Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Configure Initial Switch Settings
Uploaded by
Daniel PalaciosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Configure Initial Switch Settings
Uploaded by
Daniel PalaciosCopyright:
Available Formats
Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings
Objectives
Part 1: Verify the Default Switch Configuration
Part 2: Configure a Basic Switch Configuration
Part 3: Configure a MOTD Banner
Part 4: Save Configuration Files to NVRAM
Part 5: Configure S2
Background / Scenario
In this activity, you will perform basic switch configuration tasks. You will secure access to
the command-line interface (CLI) and console ports using encrypted and plain text
passwords. You will also learn how to configure messages for users logging into the switch.
These message banners are also used to warn unauthorized users that access is
prohibited.
Note: In Packet Tracer, the Catalyst 2960 switch uses IOS version 12.2 by default. If
required, the IOS version can be updated from a file server in the Packet Tracer topology.
The switch can then be configured to boot to IOS version 15.0, if that version is required.
Instructions
Part 1: Verify the Default Switch Configuration
Step 1: Enter privileged EXEC mode.
You can access all switch commands from privileged EXEC mode. However, because
many of the privileged commands configure operating parameters, privileged access should
be password-protected to prevent unauthorized use.
The privileged EXEC command set includes the commands available in user EXEC mode,
many additional commands, and the configure command through which access to the
configuration modes is gained.
a. Click S1 and then the CLI tab. Press Enter.
b. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command:
Open Configuration Window for S1
Switch> enable
Switch#
Notice that the prompt changed to reflect privileged EXEC mode.
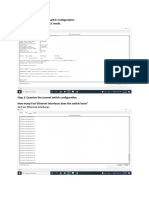
Step 2: Examine the current switch configuration.
Enter the show running-config command.
Switch# show running-config
Answer the following questions:
How many Fast Ethernet interfaces does the switch have?
How many Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does the switch have?
What is the range of values shown for the vty lines?
En total el rango total es desde 0-15
Which command will display the current contents of non-volatile random-access
memory (NVRAM)?
El comando es show startup-config
Why does the switch respond with “startup-config is not present?”
No esta presente debido a que la configuración no esta guardada en la VRAM sino en
la RAM
Part 2: Create a Basic Switch Configuration
Step 1: Assign a name to a switch.
To configure parameters on a switch, you may be required to move between various
configuration modes. Notice how the prompt changes as you navigate through the switch.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# hostname S1
S1(config)# exit
S1#
Step 2: Secure access to the console line.
To secure access to the console line, access config-line mode and set the console
password to letmein.
S1# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
S1(config)# line console 0
S1(config-line)# password letmein
S1(config-line)# login
S1(config-line)# exit
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#
Question:
Why is the login command required?
Para que todo el proceso de contraseña sea correcto se necesita estableces la contraseña
y logearse con el código respectivo.
Step 3: Verify that console access is secured.
Exit privileged mode to verify that the console port password is in effect.
S1# exit
Switch con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
User Access Verification
Password:
S1>
Note: If the switch did not prompt you for a password, then you did not configure
the login parameter in Step 2.
Step 4: Secure privileged mode access.
Set the enable password to c1$c0. This password protects access to privileged mode.
Note: The 0 in c1$c0 is a zero, not a capital O. This password will not grade as correct until
after you encrypt it in Step 8.
S1> enable
S1# configure terminal
S1(config)# enable password c1$c0
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#
Step 5: Verify that privileged mode access is secure.
a. Enter the exit command again to log out of the switch.
b. Press <Enter> and you will now be asked for a password:
User Access Verification
Password:
c. The first password is the console password you configured for line con 0. Enter this
password to return to user EXEC mode.
d. Enter the command to access privileged mode.
e. Enter the second password you configured to protect privileged EXEC mode.
f. Verify your configuration by examining the contents of the running-configuration file:
S1# show running-config
Notice that the console and enable passwords are both in plain text. This could pose a
security risk if someone is looking over your shoulder or obtains access to config files
stored in a backup location.
Step 6: Configure an encrypted password to secure access to privileged mode.
The enable password should be replaced with the newer encrypted secret password using
the enable secret command. Set the enable secret password to itsasecret.
