Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Human:: Input Output Channel
Uploaded by
ShashankOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Human:: Input Output Channel
Uploaded by
ShashankCopyright:
Available Formats
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is
a multidisciplinary field of study focusing on the
design of computer technology and, in particular, the interaction between humans (the
users) and computers.
The Human:
Input Output Channel:
There are five major senses: sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell. Of these, the first three are the
most important to HCI. Taste and smell do not currently play a significant role in HCI, and it is not
clear whether they could be exploited at all in general computer systems
1. Visual(Eye)
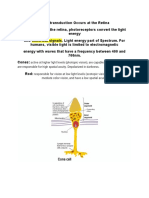
The eye is a mechanism for receiving light and transforming it into electrical
energy. Light is reflected from objects in the world and their image is focussed
upside down on the back of the eye. The receptors in the eye transform it into
electrical signals which are passed to the brain.
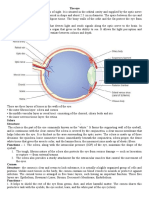
The eye has a number of important components. The cornea and lens at the
front of the eye focus the light into a sharp image on the back of the eye, the retina.
The retina is light sensitive and contains two types of photoreceptor: rods and cones.
Rods are highly sensitive to light and therefore allow us to see under a low
level of illumination. They are unable to resolve fine detail and are subject to light
saturation. This is the reason for the temporary blindness we get when moving from
a darkened room into sunlight: the rods have been active and are saturated by the
sudden light. The cones do not operate either as they are suppressed by the rods.
We are therefore temporarily unable to see at all. There are approximately 120
million rods per eye which are mainly situated towards the edges of the retina. Rods
therefore dominate peripheral vision.
Cones are the second type of receptor in the eye. They are less sensitive to
light than the rods and can therefore tolerate more light. There are three types of
cone, each sensitive to a different wavelength of light. This allows color vision. The
eye has approximately 6 million cones, mainly concentrated on the fovea, a small
area of the retina on which images are fixated.
The retina is mainly covered with photoreceptors there is one blind spot
where the optic nerve enters the eye. The blind spot has no rods or cones, our visual
system compensates for this so that in normal circumstances we are unaware of it.
The retina also has specialized nerve cells called ganglion cells.
There are two types: X-cells, which are concentrated in the fovea and are
responsible for the early detection of pattern; and Y-cells which are more widely
distributed in the retina and are responsible for the early detection of movement.
The distribution of these cells means that, while we may not be able to detect
changes in pattern in peripheral vision, we can perceive movement.
You might also like
- Human SensesDocument6 pagesHuman Sensesvicky7No ratings yet
- Human Visual System (Disowner)Document4 pagesHuman Visual System (Disowner)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Document13 pagesChapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Sidra.kNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear Physiological Foundations 2Document21 pagesEye and Ear Physiological Foundations 2Pulak DixitNo ratings yet
- Biology Eye NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Eye NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument17 pagesPhysioRicajoy RicohermosoNo ratings yet
- Visual and AuditoryDocument7 pagesVisual and AuditoryChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Psychology - Topic A - Lesson 01 The Biology of The EyeDocument2 pagesYear 10 Psychology - Topic A - Lesson 01 The Biology of The EyejosephsparksNo ratings yet
- Nes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedDocument25 pagesNes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- CHP 2Document22 pagesCHP 2Muskaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Eye and VisionDocument70 pagesThe Eye and VisionLedkos SLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Sensation and Perception: ThresholdsDocument8 pagesLecture 5: Sensation and Perception: ThresholdsT-Bone02135No ratings yet
- The Human Eye: A Simple CameraDocument18 pagesThe Human Eye: A Simple CameraljieNo ratings yet
