Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 9
Uploaded by
Usama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesMicrometer calibration
Original Title
1588415052-lab-9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicrometer calibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesLab 9
Uploaded by
UsamaMicrometer calibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Experiment No: 9
Title: Micrometer calibration by Slip Gauges
Objectives:
i. to know the use and working of slip gauges,
ii. to know the classification and working of slip gauges,
Theory:
Slip gauges are end standards used in linear measurements.
They are used in workshop for work where a tolerance as low as
0.001mm is needed.
Slip gauges were invented by Swedish engineer, C.E. Johnson, so they
are also called Johnson gauges.
Slip gauges are rectangular blocks, made of high grade steel, having
cross section about 30mm X10mm.
These blocks are made into required sizes and hardened to resist
wear and allowed to stabilize so as to relieve internal stresses.
This prevents occurrence of size and shape variations. After hardening
the blocks, measuring faces are carefully finished to fine degree of
surface finish, flatness and accuracy.
This high grade surface finish is obtained by super finishing process
known as lapping.
Wringing of slip gauges:
The measuring face of the gauges is flat and it possesses high surface
finish.
If two slip gauges are forced against each other on measuring faces,
because of contact pressure, gauges stick together and considerable
force is required to separate these blocks. This is known as wringing of
slip gauges.
Thus, wringing refers to condition of intimate and complete contact and
of permanent adhesion between measuring faces.
Slip gauges are wrung to build desired dimension. Slip gauges are
wrung together by hand and no other external means.
Figure shows 1) Parallel wringing of slip gauges and 2) Cross wringing of
slip gauges.
In cross wringing – the two slip gauges are first cleaned to remove dirt, then
they are placed together at right angles in the form of cross and then
rotated through 90o, while being pressed together. This method causes less
rubbing of surfaces.
Almost any dimension may be built by suitable combination of gauges.
Wringing phenomenon is purely due to surface contact and molecular
adhesion of metal of blocks.
Hence, “wringing is defined as the property of measuring faces of gauge
blocks of adhering, by sliding or pressing the gauge against measuring
faces of other gauge blocks or reference faces or datum surfaces without
the use of external means.”
Uses of slip gauges.
1. As a reference standard.
2. For verification and calibration of measuring apparatus.
3. For adjustment of indicating devices.
4. For direct measurement.
5. For setting of various types of comparators
EXAMPLE:
Determining the dimension of 29.758mm by M45 slip gauge set:
Rule 1:-Minimum number of slip gauges should be used to build
dimension.
Rule 2:- Always start with the last decimal place.
Hence to build the dimension of 29.758 we need slip gauges of
20mm, 6mm, 1.7mm, 1.05mm and 1.008mm.
Procedure of performing experiment:
(1) Clean the fixed vice and micrometer
(2) Clamp the micrometer in vice putting cushioning material between
micrometer and jaws of vice to protect the micrometer from probable
damage due to clamping force.
(3) Make pile of guage blocks and insert between two anvils of the
micrometer and take reading.
(4) Increase the value of gauge blocks pile and take next few
readings.
(5) Then decrease the value of gauge blocks pile and take same
readings in decreasing order.
(6) Tabulate the readings
(7) After cleaning the place the gauge blocks should be placed in their
respective places.
Graphs: Following graphs are to be drawn:
(1) Slip gauges combination – Micrometer average
(2) Slip gauges combination – Error
(3) Micrometer average reading – correction
You might also like
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Micrometer Calibration Using Slip GaugesDocument6 pagesMicrometer Calibration Using Slip GaugesMachineryeng67% (6)
- Film Interpretation and Reference RadiographsDocument7 pagesFilm Interpretation and Reference RadiographsEnrique Tavira67% (3)
- Amazon VS WalmartDocument5 pagesAmazon VS WalmartBrandy M. Twilley100% (1)
- ARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandDocument13 pagesARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandCheGus AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Linear MeasurementsDocument52 pagesLinear MeasurementsO20 0023 Chandrasekaran. S. [PT]No ratings yet
- A Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersDocument26 pagesA Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology InstrumentsDocument17 pagesEngineering Metrology InstrumentsAnilChauvanNo ratings yet
- Experiment Measurement of Lengths, Heights, Diameters, Vernier CaliperDocument11 pagesExperiment Measurement of Lengths, Heights, Diameters, Vernier Caliperv sharvan kumar asst.prof(mech)No ratings yet