S1# config t
S1(config)# enable secret itsasecret
S1(config)# exit
S1#
Note: The enable secret password overrides the enable password. If both are configured
on the switch, you must enter the enable secret password to enter privileged EXEC mode.
Step 7: Verify that the enable secret password is added to the configuration file.
Enter the show running-config command again to verify the new enable secret password is
configured.
Note: You can abbreviate show running-config as
S1# show run
Questions:
What is displayed for the enable secret password?
Why is the enable secret password displayed differently from what we configured?
Porque al ser una clave secreta no puede mostrarse debido a problemas de seguridad.
Step 8: Encrypt the enable and console passwords.
As you noticed in Step 7, the enable secret password was encrypted, but
the enable and console passwords were still in plain text. We will now encrypt these plain
text passwords using the service password-encryption command.
S1# config t
S1(config)# service password-encryption
S1(config)# exit
Question:
If you configure any more passwords on the switch, will they be displayed in the
configuration file as plain text or in encrypted form? Explain.
Las contraseñas presentes y futuras serán secretas ya que el comando funciona
justamente para eso.
Part 3: Configure a MOTD Banner
Step 1: Configure a message of the day (MOTD) banner.
The Cisco IOS command set includes a feature that allows you to configure messages that
anyone logging onto the switch sees. These messages are called message of the day, or
MOTD banners. Enclose the banner text in quotations or use a delimiter different from any
character appearing in the MOTD string.
S1# config t
S1(config)# banner motd "This is a secure system. Authorized
Access Only!"
S1(config)# exit
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#
Questions:
When will this banner be displayed?
Why should every switch have a MOTD banner?
Para dar a conocer que solo personas autorizadas y con la contraseña esta permitida para
el ingreso.
Part 4: Save and Verify Configuration Files to NVRAM
Step 1: Verify that the configuration is accurate using the show run command.
Save the configuration file. You have completed the basic configuration of the switch. Now
back up the running configuration file to NVRAM to ensure that the changes made are not
lost if the system is rebooted or loses power.
S1# copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]?[Enter]
Building configuration...
[OK]
Close Configuration Window for S1
Questions:
What is the shortest, abbreviated version of the copy running-config startup-
config command?
Cop r st
Examine the startup configuration file.
Which command will display the contents of NVRAM?
Are all the changes that were entered recorded in the file?
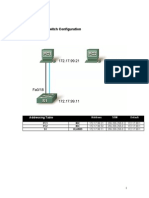
Part 5: Configure S2
You have completed the configuration on S1. You will now configure S2. If you cannot
remember the commands, refer to Parts 1 to 4 for assistance.
Configure S2 with the following parameters:
Open Configuration Window for S2
a. Device name: S2
b. Protect access to the console using the letmein password.
c. Configure an enable password of c1$c0 and an enable secret password of itsasecret.
d. Configure an appropriate message to those logging into the switch.
e. Encrypt all plain text passwords.
f. Ensure that the configuration is correct.
g. Save the configuration file to avoid loss if the switch is powered down.
