Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electron Transport System: Nad +uqh
Electron Transport System: Nad +uqh
Uploaded by
Karl Capilitan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
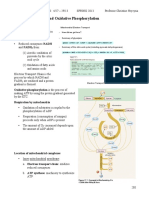
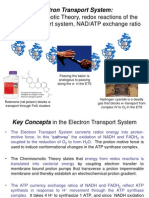
7 views3 pagesThe electron transport system (ETS) consists of four protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. [1] The complexes work together to transfer electrons from electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 through a series of redox reactions down the electron transport chain to oxygen, coupled to the pumping of protons across the membrane. [2] This creates an electrochemical gradient that is used by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to ATP, a process called oxidative phosphorylation. [3] There are three sites in the ETS where this phosphorylation occurs, producing up to 3 ATP per NADH or 2 ATP per FADH2.
Original Description:
Grade 11 topic
Original Title
1627303056
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe electron transport system (ETS) consists of four protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. [1] The complexes work together to transfer electrons from electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 through a series of redox reactions down the electron transport chain to oxygen, coupled to the pumping of protons across the membrane. [2] This creates an electrochemical gradient that is used by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to ATP, a process called oxidative phosphorylation. [3] There are three sites in the ETS where this phosphorylation occurs, producing up to 3 ATP per NADH or 2 ATP per FADH2.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesElectron Transport System: Nad +uqh
Electron Transport System: Nad +uqh
Uploaded by
Karl CapilitanThe electron transport system (ETS) consists of four protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. [1] The complexes work together to transfer electrons from electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 through a series of redox reactions down the electron transport chain to oxygen, coupled to the pumping of protons across the membrane. [2] This creates an electrochemical gradient that is used by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to ATP, a process called oxidative phosphorylation. [3] There are three sites in the ETS where this phosphorylation occurs, producing up to 3 ATP per NADH or 2 ATP per FADH2.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
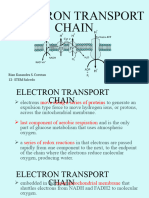
Electron transport system
Pinaki Kr. Rabha
In Krebs’s cycle, there are four dehydrogenation steps which results
formation of NAD+ to NADH and FAD+ to FADH. These compounds are
reoxidized within the mitochondria. Although this oxidation involves O2 uptake
and H2O production, neither NADH nor FAD can combine directly with O2 to form
H2O. Rather their electrons are transferred via several intermediate compounds and
constitute the electron transport system of mitochondria. This ETS also referred
as respiratory chain.
In ETS, electrons flow through the chain in a stepwise manner from more
electronegative compounds to more electropositive compounds. The electron
will flow from a higher to a lower energy level. In each step of the system, the
energy level of the electron is lowered and this energy difference is transformed
into phosphate bond energy by the conversion of ADP to ATP. The process is
called oxidative phosphorylation.
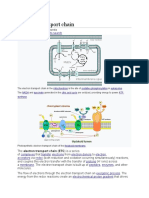
The ETS consists of four multi-protein complexes.
1. Complex-I: It consists of NADH-dehydrogenenase which contains a
flavoprotein FMN and is associated with non-heme iron-sulphur( Fe-S)
proteins. It is responsible for passing electrons from mitochondrial NADH to
Ubiquinone (UQ).
NADH + UQ +H+ ⇆NAD+ +UQH2
2. Complex-II: This complex consists of succinate dehydrogenase which
contains a flavoprotein called FAD and is associated with non-heme iron
–sulphur( Fe-S) proteins. This complex receives electrons from succinic acid
and passes them to Ubiquinone( UQ).
Succinate +UQ → Fumarate + UQH2
3. Complex-III: This complex consists of Dihydroubiquinone(UQH2):
Cytochrome- C Oxidoreductase, two forms of cytochrome b, Fe-S proteins
and Cytochrome C1. This complex receives electrons from UQH2 and passes
them to Cytochrome C. The protons received from are released out.
UQH2+ 2 ferricytochrome C ⇆UQ +2 ferrocytochrome C + 2H+
4. Complex-IV: This complex consists of Cytochrome C: Cytochrome oxidase,
Cytochrome- a and Cytochrome a3. The enzyme cytochrome oxidase
contains two atoms of cupper in addition to two molecules of heme iron.
This complex receives electrons from cytochrome C and passes them to
1/2O2. Two protons are needed and an H2O.molecule is formed.
2 ferrocytochrome –C+2H+ + 1/2O2 ⇆ 2 ferricytochrome-C +H2O.
The transfer of electrons from NADH to O2 via complex I through IV coupled to
the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate is known as oxidative
phosphorylation. There are three sites of phosphorylation during ETS.
