should be important to be sure that all
mentioned authors are really contributed to the work and they are agreeing to submit the
manuscript to the specific journal.
[4]
On the other hand, reviewer should stick to the basic principles of peer reviewing that
include:
Only agree to review manuscripts for which they have the subject expertise required to
carry out a proper assessment and which they can assess in a timely manner.
Respect the confidentiality of peer review and not reveal any details of a manuscript or its
review, during or after the peer-review process, beyond those that are released by the
journal.
Not use information obtained during the peer-review process for their own or any other
person’s or organization’s advantage, or to disadvantage or discredit others.
Declare all potential conflicting interests, seeking advice from the journal if they are
unsure whether something constitutes a relevant interest.
Not allow their reviews to be influenced by the origins of a manuscript, nationality,
religious or political beliefs, gender, or other characteristics of the authors, or by
commercial considerations.
Be objective and constructive in their reviews, refraining from being hostile or
inflammatory and from making libelous or derogatory personal comments.
Acknowledge that peer review is largely a reciprocal endeavor and undertake to carry out
their fair share of reviewing and in a timely manner.
Provide journals with personal and professional information that is accurate and a true
representation of their expertise.
Recognize that impersonation of another individual during the review process is
considered serious misconduct.
Journal ethics are generally declared by the journal and can be found in the journal website.
Sometimes sent by the journal editor to the reviewer.
Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting
integrity in research and its publication.[4]
(COPE is committed to educating and supporting editors, publishers and those involved in
publication ethics with the aim of moving the culture of publishing towards one where ethical
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 178
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
practice become a normal part of the publishing culture. Its approach is firmly in the direction
of influencing through education, resources and support its members, alongside the fostering
of professional debate in the wider community).[4]
Publication Peer Review
Peer review is a proven system that used to do the following:
1. Assess the quality of research and its presentation, prior to publication.
2. Gives authors feedback to improve the quality of their research papers before
publication.[2]
The peer review process judges:
The validity of the work,
The significance of the work, and
The originality of the work.
Peer review in all its forms plays an important role in ensuring the integrity of the scholarly
record. The process depends to a large extent on trust and requires that everyone involved
behaves responsibly and ethically. Peer reviewers play a central and critical part in the peer-
review process.
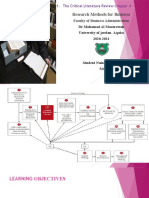
The peer review process is based on three entities; the authors, the editors, and the reviewers.
Its circulation depends to some extend on the journal and its peer review model adopted. A
sample of peer review process can be summarized as follows:
1. It always starts by the author who responsible to submit the article to the journal for
publication. Author should take into consideration all ethics concerned.[6]
2. The journal editor sends the article to reviewers relevant to the same field of the article.
3. The reviewers provide feedback after evaluating the work. And judge whether they think
the study is of high enough quality to be published.
4. The authors may then revise the manuscript article according to the reviewer comment
and resubmit it back to the editor.
5. Articles that meet the required standards are accepted for publication.
The following model of peer review process is taken after Wiley.[2]
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 179
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
Fig. 2: Peer review process (After Wiley).
Types of Peer Review
The three most common types or models of peer review are single blind, double blind, and
open peer review. Overtime, new models have developed such as collaborative, third party,
post publication, Transferrable, and transparent peer review, which are key variations from
the standard approach.[1]
1. Single blind: Author does not know the identity of the reviewer.
2. Double blind: Reviewer does not know the identity of the author, and vice-versa.
3. Open peer review: The identity of the author and the reviewer is known by all
participants, during or after the review process.
4. Collaborative: Two or more reviewers work together to submit a unified report. Or
Author revises manuscript under the supervision of one or more reviewers.
5. Third party: Authors make change to their manuscript base on an independent peer
review service. Then submit it to the journal
6. Post publication: With this type, assessment and revision of a paper continues / or occurs
after publication. This may take the form of a comments page or discussion forum
alongside the published paper.
7. Transferrable or Cascading peer review: Some of journals participate in a Manuscript
Transfer Program (MTP). If an author’s initial submission is not accepted, they may
choose to transfer their manuscript to a more suitable journal. If the manuscript was peer
reviewed, the reviewer reports will transfer to the new journal along with the manuscript
files, to be considered by the new journal’s editor.