- Linear & Angular MeasurementsDocument110 pagesLinear & Angular Measurementsavutu_kunduruNo ratings yet
- CP-004 - Calibration of External MicrometerDocument5 pagesCP-004 - Calibration of External MicrometerSUNIL100% (1)
- VDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentDocument36 pagesVDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentR JNo ratings yet
- 1980 - William Golding - Rites of PassageDocument161 pages1980 - William Golding - Rites of PassageZi Knight100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- C134Document4 pagesC134maria tNo ratings yet
- The Meanings of Goddess PT IIIDocument14 pagesThe Meanings of Goddess PT IIILevonce68No ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: 3LD 450 3LD 510 3LD 450/S 3LD 510/S 4LD 640 4LD 705 4LD 820Document33 pagesWorkshop Manual: 3LD 450 3LD 510 3LD 450/S 3LD 510/S 4LD 640 4LD 705 4LD 820Ilie Viorel75% (4)
- Case Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Document15 pagesCase Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Deepak BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Session: 1: Problem StatementDocument9 pagesLab Session: 1: Problem StatementMaria MeharNo ratings yet
- Applied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringFrom EverandApplied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Burj Khalifa: Engineer Abdul MananDocument29 pagesBurj Khalifa: Engineer Abdul MananabdulmananNo ratings yet
- Experiment N 3Document4 pagesExperiment N 3G. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- Metrology (Atharv Sawant)Document9 pagesMetrology (Atharv Sawant)shashikantsawanttraderNo ratings yet
- Murali - Metrology & Measurements Lab ManualDocument30 pagesMurali - Metrology & Measurements Lab ManualsubhashNo ratings yet
- Measurements Lab Manual, Mechanical Engineering, MG UniversityDocument29 pagesMeasurements Lab Manual, Mechanical Engineering, MG Universitypramodkb_cusat100% (1)
- Q11What Are The Construction Requirement of A Good Sine BarDocument4 pagesQ11What Are The Construction Requirement of A Good Sine Baramal lohchabNo ratings yet
- Lab No: 06 "To Study Gauge Blocks and Dial Indicator" ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab No: 06 "To Study Gauge Blocks and Dial Indicator" ObjectiveKashif RazaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Gaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Tapers: Type Equation HereDocument11 pagesMeasurement of Tapers: Type Equation Hereimma coverNo ratings yet
- Hand Out NDT - 1437658138730Document7 pagesHand Out NDT - 1437658138730deveki nandan shuklaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3Document3 pagesExperiment No 3pomar026100% (1)
- Metrology and MeasurementsDocument58 pagesMetrology and MeasurementsShishir Fawade75% (4)
- MEC 112 Lectures 20182019Document54 pagesMEC 112 Lectures 20182019vargas100% (3)
- Lab ManualDocument19 pagesLab ManualAjij Mujawar100% (1)
- Metrology 2 - Slip GuagesDocument14 pagesMetrology 2 - Slip GuagesShyam VimalKumarNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesMetrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAliNo ratings yet
- Astm B557-06Document78 pagesAstm B557-06Saleh SulimanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Linear and Angular MeasurementsDocument22 pagesUnit 3 Linear and Angular Measurementsbhuyanuttam7No ratings yet
- MMM Experiment No.3 PDFDocument5 pagesMMM Experiment No.3 PDFঅর্ঘ্য রায়No ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology PDFDocument5 pagesEngineering Metrology PDFTrupti Ranjan SahuNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument39 pagesMetrology Lab ManualNivedh Vijayakrishnan0% (1)
- By The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToDocument33 pagesBy The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToMichael Castro AbuduNo ratings yet
- Slide 2newDocument99 pagesSlide 2newHeemaniNo ratings yet
- Ramkrishna Mahato Government Engineering College: S0Lid Mechanics LaboratoryDocument34 pagesRamkrishna Mahato Government Engineering College: S0Lid Mechanics LaboratoryMaynak DeyNo ratings yet
- BME Mannual BT 203-1Document41 pagesBME Mannual BT 203-1shivanshu tiwariNo ratings yet
- 18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Document5 pages18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Waqar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii 3Document30 pagesUnit-Ii 3k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- 17me64 Dme-2 Module 1Document15 pages17me64 Dme-2 Module 1GgghhNo ratings yet
- Roundness ExperimentDocument8 pagesRoundness ExperimentLanceal TanNo ratings yet
- Gauge BlockDocument7 pagesGauge Blockprakashrs295No ratings yet
- Experiment: 1 Measurement of Length, and Diameter by Vernier Caliper, Vernier Height Gauge, and MicrometerDocument51 pagesExperiment: 1 Measurement of Length, and Diameter by Vernier Caliper, Vernier Height Gauge, and Micrometerabeauty silungweNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Impact ValueDocument2 pagesAggregate Impact ValueYasir DharejoNo ratings yet
