Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Organization
Uploaded by
Nicole BonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Organization
Uploaded by
Nicole BonCopyright:
Available Formats
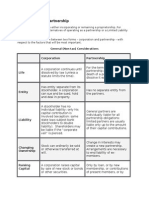
Difference between Sole Proprietorship and One Person Corporation
Definition
Sole Proprietorship Is a business structure that is owned by a single individual. The
owner owns all the assets and has unlimited personal liability for losses since there is
no legal distinction between the owner and the business.
While the One Person Corporation (OPC) is a corporation with a single stockholder. In
the former corporation law, you need to have at least 5 incorporators to form a
Corporation. But with OPC, no need for 4 other incorporators and no need for a board of
directors.
Liability
Sole Proprietorship is directly liable. This means the law does not put any distinction
between the company and the individual. The person inherits both the assets and
income of the business, but also its debts and losses.
While an OPC is a separate entity from the owner. Should the company lose money or
go in debt, the personal assets of the owner will not be affected.
Succession
When a sole proprietor dies, the assets and liabilities of his/her business will be
transferred to his/her children/heirs, and the license over the business will expire. If the
children/heirs want to continue the business, they need to secure a new business
license.
For OPC, there is continuity even if the owner dies. In the event of death or incapacity of
the OPC owner, the nominee will take over to continue the business operations until the
successful transfer to the heirs. The heirs then can continue to operate the business
without the need to register a new corporation.
Difference between Corporation Sole and One Person Corporation
Definition
A corporation sole is an individual person who represents an official position which has
a single separate legal entity. The death of the individual will not affect the corporation
as there is a right of succession. The Crown, bishops, deans and vicars are examples of
a corporation sole. A corporation sole can only be created by statute. It is also one of
the type of corporation ( the other types is corporation aggregate).
While one person corporation is a type of company that beneficial for micro, small, and
medium-sized businesses. One of the key benefits of OPC is that the shareholder’s
liability is limited to the extent of the shareholder’s assets.
Difference between Partnership and Joint Venture
Definition
Joint Venture is a business formed by two or more than two persons for a limited period
and a specific purpose.
While Partnership is business arrangement where two or more persons agree to carry
on business and have mutual share in the profits and losses.
Purpose
A partnership’s purpose is not limited to a single project or goal. It is oriented towards
running a business or long-term enterprise and making a profit.
While Joint ventures are designed to accomplish a specific goal. Each party contributes
their share to an agreed-upon task. Profit may not be on the list of goals of the joint
venture at all.
How it is Made
Partnerships are usually formed with a partnership agreement or contract between the
individuals who make up the partnership. The partnership agreement lays out the terms
of the partnership covering topics such as sharing in profits and losses, how partners
can leave the partnership, the percentage of control held by each partner, and similar
issues.
While Joint ventures may not necessarily have an agreement in place. Or, if there is an
agreement, it is a short-term and very specific contract that addresses the particular
project that is going to be undertaken.
How long does it Last
Partnerships are designed to last for the life of the business. They can run infinitely.
In contrast, joint ventures are meant for short-term project lifetimes. They are not meant
to last forever, just long enough to allow the parties to reach a particular goal.
Accountability
When a partnership goes wrong and causes a moral hazard, only the offending party is
faced with fault. Even though the deal is for the long-term, this protects partners that
have entered a deal unwittingly before a disaster.
In the case of a joint venture both parties are seen at fault in the case of a moral hazard
or criminal wrongdoing. Accountability greatly increases. This makes joint ventures
riskier in the short-term.
You might also like
- How Jewry Turned England Into A Plutocratic State - World-Service (1940)Document22 pagesHow Jewry Turned England Into A Plutocratic State - World-Service (1940)Angelo Capello LinaresNo ratings yet
- Legal Structures Shape Your Journey As A BusinessDocument3 pagesLegal Structures Shape Your Journey As A BusinesszaraNo ratings yet
- Business Ownerhsip - BoholDocument7 pagesBusiness Ownerhsip - BoholJohn Kenneth BoholNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganisationDocument11 pagesForms of Business Organisationuche0% (1)
- Efficient Use of Paper Rule (A.M. No. 11-9-4-SC) - Philippine E-Legal ForumDocument4 pagesEfficient Use of Paper Rule (A.M. No. 11-9-4-SC) - Philippine E-Legal ForumkeouhNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A Sole ProprietorshipDocument3 pagesAdvantages of A Sole Proprietorshiplaur33nNo ratings yet
