Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Cardiovascuar Systerm-ÔN TẬP-NN1
Uploaded by
Thành ĐinhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Cardiovascuar Systerm-ÔN TẬP-NN1
Uploaded by
Thành ĐinhCopyright:
Available Formats
The Cardiovascular Systerm
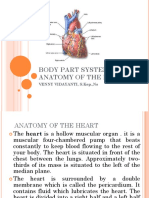
A.THE HEART
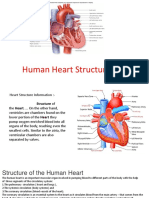
I.The Anatomy Of The Heart
II.The Wall of the Heart
1.In what cavity are the lungs and heart located? Throracic
2.What are the three layers of the heart wall? - pericardium - myocardium - endocardium
3.Which layer of the heart wall actually does the pumping of blood? myocardium
4.What is the name of the inner layer of the heart wall? endocardium
5.Where do you find the pericardial fluid? Between the two layers of pericardium
6.Why does the heart need pericardial fluid? Protects the heart from damage as it beats against the wall of the chest cavity
III.The Chambers and Valves of the Heart
1.The vessel that takes blood to the lungs is the pulmonary artery
2.The smaller chambers at the ‘’top’’ of the heart are called atria
3.A ‘’door’’ between two chambers of the heart is called a valve
4.The strings that keep valves from opening in the wrong direction are called chordae tendineae
5.A valve with three flaps is the tricuspid
6.A valve that has flaps that look like half-moons is the semilunar valve
IV.Tracing the Path of Blood through the Heart
V.How the Heart Pumps Blood
1.cardiac muscle fibers are able to contract without outside stimulation. They are said to be ......Autorrhythmic........
2.The .......conduction........ system of the heart sends signals to all the cardiac muscle fibers
3.The rate of contraction is determinded by the .........sinoatrial node...... ( also called the ......pacemaker........ )
4.when the blood supply to a part of the heart is blocked, the person may feel pain in that area. This pain is called .....angina pectoris...…
5.when cardiac muscle cells die from lack of oxygen, the person may experience a heart attack or ....myocardial infarction.....
B.MEASURING HEART HEALTH
I.Heart Rate
1.heart rate is measured with ...pulse rate...
2.Normal resting heart rate is ...72... beats per minute
3.sympathetic nervous system cause the heart rate to ....increase.....
4.your heart rate increase during ....exercise....
5.heart rate increase during ..fever...
6.resting heart rate ..decreases... with age
7.heart rate ....increase.... during stress
II.Hear Sounds
1.the doctor listens to heart sounds with a ...… stethoscope
2.the first heart sound is caused by the closing of the ........AV valves
3.the second heart sound is caused by the closing of the ......semilunar valves
4.the ....second..... heart sound is shorter and more high-pitched
5.An unusual sound in the heart is called a heart ....murmur....
6.A ......stenotic..... valves is not as flexible, doesn't open as easily, and allows less blood throught it
7.A......incompetent..... valves doesn't close very well and thus blood leaks throught it.
8.the ...first.... heart sound is longer and more low-pitched
III.EKG
IV.Blood Pressure
1.Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood on the walls of the blood vessels
2.In a blood pressure reading of 120/80, the 80 represents the diastolic pressure
3.The systolic pressure is the pressure when the ventricles are contracting
4.An increase in blood volume increases blood pressure
5.When the heart pumps less blood per contraction, this decreases blood pressure
6.Vasoconstriction increases blood pressure
7.If someone has lost a lot of blood, his blood pressure has decreased
C.THE BLOOD VESSELS
I.Types of Blood vessels
1.A ...capillary bed.... is a network of capillaries that supplies a tissue with oxygen and nutrients and removes wastes
2.The ...systemic circuit.... is a network of blood vessels that carries blood from the heart to other areas of the body and back to the heart
3.....arterioles..... are vessels that have muscular walls and deliver blood to capillaries
4......venules... are small vessels that receive blood from capillaries and deliver it to vein
5....arteries... carry blood directly from the heart. They have thick, muscular walls
6...Vein... carry blood back to the heart and sometimes have valves
7.the ....pulmonary circuit.... is a network of blood vessels that carry blood between the heart and the lungs
II.The Major Blood Vessels of the Body
1.the ..brachial.... artery is located in the upper arm
2.the ....abdominal aorta.... is the main artery that brings blood to the abdomen
3.the ..carotid.... artery travels throught the neck to the head
4.the ....femoral.... artery is a found in the upper leg
5.the ..radial... artery is found in the lower arm and wrist
6.the ....pulmonary..... artery takes blood to the lungs
7.the ..great saphenous ... vein is found in the inner thigh
8.the ..cephalic... vein is located in the upper arm
9.the ..pulmonary... vein delivers blood from the lungs to the heart
10.the ...common iliac.... vein is a main branch of the inferior vena cava
11.the ...brachiocephalic... vein is a main branch of the superior vena cava
12.the ...anterior tibial.... is found in the lower leg
D.THE LYMPHATIC VESSELS
1.Lymphatic vessels return fluid to the veins
2.More fluid leaves the blood capillaries at the tissues than Is returned
3.Lymph is a milky fruid containing fats, dissolved molecules, and water.