- Highway Engg Lab ExperimentsDocument9 pagesHighway Engg Lab Experimentskamalkumarbal77No ratings yet
- ME001L Lesson 2 - Measuring and Marking Out Work (Part 1)Document22 pagesME001L Lesson 2 - Measuring and Marking Out Work (Part 1)makoto kirishimaNo ratings yet
- Micrometer Screw GaugeDocument13 pagesMicrometer Screw GaugeLugafloNo ratings yet
- 1 Metrology 1.1 Objectives: 1.3.1 MicrometersDocument11 pages1 Metrology 1.1 Objectives: 1.3.1 MicrometersjoyelpaulNo ratings yet
- Metrology & Instrumentation Course File1Document112 pagesMetrology & Instrumentation Course File1harshith pondeNo ratings yet
- Workshop Theory Tools and Equipment in Bench WorkDocument4 pagesWorkshop Theory Tools and Equipment in Bench WorkFelix De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument33 pagesMetrology Lab ManualRachit_Goyal25_10No ratings yet
- Rollers and Slip GaugesDocument6 pagesRollers and Slip GaugesAnand Babu50% (2)
- MQC ManualDocument32 pagesMQC ManualPavan WaghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Linear MeasurementsDocument25 pagesChapter 3 - Linear MeasurementsJJ PJNo ratings yet
- M2 Geometrical Measurement TMM CMM PDFDocument17 pagesM2 Geometrical Measurement TMM CMM PDFRohith M. AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Hinds2000 PDFDocument14 pagesHinds2000 PDFASHUTOSH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Layout For Tutorial VideoDocument21 pagesLayout For Tutorial VideoAnkit MishraNo ratings yet
- MQA Lab Manual 2018-2019Document27 pagesMQA Lab Manual 2018-2019poluri manicharanNo ratings yet
- Metorology Lab 1 Experiment 2Document7 pagesMetorology Lab 1 Experiment 2Mathan kuttyNo ratings yet
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System (EFI) - Architecture, Types, ApplicationsDocument7 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System (EFI) - Architecture, Types, ApplicationsUsamaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3b. Fuel Injection System in CI EngineDocument28 pagesLec 3b. Fuel Injection System in CI EngineAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Vibrations: Free Response of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument8 pagesVibrations: Free Response of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsCharlie TejNo ratings yet
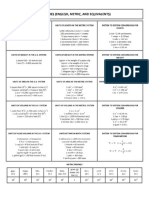
- Measures-English, Metric, and EquivalentsDocument1 pageMeasures-English, Metric, and EquivalentsUsamaNo ratings yet
- PLC 1 3Document44 pagesPLC 1 3Sayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Assignment 3 1Document2 pagesUnit 3 Assignment 3 1UsamaNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument18 pagesDynamicsSon TranNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project Report ANALYSIDocument60 pagesSummer Internship Project Report ANALYSIKshitija KudacheNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetDocument3 pagesCHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetTaylor ComansNo ratings yet
- Ahu 1997 22 1 95Document15 pagesAhu 1997 22 1 95Pasajera En TranceNo ratings yet
- GMDSSDocument1 pageGMDSSRahul rajeshNo ratings yet
- Enterprise GRC Solutions 2012 Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesEnterprise GRC Solutions 2012 Executive SummarySanath FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Tasks: Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction To 20Document2 pagesLesson Tasks: Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction To 20Марина СтанојевићNo ratings yet
- Thesis Preliminary PagesDocument8 pagesThesis Preliminary Pagesukyo0801No ratings yet
- Pelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi GuruDocument6 pagesPelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi Guruhenry jakatariNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Week 3-4Document2 pagesMath 10 Week 3-4Rustom Torio QuilloyNo ratings yet
- Lifecycle of A Frog For Primary StudentsDocument10 pagesLifecycle of A Frog For Primary StudentsMónika KissNo ratings yet
- First Semester-NOTESDocument182 pagesFirst Semester-NOTESkalpanaNo ratings yet
- Project 2 Analysis of Florida WaterDocument8 pagesProject 2 Analysis of Florida WaterBeau Beauchamp100% (1)
- Dial 1298 For Ambulance - HSBCDocument22 pagesDial 1298 For Ambulance - HSBCDial1298forAmbulanceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Document75 pagesIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiNo ratings yet
- PNP Loan Application Form February 2021 16Document6 pagesPNP Loan Application Form February 2021 16Wilhelm RegaladoNo ratings yet
- M 995Document43 pagesM 995Hossam AliNo ratings yet
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAbilu Bin AkbarNo ratings yet
- Second Language Learning in The Classroom PDFDocument2 pagesSecond Language Learning in The Classroom PDFThanh Phương VõNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDarence Fujihoshi De AngelNo ratings yet
- Vishakha BroadbandDocument6 pagesVishakha Broadbandvishakha sonawaneNo ratings yet