8. Transparent Peer review: Review report is posted with the published article. Reviewer
can choose if they want to share their identity.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 180
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
REVIEW REPORT
A review report written by the reviewer should assess the layout and the contents and make a
recommendation towards a manuscript paper.
Manuscripts will include an introduction, methods (including proposed analyses), and data
(where applicable), results, discussion, and references. Reviewers will be responsible to
assess:
1. The importance of the research question(s), for journals that normally include this as a
criterion for acceptance.
2. The logic, basis, and credibility of the proposed hypotheses.
3. The soundness and feasibility of the methodology and analysis.
4. Whether the clarity and degree of methodological detail is sufficient to exactly replicate
the proposed experimental procedures and analysis.
5. Whether the authors have pre-specified sufficient outcome-neutral tests for ensuring that
the results obtained are able to test the stated hypotheses, including positive controls and
quality checks.
A recommendation of the reviewer usually be one of the following:
1. Accepted,
2. Offered the opportunity to revise, or
3. Rejected outright.
Each journal offers its own review template. Figure (3) below is a sample of which. It can be
available to the reviewer through journal website or send via email.
Fig. 3: Sample of review form (After Journal of Mountain Science).
A letter of acceptance will be issued by the journal editor to manuscripts that pass peer
review indicating that the article will be published pending successful completion of the
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 181
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
study according to the pre-registered methods and analytic procedures, as well as a defensible
and evidence-based interpretation of the results.
Copywriting is the act or occupation of writing text for the purpose of publication.
On the other hand, manuscripts that offered the opportunity to revise are suspended till
performing the required remarks recoded by the reviewers.
PLAGIARISM
Plagiarism is the practice of taking someone else's work or ideas and passing them off as
one's own.[5] Or the appropriation of another person's ideas, processes, results, or words
without giving appropriate credit.[3]
It can be classified into different types. All of which are serious and contradicts publication
ethics. The most common types of plagiarism are; Direct Plagiarism, Self-plagiarism, Mosaic
plagiarism and Accidental plagiarism.
1. Direct Plagiarism: is the word-for-word transcription of a section of someone else’s work,
without attribution and without quotation marks.
2. Self-Plagiarism: occurs when an author submits his own previous work, or mixes parts of
previous works, without permission from all professors involved.
3. Self-plagiarism also applies to submitting the same work for in different journals with
different titles.
4. Mosaic Plagiarism: occurs when an author borrows phrases from a source without using
quotation marks or finds substitutes for the author’s language while keeping to the same
general structure and meaning of the original. Sometimes called “patch writing,”
5. Accidental Plagiarism: occurs when a person neglects to cite their sources, or misquotes
their sources, or unintentionally paraphrases a source by using similar words, groups of
words, and/or sentence structure without attribution.
FALSIFICATION AND FABRICATION OF DATA
Falsification is the practice of omitting or altering research materials, equipment, data, or
processes in such a way that the results of the research are no longer accurately reflected in
the research record.[3]
Fabrication is the practice of creating data or results and recording and/or reporting them in
the research record.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 182
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
Both falsification and fabrication are probably among the most serious offenses in scientific
research as they challenge the credibility of everyone, and everything involved in a research
effort.
These offenses make it very difficult for scientists to move forward as it is unclear to anyone
what if anything is true and can be trusted. Fabrication can lead students and colleagues to
waste precious time, effort, and resources investigating dead ends.[7]
Falsification and fabrication of data are hard uncovered. This is so because research studies
are difficult to replicate. Sometimes results are not wrong, but the data are false.
Falsification and fabrication of data represent a problem because they send other researchers
down to wrong track. Wastes time and money. Besides, in some fields such as medicine can
represent danger.[7]
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
Lack of experience in scientific publishing makes those interested in an essential need to
know how to write and publish scientific article.
From topics reviewed above, it can be concluded with that it is necessary for schoolers to be
aware of:
Correct writing of journal article.
Identifying the type of the article to be written.
Knowing peer review process and common types of peer review models.