4.Edema occurs when the lymphatic vessels fai to do their job
5.The lymphatic vessels helps to maintain homeostasis of blood volume
You might also like
- Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Human Heart StructureDocument9 pagesHuman Heart StructureSayali Patil100% (2)
- Brain Breaks: Animal WalksDocument6 pagesBrain Breaks: Animal WalksMárcia DiasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemkaz92100% (6)
- Notes On The Qliphoth and PsychoanalysisDocument7 pagesNotes On The Qliphoth and PsychoanalysisAstarte Kali100% (1)
- The Tell Tale Heart QuestionsDocument8 pagesThe Tell Tale Heart QuestionsAmina SalahNo ratings yet
- F31 Measurement 2 PDFDocument348 pagesF31 Measurement 2 PDFJoseph WarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Overview and PositionDocument11 pagesThe Heart: Overview and PositionLil_QuinceNo ratings yet
- Heart Circulatory System Study GuideDocument10 pagesHeart Circulatory System Study GuideKyle YiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Pig Heart DissectionDocument7 pagesPig Heart DissectionJannah Renee TANGONNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection WorksheetDocument5 pagesHeart Dissection Worksheetapi-237875296100% (1)
- ESWT - For Myositis Ossificans CaseDocument13 pagesESWT - For Myositis Ossificans CaseSienriesta NovianaNo ratings yet
- Worthington RollairDocument32 pagesWorthington RollairLucyan Ionescu100% (1)
- Anil Ghom - Textbook of Oral Radiology - 2nd Ed - WWW - Thedentalhub.org - inDocument928 pagesAnil Ghom - Textbook of Oral Radiology - 2nd Ed - WWW - Thedentalhub.org - inSatavisha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystermDocument4 pagesThe Digestive SystermThành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Name: Cristina Silva Period: 3rd Heart Worksheet (Put Answers in Color)Document3 pagesName: Cristina Silva Period: 3rd Heart Worksheet (Put Answers in Color)api-334907221No ratings yet
- Sheep Heart DissectionDocument4 pagesSheep Heart Dissectionapi-303657529No ratings yet
- Lab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument4 pagesLab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Answer KeyDocument24 pagesCh15 Answer Keybhupinder09100% (1)
- 6 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages6 - The Cardiovascular SystemKolea 2003No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksNo ratings yet
- Syok Hipovolemik EnglishDocument25 pagesSyok Hipovolemik Englishatmarida 123No ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFDocument11 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFAnonymous e6LINHNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Mariam MohammedDocument16 pagesThe Heart: Mariam Mohammedmemomnmnm78No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsDocument33 pagesCardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsnoshNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory SystemPuguh HadiNo ratings yet
- DomingoDocument3 pagesDomingoMikaellah DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissueDocument4 pagesThe Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissuehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesELYANNo ratings yet
- Pre Reading Cardio Vascular System AssessmentDocument10 pagesPre Reading Cardio Vascular System AssessmentShahbaz aliNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Long ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory Long Activity26jmuzychenkoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The HeartShara QueenNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris (Jantung)Document12 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris (Jantung)Nia Mldyni100% (1)
- Anatomy WordDocument4 pagesAnatomy Wordarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- Acfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Document60 pagesAcfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Bala GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Heart As A Pump: DMS ReportDocument12 pagesHeart As A Pump: DMS ReportYateesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 77Document2 pages77Alina KolosovaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument16 pagesCardiovascular SystemMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Project BioDocument18 pagesProject Bioyanshu falduNo ratings yet
- CVS Heart Complete PDFDocument364 pagesCVS Heart Complete PDFNabeel HamzaNo ratings yet
- Sayed Daniyal Ali - Blood-Vessels-worksheetDocument1 pageSayed Daniyal Ali - Blood-Vessels-worksheetSayed Daniyal AliNo ratings yet
- System CardiovascularDocument22 pagesSystem Cardiovascularvk seruniNo ratings yet