You might also like
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Codelab: Get Started With DialogflowDocument41 pagesCodelab: Get Started With DialogflowCandiceNo ratings yet
- Basic Switch Part1Document6 pagesBasic Switch Part1BasilNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet TracerDocument6 pages2.2.3.4 Packet TracerFrans TariganNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument7 pages2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsClareAustinNo ratings yet
- Autocad Training ReportDocument43 pagesAutocad Training Reportranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument9 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsParthPatel100% (1)
- 2.2.3.4. Configuring Initial Switch Settings ILMSTUDENTDocument6 pages2.2.3.4. Configuring Initial Switch Settings ILMSTUDENTanie lovesuNo ratings yet
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsDocument4 pages6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsSergio Monte100% (3)
- Configure Initial Router SettingsDocument4 pagesConfigure Initial Router SettingsIzzat NadzriNo ratings yet
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMDocument10 pages2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMKevin KimNo ratings yet
- OS Lab ManualDocument55 pagesOS Lab ManualAbhishek VyasNo ratings yet
- Python Bootcamp Course OverviewDocument50 pagesPython Bootcamp Course OverviewIdo RaizbergNo ratings yet
- Configure Switch Settings - Initial Switch Config, Passwords, BannersDocument6 pagesConfigure Switch Settings - Initial Switch Config, Passwords, BannersGiroNo ratings yet
- LAB 03 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pagesLAB 03 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsCorrine LozanoNo ratings yet
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pagesConfigure Initial Switch SettingsHeriyanto TanNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument6 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settingsjeneil valenzNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsYousef A SalemNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument6 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsJoyce ChocaNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings - 1207050038 - Faza Mohamad FarsyafatDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings - 1207050038 - Faza Mohamad Farsyafatfaza farsyafatNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings PDFDocument6 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings PDFChadNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settingskds20850No ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings AnsweredDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings AnsweredKoro SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pagesChapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsFedasa BoteNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del SwitchDocument5 pages2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del Switchpuyo.dc.22No ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsKaung KaungNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch SettingsjamesNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPacket Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settings: Objectiveszvezda dieslowNo ratings yet
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument6 pagesConfigure Initial Switch SettingsБогдан МарчукNo ratings yet
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsAnthony Josh LegoNo ratings yet
- Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument9 pagesConfigure Initial Switch Settingsabdulrahman khaldiNo ratings yet
- PT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationDocument2 pagesPT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationmanNo ratings yet
- B3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 1Document17 pagesB3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 1sai.22220063No ratings yet
- Configure Switch Settings and PasswordsDocument2 pagesConfigure Switch Settings and PasswordsmanNo ratings yet
- 03 135222 010 114406102443 28092023 053141pmDocument5 pages03 135222 010 114406102443 28092023 053141pmasfa rehmanNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument22 pagesPacket Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsDocument6 pages2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsJosCarr14970% (1)
- 2.5.5 Configure Initial Switch Settings QuisaguanoDocument7 pages2.5.5 Configure Initial Switch Settings QuisaguanoFernandoQuisaguanoNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsDocument6 pages2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings InstructionsLaura SuarezNo ratings yet
- Title Build, Configure, and Simulate Switch Setting in Network TopologyDocument7 pagesTitle Build, Configure, and Simulate Switch Setting in Network TopologyHadia RashidNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeDocument20 pagesTask 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeAdnan YousafNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument6 pages2.2.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsRafael DiazNo ratings yet
- lab3Document8 pageslab3toto071902No ratings yet
- Introduction to Switch Configuration with IOSDocument26 pagesIntroduction to Switch Configuration with IOSMaxamed SaalaxNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdDocument9 pages2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdstevehrccNo ratings yet
- Topic 7A. Configuring A CISCO IOS SwitchDocument20 pagesTopic 7A. Configuring A CISCO IOS SwitchsimonnjauNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 1Document6 pagesLab Activity 1Muzammil khanNo ratings yet