Using correct data and avoid plagiarism and commit to research ethics.
It is also necessary to have an idea about how article is evaluated, and review report is
written.
Peer review has different models, but in its all models represents an important role in
ensuring the integrity of the publications.
REFERENCES
1. http://www.bates.edu/biology/student‐resources/resources/.
2. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/.
3. https://ori.hhs.gov/definition-misconduct.
4. https://publicationethics.org/about/our-organisation.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 183
Nagi. World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology
5. https://uncw.edu/ulc/services/writing/avoidplagiarism.html#:~:text=The%20Oxford%20E
nglish%20Dictionary%20(OED,%22%20(%22Plagiarism%22).
6. https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/howscienceworks_16.
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
8. https://www.springer.com/gp/authors editors/authorandreviewertutorials/writing-a-journal
manuscript/types-of-journal-articles/10285504.
www.wjert.org ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified Journal 184
You might also like
- ChatGPT: GUIDE TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PAPER FOR ENGINEERS, RESEARCHERS, AND SCIENTISTSFrom EverandChatGPT: GUIDE TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PAPER FOR ENGINEERS, RESEARCHERS, AND SCIENTISTSNo ratings yet
- Research Report Writing: BY: Akshhaya.M Subha.R Mujebu Rahman Christoffer PsDocument37 pagesResearch Report Writing: BY: Akshhaya.M Subha.R Mujebu Rahman Christoffer PsSHANTHA RUPANo ratings yet
- Researcher's Guide: Templates and guidelines for Research article in SCI journalFrom EverandResearcher's Guide: Templates and guidelines for Research article in SCI journalNo ratings yet
- Journal of Natural Science and TechnologiesDocument172 pagesJournal of Natural Science and TechnologiesAbidin KILIÇNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Guide to Scientific Thesis Writing: AI Research writing assistance for UG, PG, & Ph.d programsFrom EverandChatGPT Guide to Scientific Thesis Writing: AI Research writing assistance for UG, PG, & Ph.d programsNo ratings yet
- How To Publish A Research Article: December 2019Document9 pagesHow To Publish A Research Article: December 2019nouha jhiderNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide to Qualitative Research: A Guide for Research Students, Supervisors, and Academic AuthorsFrom EverandA Practical Guide to Qualitative Research: A Guide for Research Students, Supervisors, and Academic AuthorsNo ratings yet
- Publishing Misconduct: A Need of Understanding and ReductionDocument7 pagesPublishing Misconduct: A Need of Understanding and ReductionLavanyaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Effective Research to Publication: A Concise ApproachFrom EverandGuidelines for Effective Research to Publication: A Concise ApproachNo ratings yet
- Engineering Origami A Comprehensive Review of RecentApplications, Design Methods, and Tools - ReviewDocument5 pagesEngineering Origami A Comprehensive Review of RecentApplications, Design Methods, and Tools - ReviewALAHAKOON T.No ratings yet
- RM 3 LiteratureReviewDocument49 pagesRM 3 LiteratureReviewmeyu721No ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Proposal?Document7 pagesHow To Write A Research Proposal?Apple TreeNo ratings yet
- Gec 004 Week 16 Instructional ModuleDocument7 pagesGec 004 Week 16 Instructional ModuleNicole ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Tips For A Streamlined Peer Review ProcessDocument5 pagesTips For A Streamlined Peer Review ProcessUtah Journal of CommunicationNo ratings yet
- Lect 5 RM ME5703 Attributions and Citations-Giving Credit Wherever Due - 094332Document46 pagesLect 5 RM ME5703 Attributions and Citations-Giving Credit Wherever Due - 094332usmanshahid866No ratings yet
- Violation of Publication Ethics, Authorship and Contributorship: RulesDocument7 pagesViolation of Publication Ethics, Authorship and Contributorship: RulesIJAR JOURNAL100% (3)
- Assignment PHD 2Document7 pagesAssignment PHD 2mrunal shethiyaNo ratings yet
