Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 Reading Material
Uploaded by
priyeshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 Reading Material
Uploaded by
priyeshCopyright:
Available Formats
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Repeater:
A repeater is an electronic device that amplifies the signal it receives. You can
think of repeater as a device which receives a signal and retransmits it at a
higher level or higher power so that the signal can cover longer distances,
more than 100 meters for standard LAN cables. Repeaters work on the
Physical layer.
A repeater operates at the physical layer. Its job is to regenerate the signal
over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted so
as to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same
network. An important point to be noted about repeaters is that they do not
amplify the signal. When the signal becomes weak, they copy the signal bit
by bit and regenerate it at the original strength. It is a 2-port device.
When an electrical signal is transmitted via a channel, it gets attenuated
depending upon the nature of the channel or the technology. This poses a
limitation upon the length of the LAN or coverage area of cellular networks.
This problem is alleviated by installing repeaters at certain intervals.
Repeaters amplifies the attenuated signal and then retransmits it. Digital
repeaters can even reconstruct signals distorted by transmission loss. So,
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
repeaters are popularly incorporated to connect between two LANs thus
forming a large single LAN.
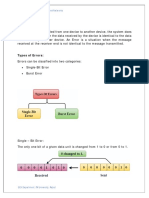
Types of Repeaters
According to the types of signals that they regenerate, repeaters can be
classified into two categories −
Analog Repeaters − They can only amplify the analog signal.
Digital Repeaters − They can reconstruct a distorted signal.
According to the types of networks that they connect, repeaters can be
categorized into two types −
Wired Repeaters − They are used in wired LANs.
Wireless Repeaters − They are used in wireless LANs and cellular
networks.
According to the domain of LANs they connect, repeaters can be divided into
two categories −
Local Repeaters − They connect LAN segments separated by small
distance.
Remote Repeaters − They connect LANs that are far from each other.
Advantages of Repeaters
Repeaters are simple to install and can easily extend the length or the
coverage area of networks.
They are cost effective.
Repeaters don’t require any processing overhead. The only time they
need to be investigated is in case of degradation of performance.
They can connect signals using different types of cables.
Disadvantages of Repeaters
Repeaters cannot connect dissimilar networks.
They cannot differentiate between actual signal and noise.
They cannot reduce network traffic or congestion.
Most networks have limitations upon the number of repeaters that can
be deployed.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Hub: -
Hub is a centralized device that connects multiple devices in a single LAN
network. When Hub receives the data signals from a connected device on any
of its port, except that port, it forwards those signals to all other connected
devices from the remaining ports. Usually, Hub has one or more uplink ports
that are used to connect it with another Hub.
A hub is the simplest in the family of network connecting devices because it
connects LAN components with identical protocols.
A hub can be used with both digital and analog data, provided its settings
have been configured to prepare for the formatting of the incoming data. For
example, if the incoming data is in digital format, the hub must pass it on as
packets; however, if the incoming data is analog, then the hub passes it on in
signal form.
Hubs do not perform packet filtering or addressing functions; they just send
data packets to all connected devices.
A hub is basically a multiport repeater. A hub connects multiple wires coming
from different branches, for example, the connector in star topology which
connects different stations.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
There are two types of the Hub.
Passive Hub: - It forwards data signals in the same format in which it receives
them. It does not change the data signal in any manner.
Active Hub: - It also works same as the passive Hub works. But before
forwarding the data signals, it amplifies them. Due to this added feature, the
active Hub is also known as the repeater.
Bridge:
Bridges are operated at Layer 2 – Data Link layer of OSI reference model.
A bridge is a repeater, with add on the functionality of filtering content by
reading the MAC addresses of source and destination. It is also used for
interconnecting two LANs working on the same protocol. It has a single input
and single output port, thus making it a 2-port device.
A bridge is a network device that connects multiple LANs (local area networks)
together to form a larger LAN. The process of aggregating networks is called
network bridging. A bridge connects the different components so that they
appear as parts of a single network.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Bridges connects two or more different LANs that has a similar protocol and
provides communication between the devices (nodes) in them.
By joining multiple LANs, bridges help in multiplying the network capacity of
a single LAN.
Since they operate at data link layer, they transmit data as data frames. On
receiving a data frame, the bridge consults a database to decide whether to
pass, transmit or discard the frame.
If the frame has a destination MAC (media access control) address in
the same network, the bridge passes the frame to that node and then
discards it.