- How Vision Works: The Science Behind SightDocument6 pagesHow Vision Works: The Science Behind SightmwxNo ratings yet
- Sensing and Perceiving 4.2Document18 pagesSensing and Perceiving 4.2Dami TepedeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESDocument12 pagesUNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESKristine Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- Human Eye: A Human Eyeball Is Like A Simple Camera!Document18 pagesHuman Eye: A Human Eyeball Is Like A Simple Camera!fidansekizNo ratings yet
- Eye Anatomy - Review 6Document7 pagesEye Anatomy - Review 6Vidini Kusuma AjiNo ratings yet
- Crash Course VisionDocument2 pagesCrash Course VisionReem SleemNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument3 pagesSensation and PerceptionjdmacatuladNo ratings yet
- EyesDocument30 pagesEyesAlfredJoshuaMirandaNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5Document3 pagesLecture Notes 5Carol RiveraNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument67 pagesSensation and PerceptionWahyu Nidar MelasaniNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument3 pagesThe Human EyeKajetano GraucosNo ratings yet
- Vision:: 1-Outer LayerDocument3 pagesVision:: 1-Outer LayerAimal IhsasNo ratings yet
- BMB 413 Neuroscience Online Notes Vol4Document19 pagesBMB 413 Neuroscience Online Notes Vol4Moose KeNo ratings yet
- Bio Psychology Lecture Notes Chapter 6 The Visual SystemDocument7 pagesBio Psychology Lecture Notes Chapter 6 The Visual SystemGeneric_Persona50% (2)
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of The Human EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Eyes Notes BiologyDocument5 pagesEyes Notes Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Phototransduction Occurs at The RetinaDocument13 pagesPhototransduction Occurs at The RetinaKathleen RussellNo ratings yet
- 7' VisionDocument17 pages7' VisionZidane ZizouNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument16 pagesCommunicationbitchass niggaNo ratings yet
- Neurostiinte - Eye, Brain, Vision - David Hubel (Cap 3,4 p32-83) PDFDocument52 pagesNeurostiinte - Eye, Brain, Vision - David Hubel (Cap 3,4 p32-83) PDFgicutaNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument21 pagesThe Human EyeMichel ThorupNo ratings yet
- The Best Place for CSS Aspirants to Learn About the Anatomy and Function of the Human EyeDocument50 pagesThe Best Place for CSS Aspirants to Learn About the Anatomy and Function of the Human EyeWaqas Gul100% (1)
- CHAPTER5 Form2Document14 pagesCHAPTER5 Form2basraawi379No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2basraawi379No ratings yet
- VisualDocument3 pagesVisualMelisa HilaireNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.2 Sense OrgansDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.2 Sense OrgansYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- The Eye and Its DiseasesDocument33 pagesThe Eye and Its DiseasesbeedgaiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of EyesDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of EyesSamar Ameen SialNo ratings yet
- Color PhysicsDocument85 pagesColor PhysicsThe GentlemanNo ratings yet
- A&p ActDocument4 pagesA&p ActGURPARABJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument17 pagesPhysiology of EyeHanna ShibuNo ratings yet
- Human Input Output Channels (2)Document4 pagesHuman Input Output Channels (2)tjames445No ratings yet
- 5 Senses and Their Sense OrgansDocument21 pages5 Senses and Their Sense OrgansViswaNo ratings yet
- Eye Prepuce Labia Minora Levator Palpebrae Superioris Muscle EyelashesDocument1 pageEye Prepuce Labia Minora Levator Palpebrae Superioris Muscle EyelashesDanica MartinezNo ratings yet
- WPR 2Document5 pagesWPR 2ishika mohanNo ratings yet
- Psychology 100Document10 pagesPsychology 100extraordinarygirl99No ratings yet
- Presentation1 EyeDocument12 pagesPresentation1 EyesujithaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of SightDocument3 pagesPhysiology of SightDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Working of Human EyeDocument13 pagesWorking of Human EyeVikashKeshavNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Stages of Visual PerceptionDocument96 pagesUnderstanding the Stages of Visual PerceptionHatin1961No ratings yet
- The eye: organ of sightDocument6 pagesThe eye: organ of sightDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- The World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!From EverandThe World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Biodiversity Annexure–IB and Annexure–IIDocument14 pagesBiodiversity Annexure–IB and Annexure–IIShashankNo ratings yet