1. During the transport of electrons from NADH to UQ through Fe-S in
complex-I.
2. From within the complex-III to cytochrome C, and
3. From cytochrome a to cytochrome a3 in the complex –IV.
In this way in terminal oxidation of NADH results in the formation of 3ATP
molecules while oxidation of FADH2 results in production of 2ATP
molecules.
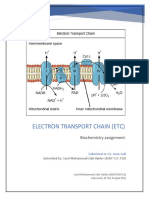
Fig: ETS. Flow of electron.
You might also like
- Biology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialDocument111 pagesBiology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialSam MishraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Review WorksheetkeyDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Review WorksheetkeyLiezel Cagais SanchezNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson SummaryDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson Summaryandrea plalu33% (6)
- Huff - ECG Workout - Exercises in Arrhythmia InterpretationDocument415 pagesHuff - ECG Workout - Exercises in Arrhythmia InterpretationWei Jie Ong93% (15)
- Electron Transport ChainDocument2 pagesElectron Transport Chainkshaf muzammil100% (1)
- 2.5 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument7 pages2.5 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylationlovelots1234100% (2)
- Electron Transport ChainDocument5 pagesElectron Transport ChainTanya Dilshad100% (1)
- Respiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument57 pagesRespiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationHanifa AffianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 ETC and Oxidative PhosphDocument29 pagesChapter 20 ETC and Oxidative PhosphSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument9 pagesElectron Transport Chainalokesh1982100% (1)
- Principles of Aerobic ExerciseDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Aerobic ExerciseAmina Sawalmeh100% (2)
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- The Anaerobic Threshold 50 Years of ControversyDocument31 pagesThe Anaerobic Threshold 50 Years of ControversyHansCristopherSaegerPizarroNo ratings yet
- Cie Alevel BiologyDocument24 pagesCie Alevel BiologyArun Ghatan100% (1)
- ATP WorksheetDocument5 pagesATP WorksheetRyan De AlloNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of CarbohydratesDocument31 pagesBiosynthesis of CarbohydratesDaniella Pasilbas Sabac100% (2)
- C 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsDocument4 pagesC 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument20 pagesElectron Transport ChainAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- The Electron Transport System Also Called The Electron Transport ChainDocument5 pagesThe Electron Transport System Also Called The Electron Transport ChainRe UpNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT NO2 ChemDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENT NO2 ChemD AmanatNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Glucose Coenzymes Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle: Electron TransportDocument4 pagesOxidation Glucose Coenzymes Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle: Electron TransportHabibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument16 pagesBiology ProjectSoumya Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument3 pagesElectron Transport ChainEmma MelNo ratings yet
- ETCDocument8 pagesETCRy L.No ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument18 pagesElectron Transport ChainArlyn Pasion BungbongaNo ratings yet
- In Relation To Lsm2101 Lec 2Document11 pagesIn Relation To Lsm2101 Lec 2jojolim18No ratings yet
- Cells and Sugars 09 Mitochondria and Ox Phos StudentDocument21 pagesCells and Sugars 09 Mitochondria and Ox Phos StudenttyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Biological OxidationDocument71 pagesCh. 9 Biological OxidationKrishna KanthNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument10 pagesBiochemHoàng LâmNo ratings yet
- The Electron Transport Chain Consists of Four Protein ComplexesDocument4 pagesThe Electron Transport Chain Consists of Four Protein ComplexesMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Fosforilasi OksidatifDocument82 pagesFosforilasi OksidatifSanti WilujengNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainetcDocument19 pagesElectron Transport Chainetcpk kaleenaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain - WikipediaDocument53 pagesElectron Transport Chain - WikipediaLsaurusNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis-5thDocument68 pagesElectron Transport and Chemiosmosis-5tholawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesElectron Transport Chain: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument14 pagesRegulation of Oxidative Phosphorylationmaaz629No ratings yet
- BotanyDocument2 pagesBotanyIrish Diana De AldayNo ratings yet
- Bioemergetics Cellular RespDocument59 pagesBioemergetics Cellular RespHassan Abib BasalNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain BSBT025F18 PDFDocument7 pagesElectron Transport Chain BSBT025F18 PDFZaki SyedNo ratings yet
- Etc PDFDocument14 pagesEtc PDFjamalNo ratings yet
- Biological Ions and Oxid PhospDocument67 pagesBiological Ions and Oxid PhospRamesh KetaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy TransactionsDocument3 pagesCellular Energy TransactionsDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument38 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationSyedaNaveenBatoolNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument34 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylationapi-321453350No ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument34 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationAbeWatanabeNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument15 pagesElectron Transport ChainKimber ManiulitNo ratings yet