- Cardiology: Patent LumenDocument5 pagesCardiology: Patent LumenDeepthi VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1Yenny YenNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument19 pagesHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Term 4Document40 pagesTerm 4thatolebelo9No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The HeartxXjhmXxNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument7 pagesHeartKaryll AguilaNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection: Background InformationDocument9 pagesHeart Dissection: Background Informationapi-482694849No ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument20 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisInas NadaaNo ratings yet
- THE Circulatory System: Anatomy & Physiology 12Document15 pagesTHE Circulatory System: Anatomy & Physiology 12Vanesa VorpsiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Systemapi-297526590No ratings yet
- How The Heart Work..con'tDocument1 pageHow The Heart Work..con'tAnonymous cekPJylABoNo ratings yet
- The Heart and The Immunity BsoaDocument26 pagesThe Heart and The Immunity BsoaJaniegh LJan CerxyseNo ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument35 pagesHuman HeartJuliet Aira Cabero QuibilanNo ratings yet
- Human Heart ScienceDocument7 pagesHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument20 pagesAngina PectorisJyoti singhNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument9 pagesThe Cardiovascular System The HeartMarjorie AbelgasNo ratings yet
- Heart by Aritra SahaDocument15 pagesHeart by Aritra SahaAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Semis ReviewerDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System Semis ReviewerReggie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Family: Word)Document16 pagesFamily: Word)Thành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System-ÔN TẬP-NN1Document2 pagesThe Respiratory System-ÔN TẬP-NN1Thành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- The Digestive Systerm-ÔN TẬP-NN1Document2 pagesThe Digestive Systerm-ÔN TẬP-NN1Thành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- KT nn2 l2Document13 pagesKT nn2 l2Thành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- NN 2Document10 pagesNN 2Thành ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Camy Plants: RT Offer LetterDocument1 pageCamy Plants: RT Offer LetterShailesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Presentation Jo Wykes 2Document27 pagesEpilepsy Presentation Jo Wykes 2Sana SajidNo ratings yet
- Indumax CLS54D EN - 0218Document12 pagesIndumax CLS54D EN - 0218Carlos LeonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electrical CodeDocument14 pagesPhilippine Electrical CodeJohn Oyan EstilloreNo ratings yet
- REVISED Syllabus GR 6-8 Science CambridgeDocument10 pagesREVISED Syllabus GR 6-8 Science CambridgePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAP3 - Evaporation & Infiltr.Document39 pagesCHAP3 - Evaporation & Infiltr.Aisyah MustafaNo ratings yet
- Review On Metallization Approaches For High-Efficiency Silicon Heterojunction Solar CellsDocument16 pagesReview On Metallization Approaches For High-Efficiency Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells蕭佩杰No ratings yet
- Gender Neutrality of Criminal Law in India A Myth or Reality With Special Reference To Criminal Law Amendment Bill 2019Document19 pagesGender Neutrality of Criminal Law in India A Myth or Reality With Special Reference To Criminal Law Amendment Bill 2019AbhiNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMDocument12 pages2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Deltaweld 453 MilDocument40 pagesDeltaweld 453 MilHugo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument7 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFaulia rahmiNo ratings yet
- Question Epidmiolgy PDFDocument7 pagesQuestion Epidmiolgy PDFzkalel_mNo ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument1 pageAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Group BehaviorDocument31 pagesFoundations of Group BehaviorRaunakNo ratings yet
- Cake Makers GuidanceDocument16 pagesCake Makers GuidancegenebabaNo ratings yet
- Indian Penal Code (IPC) Detailed Notes and Study Material - LexFortiDocument46 pagesIndian Penal Code (IPC) Detailed Notes and Study Material - LexFortiQasim Sher HaiderNo ratings yet
- Types of CompressorsDocument44 pagesTypes of Compressorsjezreeleda.limNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Concrete Cracks Repair Using Epoxy ResinDocument18 pages(PDF) Concrete Cracks Repair Using Epoxy ResinAakanksha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Astm g21 g22Document7 pagesAstm g21 g22ENZO CORSI0% (1)
- Optional 17 - DisplayDocument2 pagesOptional 17 - DisplayHà Ngọc ĐặngNo ratings yet
- COMEDK UGET-2011 Medical Rank ListDocument147 pagesCOMEDK UGET-2011 Medical Rank ListiamvarkeyNo ratings yet
- Doc22 PDFDocument78 pagesDoc22 PDFAmelia BrownNo ratings yet
- DP27, DP27E, DP27R and DP27Y Pilot Operated Pressure Reducing ValvesDocument36 pagesDP27, DP27E, DP27R and DP27Y Pilot Operated Pressure Reducing ValvesAntonio FedatoNo ratings yet