- AccountsDocument8 pagesAccountsAlveena UsmanNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganizationsDocument27 pagesForms of Business OrganizationsArminda Villamin100% (1)
- Corporation vs. PartnershipDocument4 pagesCorporation vs. PartnershipPau Che100% (1)
- Criminal Revision Draft For StudentsDocument9 pagesCriminal Revision Draft For StudentsAayushNo ratings yet
- Joint Stock CompaniesDocument16 pagesJoint Stock CompaniesJoynul Abedin100% (8)
- Module 5 1Document6 pagesModule 5 1Manvendra Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Business Structure Sample PDFDocument5 pagesBusiness Structure Sample PDFAnujAggarwalNo ratings yet
- CUPINO AND COLOCADO vs. PACIFIC REHOUSE CORPORATIONDocument3 pagesCUPINO AND COLOCADO vs. PACIFIC REHOUSE CORPORATIONMac SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sabeed Ejaz Types of PartnershipDocument3 pagesSabeed Ejaz Types of PartnershipSidra JamilNo ratings yet
- The 3 Major Forms of Business OrganizationDocument2 pagesThe 3 Major Forms of Business OrganizationXienaNo ratings yet
- Types of OrganizationDocument2 pagesTypes of OrganizationNongstan Jie Jie ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Companies Law (Or The Law of Business Associations) Is The Field ofDocument11 pagesCompanies Law (Or The Law of Business Associations) Is The Field ofsubendNo ratings yet
- The Law of PartnershipDocument7 pagesThe Law of PartnershipAbu AsadNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law AssignmentDocument8 pagesCommercial Law AssignmentMemory ApiyoNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A Sole ProprietorshipDocument4 pagesAdvantages of A Sole Proprietorshipdin shaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Finals - AFM101Document10 pagesNotes For Finals - AFM101MHIL RAFAEL DAUGDAUGNo ratings yet
- Busl Assignment2 M.P.K SrihariDocument14 pagesBusl Assignment2 M.P.K Sriharimpk srihariNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Course WorkDocument9 pagesFinancial Accounting Course WorkProsper TimothyNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument21 pagesBusiness LawUMAR FAROOQ TIPUNo ratings yet
- Week 2-AFDocument15 pagesWeek 2-AFZainab AshrafNo ratings yet
- Sole ProprietorshipDocument6 pagesSole ProprietorshipEron Roi Centina-gacutanNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument16 pagesPartnershipJasmandeep brar100% (1)
- Lengua y Derecho IDocument56 pagesLengua y Derecho ICarolina BlancoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Forms of Business OrganisationDocument9 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Forms of Business OrganisationdivineauramasterNo ratings yet
- Forms of BusinessDocument2 pagesForms of BusinessCher NaNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument26 pagesLecture TwoAnsumanan FeikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Ownership Part-IIDocument18 pagesChapter 2 - Forms of Business Ownership Part-IIQwRasel0% (1)
- Hashiii B.LawDocument6 pagesHashiii B.LawWazeeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, CorporationDocument4 pagesForms of Business: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, CorporationLaurever CaloniaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OwnershipDocument17 pagesForms of Business OwnershipnatembeatalliaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Quiz - EssayDocument3 pagesWeek 5 Quiz - EssayJohn Edwinson JaraNo ratings yet
- Hashiii B.LawDocument7 pagesHashiii B.LawWazeeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- BE Chapter 2Document111 pagesBE Chapter 2Bell BottleNo ratings yet
- Definition of Partnership FirmDocument3 pagesDefinition of Partnership FirmAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Limited PartnershipDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Limited Partnershipsonali mahajan 833No ratings yet
- Accounting For PartnershipDocument8 pagesAccounting For PartnershipsmlingwaNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Business Organizations: By: Ma. Beatrix D. Sampang Bsa - 4Document17 pagesDifferent Forms of Business Organizations: By: Ma. Beatrix D. Sampang Bsa - 4anon_855990044No ratings yet
- Corporate Law (Dba354)Document67 pagesCorporate Law (Dba354)Awini ShadrachNo ratings yet
- 13 Desc - Tania Fitri Hanifah - d41201514 - BKPM Week 15Document5 pages13 Desc - Tania Fitri Hanifah - d41201514 - BKPM Week 15Tania FitriNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship, Sole Proprietorships, and Partnerships: What Type of Business Should I Choose?Document10 pagesEntrepreneurship, Sole Proprietorships, and Partnerships: What Type of Business Should I Choose?Loushayne MolatoNo ratings yet
- Entrep 9 Lesson 3 Differentiate The Legal Forms of Business OwnershipDocument3 pagesEntrep 9 Lesson 3 Differentiate The Legal Forms of Business OwnershipAlyanna Gyka AnoNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument4 pagesPartnershipqwertyNo ratings yet
- People: in Order To Manifest A Partnership, at Least Two People Must Share A Common Goal. inDocument2 pagesPeople: in Order To Manifest A Partnership, at Least Two People Must Share A Common Goal. inRafleah RiojaNo ratings yet