- 1 Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages1 Oxidative PhosphorylationRoland ToroNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain andDocument25 pagesElectron Transport Chain andLovely Joy Aranda CurammengNo ratings yet
- Gayatree PaniDocument23 pagesGayatree PaniGobindaSahuNo ratings yet
- Title: Electron Transport System (Aerobic)Document4 pagesTitle: Electron Transport System (Aerobic)GISRemoteSensingNo ratings yet
- AtthapuDocument21 pagesAtthapuPrashanth PuttapagaNo ratings yet
- Etc N Oxid PhoshphorylationDocument74 pagesEtc N Oxid Phoshphorylationhassanainshahi13No ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain ExplainedDocument9 pagesElectron Transport Chain Explainedmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration and The MitochondrionDocument8 pagesAerobic Respiration and The MitochondrionKawtar MenjraNo ratings yet
- Plant-Physiology by TAIZ and ZEIGER PDFDocument2 pagesPlant-Physiology by TAIZ and ZEIGER PDFshxxxNo ratings yet
- 4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IIDocument3 pages4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IILinus LiuNo ratings yet
- Catabolism of Carbohydrate's and ATP ProductionDocument19 pagesCatabolism of Carbohydrate's and ATP ProductionAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- ELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERDocument47 pagesELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERAngelikaOdimerNo ratings yet
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionDocument26 pagesRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- Essey Substrate Level Phosphorylation and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument3 pagesEssey Substrate Level Phosphorylation and Oxidative PhosphorylationBryan SantosNo ratings yet
- ChemiosmosisDocument7 pagesChemiosmosisSkenzKenzNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument11 pagesElectron Transport ChainSoofia SharifNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport SystemDocument58 pagesElectron Transport SystemSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain - Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesElectron Transport Chain - Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJan Go100% (1)
- 2 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Document25 pages2 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNo ratings yet
- Act. 6 Microbial PeraltaDocument9 pagesAct. 6 Microbial PeraltaCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 09 (1) BIO462e-Trnsprt Oxid PhosDocument22 pages09 (1) BIO462e-Trnsprt Oxid PhosAs ShahirahNo ratings yet
- Ellular Espiration Chapter Outline: 8.1 Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesEllular Espiration Chapter Outline: 8.1 Cellular RespirationKevin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument33 pagesElectron Transport ChainAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- 22 CH106 Metabolic Paths For Carbohydrates Timberlake 2ndDocument70 pages22 CH106 Metabolic Paths For Carbohydrates Timberlake 2ndEnrique LiKeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Work SheetDocument4 pagesCellular Work Sheetlow. PathNo ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument5 pagesCellular MetabolismAshNo ratings yet
- General Biology Q2W3Document2 pagesGeneral Biology Q2W3Geronimo, Jonamae S.No ratings yet
- Chemiosmotic TheoryDocument42 pagesChemiosmotic TheoryM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- White Paper EpocDocument5 pagesWhite Paper Epociaeste.ecuadorNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 1marushu valoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document70 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1nia adelleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28: Bionergetics Utilization of EnergyDocument25 pagesLesson 28: Bionergetics Utilization of EnergyFlorence GuzonNo ratings yet
- 1 Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages1 Oxidative PhosphorylationRoland ToroNo ratings yet
- Article 1 Lactic Acid Is Not Muscles Foe, Its FuelDocument4 pagesArticle 1 Lactic Acid Is Not Muscles Foe, Its FuelSanjay JaisiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Nutrition College,: Volume 6, Nomor 4, Tahun 2017, Halaman 350-356Document7 pagesJournal of Nutrition College,: Volume 6, Nomor 4, Tahun 2017, Halaman 350-356•EZ• GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 5 - Biochemistry MCQs Cetric Acid CycleDocument9 pages5 - Biochemistry MCQs Cetric Acid CycleSantosh Bhandari100% (1)
- Biochemical Equilibria: Fadwa Odeh Advanced Physical ChemistryDocument26 pagesBiochemical Equilibria: Fadwa Odeh Advanced Physical Chemistryriyad mustafaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Quiz SCDocument2 pagesAerobic Respiration Quiz SCapi-323720899No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Cellular Energy and Cell Cycle Study Guide Honors BiologyDocument2 pagesUnit 3: Cellular Energy and Cell Cycle Study Guide Honors BiologyAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle PDFDocument32 pagesKrebs Cycle PDFSmexy PatataNo ratings yet
- Classwork On Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration and FermentationDocument3 pagesClasswork On Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration and Fermentationapi-272124446100% (1)
- Bio Circulation Sba SumnDocument6 pagesBio Circulation Sba SumnNelicia WilliamsNo ratings yet