- Resume: Name: Mobile No: 8275394783Document2 pagesResume: Name: Mobile No: 8275394783ShashankNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity GuideDocument10 pagesBiodiversity GuideShashankNo ratings yet
- OSY MergedDocument19 pagesOSY MergedShashankNo ratings yet
- Business Communication 1Document172 pagesBusiness Communication 1ShashankNo ratings yet
- Css Microproject FinalDocument19 pagesCss Microproject FinalShashankNo ratings yet
- AJP MicroprojectDocument33 pagesAJP MicroprojectShashankNo ratings yet
- Café Management SystemDocument12 pagesCafé Management SystemShashank67% (3)
- OSYDocument17 pagesOSYShashankNo ratings yet
- The Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Eye WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOS100% (2)
- Evolution of Vertebrate Eyes - How Vision EvolvedDocument14 pagesEvolution of Vertebrate Eyes - How Vision Evolvedlurolu1060No ratings yet
- Histology of The EyeDocument91 pagesHistology of The EyeFazira EkmaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Study Guide Psych 101Document34 pagesExam 2 Study Guide Psych 101raviteja100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Eye: Prepared By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, Fwacn. Lecturer - Sonm Banjul, The GambiaDocument28 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Eye: Prepared By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, Fwacn. Lecturer - Sonm Banjul, The Gambiaflex gyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Color Physics 04 SlideDocument19 pagesTheory of Color Physics 04 SlideRikta IslamNo ratings yet
- Colour Technology GuideDocument38 pagesColour Technology GuidelthyaguNo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Degenerativa de La RetinaDocument841 pagesEnfermedad Degenerativa de La RetinaMarilyn Mora100% (2)
- MelatoninDocument22 pagesMelatoninVassily RubachofNo ratings yet
- Why Red Doesn't Sound Like A Bell - Understanding The Feel of Consciousness (PDFDrive)Document287 pagesWhy Red Doesn't Sound Like A Bell - Understanding The Feel of Consciousness (PDFDrive)Roger13No ratings yet
- Optics and Human Vision: The Physics of LightDocument24 pagesOptics and Human Vision: The Physics of LightjohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument73 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesAngelika DomondonNo ratings yet
- Dibner Et Al 2010Document36 pagesDibner Et Al 2010SAMARAH SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Part 1 FRCOphth Sample MCQs 20160818 PDFDocument15 pagesPart 1 FRCOphth Sample MCQs 20160818 PDFAbdurrehman100% (1)
- PreviewpdfDocument39 pagesPreviewpdfمرام الزيوتNo ratings yet
- Field Guide To Visual and Ophthalmic Optics (2004)Document125 pagesField Guide To Visual and Ophthalmic Optics (2004)Nikhil Maha Devan100% (1)
- Notes On Eye of RabbitDocument3 pagesNotes On Eye of RabbitShailesh NiroulaNo ratings yet
- Impacts of artificial blue light on health and environmentDocument28 pagesImpacts of artificial blue light on health and environmentasta lavistaNo ratings yet
- Optogenetics PDFDocument241 pagesOptogenetics PDFdr_s_m_afzali8662No ratings yet
- AAMC Content Outline - Psych and SociologyDocument51 pagesAAMC Content Outline - Psych and SociologyShalini VijayNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13 EyeDocument46 pagesCh. 13 Eyefatucha87No ratings yet
- Ganong All MCQDocument55 pagesGanong All MCQSagor Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Khan Academy Notes - Psych and Sociology For MCATDocument238 pagesKhan Academy Notes - Psych and Sociology For MCATJuan100% (1)
- Understanding Sensation and PerceptionDocument55 pagesUnderstanding Sensation and PerceptionValerie Ah-YenNo ratings yet
- Special HistologyDocument64 pagesSpecial HistologyElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- Division of Science: Annual Report 2 0 1 8 - 2 0 1 9Document36 pagesDivision of Science: Annual Report 2 0 1 8 - 2 0 1 9Daniel FimiarzNo ratings yet
- In Search of The OriginDocument8 pagesIn Search of The OriginnappygorbyNo ratings yet
- Ca 2010-2012Document63 pagesCa 2010-2012Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- OPTHA 2.1 RETINAL DISORDERS, CHOROID AND VITREOUS - Dr. MarinDocument9 pagesOPTHA 2.1 RETINAL DISORDERS, CHOROID AND VITREOUS - Dr. MarinPatricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Human Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition4865Document8 pagesHuman Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition48651NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKANo ratings yet