- Verify and Test Network ConnectivityDocument9 pagesVerify and Test Network ConnectivityRana AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address NewportDocument4 pages2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address Newportgerardo1028No ratings yet
- Lab 2.5.1 Basic Switching Configurationv3Document15 pagesLab 2.5.1 Basic Switching Configurationv3reza3691No ratings yet
- Activity 2.3.2.5 AnswersDocument1 pageActivity 2.3.2.5 AnswersJordan Segundo100% (1)
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMDocument15 pages2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMJose Maria Rendon Rodriguez100% (1)
- Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologyDocument9 pagesLab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologybobNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.1.2 Router Password RecoveryDocument4 pagesLab 8.1.2 Router Password RecoveryPhạm Văn ThuânNo ratings yet
- CCNA3 Lab 6 2 8 enDocument7 pagesCCNA3 Lab 6 2 8 enapi-3812423No ratings yet
- Router ConfigurationDocument10 pagesRouter Configurationdhanu ekoNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 Chapter 2 Exam - Online AnswerDocument12 pagesCCNA1 Chapter 2 Exam - Online AnswerKaung KaungNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesLab 3 Computer NetworksAbdurRehmanNo ratings yet
- Configure Switch Security: Addressing TableDocument5 pagesConfigure Switch Security: Addressing TableguillcrNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Console ConfigurationDocument2 pagesCCNA - Console ConfigurationBodour MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesDocument10 pages5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesShadman SifatNo ratings yet
- 5 2 2 9 Lab Configuring Switch Security Features ILMDocument16 pages5 2 2 9 Lab Configuring Switch Security Features ILMJavier FlorianNo ratings yet
- Eigrp P62Document24 pagesEigrp P62Daniel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Configuración de Enrutamiento Estático en Redes de ComputadoraDocument33 pagesConfiguración de Enrutamiento Estático en Redes de ComputadoraDaniel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDocument5 pages1.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Network Representationlutfi0% (1)
- Navigate The IOSDocument6 pagesNavigate The IOSDaniel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Implement Basic ConnectivityDocument7 pagesImplement Basic ConnectivityDaniel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Basic Switch and End DeviceDocument2 pagesBasic Switch and End DeviceDaniel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Unix Programming LabDocument3 pagesUnix Programming LabSandeep KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Ise Upgrade Guide Chapter 01Document16 pagesIse Upgrade Guide Chapter 01JuggyNo ratings yet
- OpenShift - Container - Platform 4.3 Builds en USDocument99 pagesOpenShift - Container - Platform 4.3 Builds en USAshokNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Whats New 56Document244 pagesFortigate Whats New 56shawkyshawkatNo ratings yet
- Flow Control Dampening: Commandbatch V1.03 & Later 11/27/12Document8 pagesFlow Control Dampening: Commandbatch V1.03 & Later 11/27/12Aly AbdelhamedNo ratings yet
- DOS Internal CommandsDocument40 pagesDOS Internal CommandsabcNo ratings yet
- Multiwfn Quick StartDocument9 pagesMultiwfn Quick StartrafelNo ratings yet
- Sel Viewer User GuideDocument20 pagesSel Viewer User Guidejinish.K.GNo ratings yet
- Manual For QEMU ManagerDocument40 pagesManual For QEMU Managermy113No ratings yet
- POLYLINES AND SPLINESDocument9 pagesPOLYLINES AND SPLINESkimNo ratings yet
- HP 3PAR Windows Server 2003 Implementation GuideDocument59 pagesHP 3PAR Windows Server 2003 Implementation Guideste123456789No ratings yet
- 301B - LTM Technology Specialist: Exam BlueprintDocument7 pages301B - LTM Technology Specialist: Exam Blueprintlibingyi2010gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Tuxedo Touch User GuideDocument48 pagesHoneywell Tuxedo Touch User GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet
- WR Workbench Ocd Command Ref 2.6Document148 pagesWR Workbench Ocd Command Ref 2.6sweden043No ratings yet
- Installing Python For Windows: Windows x86-64 Executable InstallerDocument11 pagesInstalling Python For Windows: Windows x86-64 Executable InstallerScientist SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Retail Integration Bus: Operations Guide Release 13.0Document100 pagesOracle® Retail Integration Bus: Operations Guide Release 13.0varachartered283No ratings yet
- Tc14.2.0.0 READMEDocument15 pagesTc14.2.0.0 READMEgyuregabiNo ratings yet
- Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition User GuideDocument196 pagesIntel Quartus Prime Pro Edition User GuidejrnelsonNo ratings yet
- Type This To Do ThisDocument2 pagesType This To Do Thisalung bhaniNo ratings yet
- CUCM Smart Licensing Version 12.XDocument5 pagesCUCM Smart Licensing Version 12.XGeo ThomasNo ratings yet
- LED Cube 4x4x4 DIY 3D LED DisplayDocument6 pagesLED Cube 4x4x4 DIY 3D LED DisplayDusan Petrovic100% (1)
- Readme NN BHVGDocument2 pagesReadme NN BHVGJorge PauloNo ratings yet
- DD System Hardware GuideDocument74 pagesDD System Hardware GuideJaideep0550No ratings yet
- Caldera DR-DOS 7.02 User GuideDocument34 pagesCaldera DR-DOS 7.02 User GuideHuu Dinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- XeLL JTAG XBR Hack EnglishDocument20 pagesXeLL JTAG XBR Hack Englishscrescribd23No ratings yet
- 2.2 Lab - CLI Automation with Python using netmiko - ILMDocument5 pages2.2 Lab - CLI Automation with Python using netmiko - ILMAlvaro Justiniano Valencia MunozNo ratings yet