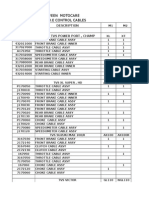
Bike Engine Parts
Function of Bike Engine
If you have ever ridden a motorcycle, you will understand how important it is to
maintain your bike well for your safety on the road. When we talk about bikes, we talk
about speed, robustness, smoothness, and stability.
Most people look for these specific trademarks before making any purchases for their
motorcycles. However, only a few of us pay attention to the origin and source of this
trademark: your motorcycle's engine.
A bike engine is a type of engine that powers a bike. These engines are usually two-
stroke or four-stroke internal combustion engines; some are liquid-cooled and air-
cooled. This engine typically drives the rear wheel, with power sent to the wheel driven
by a belt, chain, or shaft.
Furthermore, different parts inside a bike's engine are responsible for different
functions. Let us understand the role of these bike engine parts, which greatly help the
bike's engine functioning.
Related: Essential Parts of Motorcycle and Their Uses [Names & Pictures]
Parts of Bike Engine
Following are the main parts of a bike engine:
1. Cylinder head
2. Cylinders
3. Pistons
4. Connecting rod
5. Crankshaft
6. Camshaft
7. Rocker arm
8. Transmission
9. Spark plug
10. Engine valves
11. Cooling system
12. Battery
13. Fuel supply
14. Air filter
15. Exhaust
Read Also: List of Basic Car Engine Parts: Its Function (With Images)
TheEngineersPost.com Page 1
� Bike Engine Parts
#1 Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is the part of an engine that is manufactured from various materials
such as cast iron or aluminum alloy. They are essential for controlling airflow in and out
of the cylinder and fuel deployment.
The function of the cylinder head is to seal the top of the engine cylinder and retain fuel
in the engine cylinder itself. In addition, it helps to make fuel combustion safe and
limited. It also includes the combustion chamber, shaft, and valve. Different motorbikes
have different head sizes, affecting performance as some allow more space for
combustion than others.
#2 Cylinders
Cylinders play a central role in all types of vehicles. Motorcycle engines can have up to
six cylinders made of iron, capable of withstanding very high temperatures. The
purpose of cylinders is to provide a sealed space for piston movement.
Typically, cylinders are known as engine blocks and are also used to measure engine
power to determine cylinder size. A single-cylinder engine is one of the most
straightforward combustion engines (simplest type).
TheEngineersPost.com Page 2
� Bike Engine Parts
Single cylinder engine: Running a single cylinder engine is cheap, and even the most
amateur mechanic shouldn't be taxed too much. They don't have a lot of speed and not
particularly good acceleration, but they cool down much faster than most other engines.
Twin cylinder engine: These are the most common motorbike engines in the UK. The
twin cylinder engine is available in different variants, which include straight-twin, V-
twin, flat-twin, and tandem-twin. The more cylinders a motorcycle has, the better the
performance should be.
#3 Pistons
With the help of the piston, the connecting rod moves back and forth, moving up and
down. A piston is a moving component that is contained by a cylinder and made gas-
tight by piston rings.
The purpose of the piston is to transfer force from the expansion of gas in the cylinder
through the connecting rod to the crankshaft. Pistons are commonly made of cast iron,
aluminum or nickel, and steel alloys with cast iron. These pistons will move at
tremendous speed and need to be in good condition as they can cause accidents if
broken.
#4 Connecting Rod
TheEngineersPost.com Page 3
� Bike Engine Parts
A connecting rod is the part of an engine that connects the piston to the crankshaft.
The connecting rod converts the piston's reciprocating motion into the crankshaft's
rotation with the crank. Generally, the connecting steel is made of aluminum or
titanium.
The connecting rod is required to transmit compressive and tensile forces from the
piston. If there is a problem with the connecting rod, it can cause several problems.
Connecting rod problems can be challenging to diagnose, so be sure to get professional
mechanical advice if you're unsure.
#5 Crankshaft
The crankshaft is also a vital part of an engine that converts the reciprocating motion of
the pistons into rotational motion. The rotary motion of the crankshaft sets the
motorcycle chain and eventually the motorbike's wheels in motion.
It is observed that not all the pistons move simultaneously at the same time, due to
which the different timing of the motion of the different pistons sets off a rhythmic
movement throughout the system. This creates a particular demand for crankshafts and
is why each has a different and unique shape.
Read Also: A Complete List of Car Door Parts [Names & Functions]
#6 Camshaft
TheEngineersPost.com Page 4
� Bike Engine Parts
A camshaft is a rotating metal object with pointed cams, which converts rotational
motion into reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in IC engines to operate intake
and exhaust valves, mechanically controlled ignition systems, and starting electric
motor speed controllers.
The operation of engine valves depends on the camshaft and its lobes, as they are
supposed to control the valve opening and closing timing. These are typically made of
steel or cast iron and are an essential factor in determining the RPM range of an engine's
power band.
#7 Rocker Arm
The rocker arm is responsible for transmitting camshaft movement to the engine's
intake and exhaust valves. The camshaft's lobe guides one end of the rocker while the
other pushes the spring-loaded valve to open.
The exhaust and intake valve may not function properly with a faulty rocker arm, and
the cylinder attached to the faulty rocker arm will be disabled. This will eventually limit
the performance of the engine and its ability to drive the car smoothly and safely.