- How To Write Research Article For A Journal: Techniques and RulesDocument11 pagesHow To Write Research Article For A Journal: Techniques and RulesAarthi JosephNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalHertinaNo ratings yet
- Guide2writeengineeringpaper Fezari ADocument5 pagesGuide2writeengineeringpaper Fezari Akillmonger92No ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalRiajul IslamNo ratings yet
- BUS307 Unit2 B Fall2021Document20 pagesBUS307 Unit2 B Fall2021S MYLNo ratings yet
- Publication EthicsDocument34 pagesPublication EthicsArghya DasNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument6 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalZahra mahmoodNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument4 pagesJurnaleliNo ratings yet
- RM Test 2 Complet NotesDocument15 pagesRM Test 2 Complet Notesarcotech1932No ratings yet
- Legal Matter in Reasearch PaperDocument11 pagesLegal Matter in Reasearch Papersairamnagpal1985No ratings yet
- Ethical Guidelines For JournalsDocument12 pagesEthical Guidelines For JournalsrubinaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of Open Innovation Literature: March 2016Document13 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Open Innovation Literature: March 2016Oussama ELNo ratings yet
- Literature Review in Doctoral ThesisDocument4 pagesLiterature Review in Doctoral Thesisbav1dik0jal3100% (1)
- HuhiDocument6 pagesHuhikoasanak 49No ratings yet
- Revisión 2021 Ética Publicación CientíficaDocument7 pagesRevisión 2021 Ética Publicación CientíficalacsuarezNo ratings yet
- Spar 4 SLRDocument17 pagesSpar 4 SLRrpatrissiaNo ratings yet
- Dr. AK - RM&IPR - UNIT-2 - NotesDocument11 pagesDr. AK - RM&IPR - UNIT-2 - NotesBilal uddinNo ratings yet
- Publication EthicsDocument4 pagesPublication EthicsAdriana ZanellaNo ratings yet
- Qualities and Characteristics of A Good Scientific ResearchDocument6 pagesQualities and Characteristics of A Good Scientific ResearchezeNo ratings yet
- Special Editorial Publication Ethics: © 2017 Indian Journal of Ophthalmology - Published by Wolters Kluwer - MedknowDocument4 pagesSpecial Editorial Publication Ethics: © 2017 Indian Journal of Ophthalmology - Published by Wolters Kluwer - MedknowSumit MinzNo ratings yet
- Guideline To AuthorsDocument11 pagesGuideline To AuthorsHome MadeNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Writing Study: December 2019Document13 pagesResearch Proposal Writing Study: December 2019Robert MechaNo ratings yet
- GRP6 RRL Part 2 PPT GoodallDocument55 pagesGRP6 RRL Part 2 PPT GoodallMa. Lourdes LazaroNo ratings yet
- EGEN530 - 23241 - 2 GHDocument2 pagesEGEN530 - 23241 - 2 GHdeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- RMBS M2 Lecture 8aDocument52 pagesRMBS M2 Lecture 8aKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- All About ResearchDocument22 pagesAll About ResearchArjie GongonNo ratings yet
- AvenuesforpublishingDocument5 pagesAvenuesforpublishingMaria PareraNo ratings yet
- Materi Tata Cara Penulisan Dan Publikasi Paper Ilmiah Dan Update Publikasi Paper THN 2022 - Divisi SITDocument31 pagesMateri Tata Cara Penulisan Dan Publikasi Paper Ilmiah Dan Update Publikasi Paper THN 2022 - Divisi SITSkywalker nisa dpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Undergoing Research CritiqueDocument12 pagesChapter 3: Undergoing Research Critiquesibhat mequanintNo ratings yet
- Manual For Research and Publication Ethics in Science and EngineeringDocument174 pagesManual For Research and Publication Ethics in Science and EngineeringGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- Elements OF SynopsisDocument17 pagesElements OF SynopsisDharmendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- L5 - Citations and AttributionsDocument15 pagesL5 - Citations and AttributionsHashem EL-MaRimey0% (1)
- 2515-Article Text-8155-2-10-20200226Document22 pages2515-Article Text-8155-2-10-20200226ahmedali2021syriaNo ratings yet
- The Critical Literature Review Chapter4Document39 pagesThe Critical Literature Review Chapter4HBH100% (1)
- 2016 - Research Methods in Science and EngineeringDocument131 pages2016 - Research Methods in Science and EngineeringApsae S14No ratings yet