- Partnership Firm: Legal Agreement ProfitDocument11 pagesPartnership Firm: Legal Agreement ProfitShlok KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Document - 2Document9 pagesDocument - 2kakadhondupNo ratings yet
- Business Basics Handout Types of Business OwnershipDocument5 pagesBusiness Basics Handout Types of Business OwnershipToniann LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganisationDocument8 pagesForms of Business Organisationarvind123kumarNo ratings yet
- Types of BusinessesDocument3 pagesTypes of BusinessesNhư Quỳnh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Partnership NotesDocument21 pagesPartnership NotesShellian CunninghamNo ratings yet
- MNR College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument38 pagesMNR College of Engineering & TechnologyDJSATYAMNo ratings yet
- Sole Proprietorship-PartnershipDocument20 pagesSole Proprietorship-PartnershipAislinnNo ratings yet
- Pre 03Document2 pagesPre 03ArtisanNo ratings yet
- Explain The Concept of Unlimited Liability As It Relates To Sole ProprietorshipsDocument4 pagesExplain The Concept of Unlimited Liability As It Relates To Sole ProprietorshipsLeigh LynNo ratings yet
- Bussiness Law Chapter SixDocument5 pagesBussiness Law Chapter SixhussenNo ratings yet
- Saito University College: Introduction To Financial Accounting BHRM 1144 Individual AssignmentDocument15 pagesSaito University College: Introduction To Financial Accounting BHRM 1144 Individual AssignmentDehbban Sandran SkyNo ratings yet
- BL AssignmentDocument20 pagesBL AssignmentSheiryNo ratings yet
- Types of Business Ownership in MalaysiaDocument3 pagesTypes of Business Ownership in MalaysiaMardhiah Ramlan0% (1)
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics Canada in The Global Environment 10th Edition Michael Parkin Robin BadeDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Macroeconomics Canada in The Global Environment 10th Edition Michael Parkin Robin BadeAshleyHicksqdia100% (41)
- Decision Tree Exercise 2 SolDocument5 pagesDecision Tree Exercise 2 SoljitenNo ratings yet
- (Quiz 2-ANSWER) ULLC1003 - 202005Document6 pages(Quiz 2-ANSWER) ULLC1003 - 202005Jessie PcdNo ratings yet
- World War II Causes Events and ConsequencesDocument1 pageWorld War II Causes Events and ConsequenceskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Drug War: Camp General Mariano N. Castañeda, Silang, CaviteDocument3 pagesPhilippine Drug War: Camp General Mariano N. Castañeda, Silang, CaviteMarry Belle VidalNo ratings yet
- Sameer Overseas Placement Agency v. Joy Cabiles PDFDocument5 pagesSameer Overseas Placement Agency v. Joy Cabiles PDFGain DeeNo ratings yet
- Sports Academy Registration Form 2021Document2 pagesSports Academy Registration Form 2021Kartik Tyagi0% (1)
- Fast Track v. ANI - Section D - 200101054 - Deep Parag PadhDocument4 pagesFast Track v. ANI - Section D - 200101054 - Deep Parag PadhDeep PadhNo ratings yet
- IYCN Agents of Change - 2009 ReportDocument27 pagesIYCN Agents of Change - 2009 ReportChaitanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation of FIDIC Contracts 1676286007Document198 pagesDigital Transformation of FIDIC Contracts 1676286007iisisNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis On Article 2A of ConstitutionDocument15 pagesCritical Analysis On Article 2A of ConstitutionBareerah99No ratings yet
- The Law of Equivalent ExchangeDocument2 pagesThe Law of Equivalent ExchangeSphelele MaphumuloNo ratings yet
- The Mah Welfare Officers (D, Q and CoS) Rules, 1966Document14 pagesThe Mah Welfare Officers (D, Q and CoS) Rules, 1966Nanmathi Balachandran 10G 21No ratings yet
- City of Cleveland's Status Report On Cleveland Public Power Reliability InitiativesDocument3 pagesCity of Cleveland's Status Report On Cleveland Public Power Reliability InitiativesWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- CANON 4 (Mondares, Hector JR) The Practice of Civil Engineering 1.1 GeneralDocument7 pagesCANON 4 (Mondares, Hector JR) The Practice of Civil Engineering 1.1 Generalmondares hectorNo ratings yet
- HR Audit ChecklistDocument7 pagesHR Audit ChecklistPrabhu PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Public Land ActDocument31 pagesPublic Land ActBong Bong SilupNo ratings yet
- Scenic Nevada v. City of Reno Suit DismissedDocument7 pagesScenic Nevada v. City of Reno Suit DismissedBen MargiottNo ratings yet
- Rules For Court Assisted MediationDocument7 pagesRules For Court Assisted MediationjonathanNo ratings yet
- El Capitolio in La Habana, Cuba: The Past Speaks To The Contemporary ContextDocument3 pagesEl Capitolio in La Habana, Cuba: The Past Speaks To The Contemporary ContextZoé Roth-OgierNo ratings yet
- Case Study EthicsDocument3 pagesCase Study EthicsRodNo ratings yet
- Story Tenali TextDocument43 pagesStory Tenali Textmohammad karishmaNo ratings yet
- Gauhati University: Admit Card-2020Document3 pagesGauhati University: Admit Card-2020Yhh GhjvghNo ratings yet
- The Constitution and By-Laws of Jose Rizal University LAW: School Student CouncilDocument11 pagesThe Constitution and By-Laws of Jose Rizal University LAW: School Student CouncilLouie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Paul Craig RobertsDocument4 pagesPaul Craig RobertsMimis CopanoglouNo ratings yet
- Constitution. Project PDFDocument16 pagesConstitution. Project PDFPrince RajNo ratings yet