If the frame has a destination MAC address in a connected network, it
will forward the frame toward it.
In cases where the destination MAC address is not available, bridges can
broadcast data frames to each node. To discover new segments, they maintain
the MAC address table.
Bridges also connect virtual LANs (VLANs) to make a larger VLAN.
A wireless bridge is used to connect wireless networks or networks having a
wireless segment.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Switch:
Switches are networking devices operating at layer 2 or a data link layer of
the OSI model. They connect devices in a network and use packet switching
to send, receive or forward data packets or data frames over the network.
A switch has many ports, to which computers are plugged in. When a data
frame arrives at any port of a network switch, it examines the destination
address, performs necessary checks and sends the frame to the
corresponding device(s). It supports unicast, multicast as well as broadcast
communications.
It is an intelligent network device that can be conceived as a multiport
network bridge
It uses MAC addresses (addresses of medium access control sublayer) to
send data packets to selected destination ports.
It uses packet switching technique to receive and forward data packets from
the source to the destination device.
It is supports unicast (one-to-one), multicast (one-to-many) and broadcast
(one-to-all) communications.
Transmission mode is full duplex, i.e. communication in the channel occurs
in both the directions at the same time. Due to this, collisions do not occur.
Switches can perform some error checking before forwarding data to the
destined port. Number of ports may vary from 4 to 48 based on
requirements.
Types of Switch:
Unmanaged Switch − These are inexpensive switches commonly used in
home networks and small businesses. They can be set up by simply plugging
in to the network, after which they instantly start operating. When more
devices needs to be added, more switches are simply added by this plug and
play method. They are referred to as u managed since they do not require to
be configured or monitored.
Managed Switch − These are costly switches that are used in organizations
with large and complex networks, since they can be customized to augment
the functionalities of a standard switch. The augmented features may be
QoS (Quality of Service) like higher security levels, better precision control
and complete network management. Despite their cost, they are preferred in
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
growing organizations due to their scalability and flexibility. Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) is used for configuring managed switches.
Difference between Hub and Switch:
HUB SWITCH
While switch is operated on Data link
1. Hub is operated on Physical layer.
layer.
While switch is a Unicast, multicast and
2. Hub is a broadcast type transmission.
broadcast type transmission.
3. Hub have maximum 4 ports. While switch can have 24 to 28 ports.
In hub, there is only one collision While in switch, different ports have
4.
domain. own collision domain.
While switch is a full duplex
5. Hub is a half-duplex transmission mode.
transmission mode.
While in switch, Packet filtering is
6. In hub, Packet filtering is not provided.
provided.
7. Hub cannot be used as a repeater. While switch can be used as a repeater.
Hub is not an intelligent device hence it While switch is an intelligent device so
8.
is comparatively inexpensive. it is expensive.
Hub is simply old type of device and is While switch is very sophisticated
9.
not generally used. device and widely used.
Hacking of systems attached to hub is Hacking of systems attached to switch
10.
complex. is little easy.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Router:
The router is a physical or virtual internetworking device that is designed to
receive, analyze, and forward data packets between computer networks.
It operates at Layer 3 – Network Layer of OSI reference model.
A router examines a destination IP address of a given data packet, and it uses
the headers and forwarding tables to decide the best way to transfer the
packets.
It allows users to connect several LANs and WANs together.
A router is used in LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network)
environments. For example, it is used in offices for connectivity, and you can
also establish the connection between distant networks.
It shares information with other routers in networking. It uses the routing
protocol to transfer the data across a network.
It is more expensive than other networking devices like hub, switch, bridge,
etc. It uses protocols such as ICMP to communicate between two or more
networks. It is also known as an intelligent device as it can calculate the best
route to pass the network packets from source to the destination
automatically.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
A router analyzes a destination IP address of a given packet header and
compares it with the routing table to decide the packet's next path. The list of
routing tables provides directions to transfer the data to a network
destination. They have a set of rules that compute the best path to forward
the data to the given IP address.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
There are two types of tables in the router that are static and dynamic. The
static routing tables are configured manually, and the dynamic routing tables
are updated automatically by dynamic routers based on network activity.
Routers' main components are central processing unit (CPU), flash memory,
RAM, Non-Volatile RAM, console, network, and interface card.
Routers are capable of routing the traffic in a large networking system by
considering the sub-network as an intact network.