#8 Transmission
A bike engine can generate huge amounts of power transmitted to the vehicle's wheels
in a controlled manner. The motorcycle provides power to the rear wheel through
transmission structures, including the gearset, clutch, and drive system.
A gearset is a set of gears that enable a rider to move from a complete stop to a moving
speed. The clutch aims to engage and shut off the power from the engine crankshaft to
the transmission. Chains, belts, or shafts are the three basic ways of transmitting engine
power to the rear wheel of a motorcycle.
TheEngineersPost.com Page 5
� Bike Engine Parts
Chain drive: Chain drive is the most common system that uses sprockets
mounted on the transmission's output shaft. When the transmission spins the
smaller front sprocket, power is transmitted along the chain to the larger rear
sprocket, turning the rear wheel.
Belt drive: These are alternatives to chain drives. Belt drives can also change the
speed of rotation up or down, using pulleys of different sizes. Early motorcycles
often used leather belts, but today's belts are made of mesh rubber and act like
metal chains.
Shaft drive: The shaft drive system transmits power to the rear wheel via the
drive shaft. Shaft drives are famous because they are convenient and do not
require as much maintenance as chain drive systems.
#9 Spark Plug
TheEngineersPost.com Page 6
� Bike Engine Parts
Spark plugs are one of the parts of your motorbike engine's ignition system. Spark
plugs produce a spark that raises the ignition temperature of the fuel-air mixture in
the engine cylinders. Thus, the combustion engine converts chemical fuel energy into
kinetic energy.
The spark plug receives an input of 12,000-25,000 volts from the high tension ignition
coil. Timing for the spark must be precise, which is done by an electronic capacitor
discharge ignition (CDI) unit. If the spark plug isn't working, there may be a problem
with the bike battery, as you need electricity to spark the spark plug and thus ignite the
fuel.
#10 Engine Valves
Engine valves are also essential parts of a bike engine as these valves control the
passage of air and fuel in and out of the cylinder as air is vital for combustion. They also
help in exhausting the smoke and fumes that are produced as a result of combustion.
You can also successfully monitor the combustion activity and efficiency of the
cylinders if you keep your engine valves under control. In addition, you should also
regularly adjust engine valves to avoid serious and costly problems.
Read Also: What is the function of a Timing Belt In a Car? Symptoms & Replacement
#11 Cooling System
Engines normally overheat while burning fuel to generate mechanical energy. This
overheating will seize and damage engine internal components. The engine's cooling
system in the bike keeps it operating at its most efficient temperature.
Cooling is essential for all types of engines to operate and function properly. The
cooling system consists of a radiator, thermostatic valve controlled electric fan, coolant
reservoir, rubber hose, and water pump. There are commonly two types of cooling
systems used in bikes.
TheEngineersPost.com Page 7
� Bike Engine Parts
Air-cooled system: The air-cooled system draws engine heat by using the air that
hits the engine while the bike moves. Because of this, they have fins on the
outside to create more surface area for air to pass over. This cooling method is
simple and does not require any special equipment.
Liquid-cooled system: Liquid-cooled engines use a water-based liquid to cool
the engine, but they do not use regular water. They use a special coolant
containing alcohol to prevent freezing and rusting, circling through a pathway
built into the engine for cooling.
#12 Battery
TheEngineersPost.com Page 8
� Bike Engine Parts
The battery is almost the central part of the functioning of the bike engine. The primary
job of the battery is to power the bike and supply excess current when the alternator
output is less than the current draw.
It provides electrical energy to the ignition system, which converts chemical energy into
mechanical energy. Apart from this, the battery also powers the headlights. Some
motorcycles can start and run without a battery, especially smaller motorcycles that are
250 cc or less and have a kick starter.
#13 Fuel Supply or Carburetor
Carburetors have long been used to mix and pump air fuel into the inlet manifold at a
specific ratio and volume. This controls the flow of air through their central bore
(venturi), this flowing air draws in the fuel, and the mixture enters the engine through
the intake valve.
Nowadays, motorcycles are fitted with a throttle body with injectors that use various
sensors and electronic management systems to determine how much fuel is needed. The
system is highly reliable and advanced, requiring very little maintenance.
#14 Air Filter
TheEngineersPost.com Page 9
� Bike Engine Parts
An air filter is installed in the carburetor or fuel injector to ensure that contaminated air
enters the engine. The purpose of an air filter is to protect the engine from dust and
debris in the air and to improve airflow. It is also designed to increase acceleration and
boost the motorcycle's horsepower.
#15 Exhaust
Burnt combustion gases have to be ejected, and their combustion results in a high
decibel cacophony. This is where a silencer system is installed, which helps the engine
to exhaust the gases faster and more efficiently.
Closing It Up
So, for now, I hope I’ve covered everything about “Bike Engine Parts“. If you still think
I missed anything or have any doubts on this topic, you can contact us or ask in the
comments. If you like this article, then please share it with your buddies.
Want free PDFs direct to your inbox? Then subscribe to our newsletter.
1. A Comprehensive Guide to Car Body Parts [Names & Functions]
2. How does a Manual Transmission System work? Its Parts & Types
3. What is a Rotary Engine? Diagram, Parts, Working [PDF]
TheEngineersPost.com Page 10