- Sharing of Research ResultsDocument13 pagesSharing of Research ResultsCandy TuftNo ratings yet
- How To Write An Academic Research PaperDocument7 pagesHow To Write An Academic Research PaperGyanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Research Method)Document21 pagesChapter 2 (Research Method)Mesfin TadesseNo ratings yet
- Membership With Professional OrganizationDocument66 pagesMembership With Professional OrganizationmagieNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9: Ethics in Scientific Publishing Research: Sherif H. El-Gohary, PHDDocument52 pagesLecture-9: Ethics in Scientific Publishing Research: Sherif H. El-Gohary, PHDMustafa EliwaNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Presentation 01 14 23Document43 pagesSeminar - Presentation 01 14 23yichalemNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Scientific Papers - The Guidelines ProjectDocument3 pagesEvaluating Scientific Papers - The Guidelines ProjectenNo ratings yet
- Research PDFDocument182 pagesResearch PDFaregawi selemonNo ratings yet
- Johari Window ModelDocument13 pagesJohari Window ModelPegase15No ratings yet
- Erp Treatment Paper SalkovskisDocument5 pagesErp Treatment Paper SalkovskisMyraChNo ratings yet
- Overall Guidelines For Iap Applicants: Funding For Up ToDocument8 pagesOverall Guidelines For Iap Applicants: Funding For Up Toabel_kayelNo ratings yet
- HEIRS OF MARIO PACRES Vs HEIRS of CECILIA YGOADocument17 pagesHEIRS OF MARIO PACRES Vs HEIRS of CECILIA YGOAEmil BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2 IRS CODEsDocument4 pages2 IRS CODEsLuis Ewing100% (3)
- Sin and Its Consequences: I. What Is Sin?Document13 pagesSin and Its Consequences: I. What Is Sin?Mohsin ShahNo ratings yet
- ACLU BUST CARD - Know Your RightsDocument1 pageACLU BUST CARD - Know Your RightsDarren Chaker100% (40)
- Peace and Order and Public Safety PlanDocument3 pagesPeace and Order and Public Safety PlanTurado JaniceNo ratings yet
- Hiring First EmployeeDocument2 pagesHiring First EmployeeBobby DebNo ratings yet
- Module 1 1-Law & SignificanceDocument45 pagesModule 1 1-Law & SignificanceJonnalyn FabellaNo ratings yet
- Policy Formulation and EvaluationDocument12 pagesPolicy Formulation and EvaluationJanice Inquiangco CalucagNo ratings yet
- Significase of Saarc ReportDocument20 pagesSignificase of Saarc Reportneel_nknNo ratings yet
- Student Complaint ProcessDocument2 pagesStudent Complaint ProcessRizalene AgustinNo ratings yet
- Stronger Unpacked Felicity To of MistakenDocument2 pagesStronger Unpacked Felicity To of MistakenPineapple HeadNo ratings yet
- Project LawDocument72 pagesProject LawKapildev DhakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - History, Globalization, and Values-Based LeadershipDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - History, Globalization, and Values-Based LeadershipJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- Ferraris v. FerrarisDocument2 pagesFerraris v. FerrarisTrix BermosaNo ratings yet
- We Are Anonymous by Parmy OlsonDocument11 pagesWe Are Anonymous by Parmy Olsonmary eng33% (3)
- Structure of Briefs Unit 5 p1Document3 pagesStructure of Briefs Unit 5 p1api-254789374No ratings yet
- Statutory ConstructionDocument25 pagesStatutory ConstructionShasharu Fei-fei LimNo ratings yet
- COT LarpDocument78 pagesCOT LarpRebebeNo ratings yet
- Administrative LawDocument10 pagesAdministrative LawAshutosh DohareyNo ratings yet
- 拉岡講座302 the Eye and the Gaze 眼睛與凝視Document4 pages拉岡講座302 the Eye and the Gaze 眼睛與凝視Chun-hsiung ChenNo ratings yet
- American Phrenological Journal (1848)Document24 pagesAmerican Phrenological Journal (1848)Arturo OrbegosoNo ratings yet
- Business, Societal, and Ethical Contexts of Law - Week 2Document5 pagesBusiness, Societal, and Ethical Contexts of Law - Week 2Paulyn BathanNo ratings yet
- (Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Document4 pages(Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Salim RossNo ratings yet
- Legend Hotel Case DigestDocument2 pagesLegend Hotel Case DigestKian Fajardo100% (1)
- Ramadan Employee GuideDocument12 pagesRamadan Employee GuideRoubwezNo ratings yet