Brouter: A brouter is a combination of the bridge and a router. It allows
transferring the data between networks like a bridge. And like a router, it can
also route the data within a network to the individual systems. Thus, it
combines these two functions of bridge and router by routing some incoming
data to the correct systems while transferring the other data to another
network.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
Gateway:
A gateway is a network node that forms a passage between two networks
operating with different transmission protocols. The most common type of
gateways, the network gateway operates at layer 3, i.e. network layer of the
OSI (open systems interconnection) model.
However, depending upon the functionality, a gateway can operate at any of
the seven layers of OSI model. It acts as the entry – exit point for a network
since all traffic that flows across the networks should pass through the
gateway. Only the internal traffic between the nodes of a LAN does not pass
through the gateway.
In network, Gateway node is a key stopping point for data on its way to or
from other networks. The Internet would not be used to use without
Gateways.
In a workplace, the gateway is the computer that routes traffic from a
workstation to the outside network that is serving up the Web pages. For basic
Internet connections at home, the gateway is the Internet Service Provider
that gives you access to the entire Internet.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
BCA314 – Data Communication and Networks
UNIT - 9
If you have a wireless network at home that gives your entire family access
to the Internet, your gateway is the modem (or modem-router combo) your
ISP provides so you can connect to their network. On the other end, the
computer that controls all of the data traffic your Internet Service Provider
(ISP) takes and sends out is itself a node.
It forms a passage between two different networks operating with different
transmission protocols.
A gateway operates as a protocol converter, providing compatibility between
the different protocols used in the two different networks.
The feature that differentiates a gateway from other network devices is that
it can operate at any layer of the OSI model.
Unidirectional and Bidirectional gateways are available.
When used in enterprise scenario, a gateway node may be supplemented as
proxy server or firewall. It uses packet switching technique to transmit data
across the networks.
BCA Department, RK University, Rajkot
You might also like
- Computer Network Lec 8Document9 pagesComputer Network Lec 8Numan arshadNo ratings yet
- Repeater - : About Repeaters Is That They Do Not Amplify TheDocument9 pagesRepeater - : About Repeaters Is That They Do Not Amplify TheCh Abdul MoizNo ratings yet
- Connecting Devices: 1. RepeaterDocument5 pagesConnecting Devices: 1. RepeaterAadhya JyothiradityaaNo ratings yet
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Document3 pagesNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Roxanne EspirituNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Government Engineering Collage, DahodDocument5 pagesGujarat Technological University: Government Engineering Collage, DahodSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Repeater: Physical Layer OSI ModelDocument4 pagesRepeater: Physical Layer OSI Modeljhony jonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Network DevicesDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - Network DevicesGeorgia Andales TaganahanNo ratings yet
- CPH Micro ProjectDocument14 pagesCPH Micro Projectharshawardhan deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Networking DevicesDocument3 pagesNetworking DevicesUdaypratapsingh RajputNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - DevicesDocument8 pagesUnit-4 - Devicesbobbysingh727272No ratings yet
- Networking Devices: 1. Network HubDocument3 pagesNetworking Devices: 1. Network HubSaurav PooniaNo ratings yet
- CN Practicalno4Document9 pagesCN Practicalno4dkchauhanNo ratings yet
- Netcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Document40 pagesNetcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Vedant KhetanNo ratings yet
- Hardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument80 pagesHardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyKinfe BeregaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Part 1)Document5 pagesLesson 1 (Part 1)Rhealyn Galang BaduaNo ratings yet
- CN Connecting DevicesDocument3 pagesCN Connecting DevicesLife SayingsNo ratings yet