- Book 1 RPC Sy2019Document25 pagesBook 1 RPC Sy2019Anonymous VrAbKvNG5No ratings yet
- Melancholic PersonalityDocument5 pagesMelancholic PersonalityChris100% (1)
- 71 Ways to Practice English Writing: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersFrom Everand71 Ways to Practice English Writing: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 71 Ways to Practice Speaking English: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersFrom Everand71 Ways to Practice Speaking English: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Colleen Hoover The Best Romance Books Complete Romance Read ListFrom EverandColleen Hoover The Best Romance Books Complete Romance Read ListNo ratings yet
- Myanmar (Burma) since the 1988 Uprising: A Select Bibliography, 4th editionFrom EverandMyanmar (Burma) since the 1988 Uprising: A Select Bibliography, 4th editionNo ratings yet
- English Vocabulary Masterclass for TOEFL, TOEIC, IELTS and CELPIP: Master 1000+ Essential Words, Phrases, Idioms & MoreFrom EverandEnglish Vocabulary Masterclass for TOEFL, TOEIC, IELTS and CELPIP: Master 1000+ Essential Words, Phrases, Idioms & MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- David Baldacci Best Reading Order Book List With Summaries: Best Reading OrderFrom EverandDavid Baldacci Best Reading Order Book List With Summaries: Best Reading OrderNo ratings yet
- Christian Apologetics: An Anthology of Primary SourcesFrom EverandChristian Apologetics: An Anthology of Primary SourcesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Great Short Books: A Year of Reading—BrieflyFrom EverandGreat Short Books: A Year of Reading—BrieflyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Jack Reacher Reading Order: The Complete Lee Child’s Reading List Of Jack Reacher SeriesFrom EverandJack Reacher Reading Order: The Complete Lee Child’s Reading List Of Jack Reacher SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Seven Steps to Great LeadershipFrom EverandSeven Steps to Great LeadershipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Great Short Books: A Year of Reading—BrieflyFrom EverandGreat Short Books: A Year of Reading—BrieflyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Help! I'm In Treble! A Child's Introduction to Music - Music Book for Beginners | Children's Musical Instruction & StudyFrom EverandHelp! I'm In Treble! A Child's Introduction to Music - Music Book for Beginners | Children's Musical Instruction & StudyNo ratings yet
- Seeds! Watching a Seed Grow Into a Plants, Botany for Kids - Children's Agriculture BooksFrom EverandSeeds! Watching a Seed Grow Into a Plants, Botany for Kids - Children's Agriculture BooksNo ratings yet
- Patricia Cornwell Reading Order: Kay Scarpetta In Order, the complete Kay Scarpetta Series In Order Book GuideFrom EverandPatricia Cornwell Reading Order: Kay Scarpetta In Order, the complete Kay Scarpetta Series In Order Book GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bibliography on the Fatigue of Materials, Components and Structures: Volume 4From EverandBibliography on the Fatigue of Materials, Components and Structures: Volume 4No ratings yet
- Sources of Classical Literature: Briefly presenting over 1000 worksFrom EverandSources of Classical Literature: Briefly presenting over 1000 worksNo ratings yet
- My Mini Concert - Musical Instruments for Kids - Music Book for Beginners | Children's Musical InstrumentsFrom EverandMy Mini Concert - Musical Instruments for Kids - Music Book for Beginners | Children's Musical InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Political Science for Kids - Democracy, Communism & Socialism | Politics for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandPolitical Science for Kids - Democracy, Communism & Socialism | Politics for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chronology for Kids - Understanding Time and Timelines | Timelines for Kids | 3rd Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandChronology for Kids - Understanding Time and Timelines | Timelines for Kids | 3rd Grade Social StudiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)