- Hub & SwitchDocument11 pagesHub & SwitchShakeel MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument8 pagesNetwork DevicesYogesh AryaNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 Network Topologies and Networking DevicesDocument9 pagesUnit 02 Network Topologies and Networking Devicesroysayanccp05No ratings yet
- Data Communication Notes: Point-to-PointDocument12 pagesData Communication Notes: Point-to-PointychokhatNo ratings yet
- Network Devices and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesNetwork Devices and Their Functionsbekalu amenuNo ratings yet
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Document35 pagesNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Aaizah WaniNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument34 pagesUnit Vsaurav shekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Network DevicesDocument17 pagesChapter 5 Network Devicesninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- D PDFDocument29 pagesD PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- Networking Devices: Presented By: Iqra Mehraj Roll No. 18037112015Document8 pagesNetworking Devices: Presented By: Iqra Mehraj Roll No. 18037112015syedinamNo ratings yet
- Unit-I PPT2 BasicsDocument34 pagesUnit-I PPT2 BasicsTejas MahadikNo ratings yet
- The Network Devices FunctionDocument2 pagesThe Network Devices FunctionJhea ArponNo ratings yet
- 2 Network DevicesDocument19 pages2 Network DevicesSourava Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- DC Lab1Document32 pagesDC Lab1Sornali PaulNo ratings yet
- Gateways: Osi Modelphysical LayerDocument5 pagesGateways: Osi Modelphysical LayerAbhinav MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Network and Cloud Computing: Description A Computer Network Is A Group of Computers Linked To Each Other That EnablesDocument17 pagesNetwork and Cloud Computing: Description A Computer Network Is A Group of Computers Linked To Each Other That EnablesMadilaine Claire NaciancenoNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument11 pagesPrintJelai AlilioNo ratings yet
- Cisco Ccna: Switching Study GuideDocument79 pagesCisco Ccna: Switching Study GuideKurisingal Shine MathewNo ratings yet
- CNS Practical 3Document9 pagesCNS Practical 3How to download AnythingNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemDocument13 pagesPractical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemKikani JayanshuNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument15 pagesNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNo ratings yet
- LAN Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge and Switch)Document33 pagesLAN Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge and Switch)derejbuzuNo ratings yet
- 05 - Networking Components and Devices FDocument40 pages05 - Networking Components and Devices FBiniam NegaNo ratings yet
- Internetworking Devices: Cables Repeaters Hubs Bridges Switches RoutersDocument13 pagesInternetworking Devices: Cables Repeaters Hubs Bridges Switches RoutersPrashanth PrashuNo ratings yet
- W84-85 Comonent of DATA Comm SysDocument26 pagesW84-85 Comonent of DATA Comm Sysperweeng31No ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument19 pagesNetwork Devicespooja dangeNo ratings yet
- Topology Omkar GhodkeDocument17 pagesTopology Omkar GhodkesrgrgggdsgNo ratings yet
- Overview of Data Communication and NetworkingDocument11 pagesOverview of Data Communication and NetworkingSumita SarkarNo ratings yet
- CN Pract-1Document21 pagesCN Pract-1Ur MnNo ratings yet
- Connecting DevicesDocument28 pagesConnecting DevicesNirmalNo ratings yet
- DCCCONNECTINGDEVICEDocument27 pagesDCCCONNECTINGDEVICEgaikwadsamruddhi240206No ratings yet
- Network Devices, or in Other Words Network Hardware, Are Physical Devices Intended To ProvideDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices, or in Other Words Network Hardware, Are Physical Devices Intended To ProvideUterus Xbox er f u. RNo ratings yet
- Practical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBDocument3 pagesPractical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBJencyShah 2045No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Document25 pagesUnit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Sagar wagleNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument3 pagesNetwork DevicesHardeep Kaur (CSE - Assistant Professor)No ratings yet
- EP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsDocument18 pagesEP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsShazul Afizi Zulkiflee100% (1)
- CN Pracs A 60004190053Document106 pagesCN Pracs A 60004190053Jeet NakraniNo ratings yet
- Hubs Are Used To Build A LAN by Connecting Different Computers in A Star/hierarchal NetworkDocument4 pagesHubs Are Used To Build A LAN by Connecting Different Computers in A Star/hierarchal NetworkVKNCKBGNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument27 pagesComputer NetworkAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- CNM Chapter2Document13 pagesCNM Chapter2Piyush PatilNo ratings yet
- Rakibul Haque 21303166Document6 pagesRakibul Haque 2130316621303166No ratings yet
- CN Unit TestDocument17 pagesCN Unit TestRajashree SabaleNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument58 pagesData Communication and Computer NetworksMohammed JemalNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Basics of AlgorithmDocument15 pagesCH-2 Basics of AlgorithmpriyeshNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingDocument21 pagesCH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingpriyeshNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 1Document2 pagesLab Assignment 1priyeshNo ratings yet
- Stock ReportDocument3 pagesStock ReportpriyeshNo ratings yet
- HST LBP Assingment 1 2Document2 pagesHST LBP Assingment 1 2priyeshNo ratings yet
- NumberSystem Assg1Document2 pagesNumberSystem Assg1priyeshNo ratings yet
- 8 Reading MaterialsDocument15 pages8 Reading MaterialspriyeshNo ratings yet
- 12th OCM 17 05 21Document4 pages12th OCM 17 05 21priyeshNo ratings yet
- 11 MaterialDocument12 pages11 MaterialpriyeshNo ratings yet
- 8 IntroductionDocument2 pages8 IntroductionpriyeshNo ratings yet
- Installasi FASDocument4 pagesInstallasi FASaji nurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Hacking The Cable ModemDocument56 pagesHacking The Cable Modemjacprata100% (5)
- Comparison Table VxLAN Vs OTVDocument3 pagesComparison Table VxLAN Vs OTVNguyen LeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Frame Types PDFDocument2 pagesEthernet Frame Types PDFMarcoNo ratings yet
- RSA Authentication Manager Upgrade Plan and TimelineDocument5 pagesRSA Authentication Manager Upgrade Plan and TimelineBau NtutNo ratings yet
- IPv 4Document8 pagesIPv 4ThePekopeko123No ratings yet
- m600 Gps Ltos6Document169 pagesm600 Gps Ltos6Фантомас МихалычNo ratings yet
- Siemens Siprotec v4Document24 pagesSiemens Siprotec v4mmmindasNo ratings yet
- V1 7750 SR OS OAM and DiagnosDocument272 pagesV1 7750 SR OS OAM and DiagnoseNo ratings yet
- Next Genration FirewallDocument3 pagesNext Genration FirewallzaberNo ratings yet
- CISCO 1 BlendedDocument9 pagesCISCO 1 BlendedXiao Yei ChenNo ratings yet
- HPE Ipsec TroubleshootingDocument23 pagesHPE Ipsec TroubleshootingchellahariharanNo ratings yet
- Forti ADCDocument10 pagesForti ADCCarlos GomezNo ratings yet
- Blocking Internet Access While Allowing Local Area NetworkDocument4 pagesBlocking Internet Access While Allowing Local Area NetworkkumarchemNo ratings yet
- ICE-FIX TradeCapture Reference Manual 2 0 30-1Document39 pagesICE-FIX TradeCapture Reference Manual 2 0 30-1Oaken HallsNo ratings yet
- 7.1 30-07 Unique Local and Link Local AddressesDocument13 pages7.1 30-07 Unique Local and Link Local AddressesDomenico Antonio GullottaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Test (Hodder)Document8 pagesChapter 1-3 Test (Hodder)AbdulBasitBilalSheikhNo ratings yet
- Network ManagementDocument30 pagesNetwork ManagementSaravanan Nallusamy100% (1)
- Packet SwitchingDocument21 pagesPacket SwitchingMuhammad Faiz MasroorNo ratings yet
- Su WapDocument4 pagesSu Wap8051No ratings yet
- FSP3000 R7 16.3 MIB Conformance StatementDocument29 pagesFSP3000 R7 16.3 MIB Conformance StatementImisebe TelecomsNo ratings yet
- TDTS06 Computer NetworksDocument7 pagesTDTS06 Computer NetworksShalu TutejaNo ratings yet
- IJIRAE:: Tree Based Routing Method To Reduce Time Complexity of Routing in MANETDocument6 pagesIJIRAE:: Tree Based Routing Method To Reduce Time Complexity of Routing in MANETIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 18 Setting Up Letsencrypt On Freebsd Younis Said HaniwriterDocument5 pages18 Setting Up Letsencrypt On Freebsd Younis Said HaniwriterNJ LinNo ratings yet
- Istilah Bahasa Dalam MIRCDocument6 pagesIstilah Bahasa Dalam MIRCApit HidayatNo ratings yet
- Mini-Link TN 5.0 Etsi: Release NotesDocument29 pagesMini-Link TN 5.0 Etsi: Release NotesDanish RashidNo ratings yet
- Darnel ProjectDocument54 pagesDarnel ProjectJOHAN SEBASTIAN CURTIDOR ZABALANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 7 QuizAstron Smart TVNo ratings yet
- Cisco 2960 Basic Configuration - VLAN ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCisco 2960 Basic Configuration - VLAN ConfigurationCassandra ShafferNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Network TopologiesDocument9 pagesSubnetting Network TopologiesDeley18No ratings yet