Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The filtration-WPS Office 1
Uploaded by
KrishOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The filtration-WPS Office 1
Uploaded by
KrishCopyright:
Available Formats
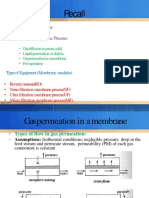
Separation mechanism:
different velocity of gas permeation (sorption, diffusion, sieving effect, desorption)
• Driving force: partial pressure gradient.
• Working pressure: up to 100 bar. Non-porous polymeric membranes:
PDMS(polydimethylsulphoxan),PS(polysulphone),PES.
• Ceramic Membranes (small pores for Knudsen).
• Metallic membranes (Pd and Ag alloys).
process
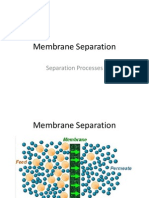
In the process as shown in fig. The feed gas at high pressure Pl contains some low molecular weight
species (molecular weight <50) to be separated from small amounts of high molecular weight species.
The other side of the membrane is maintained at much lower pressure P2 often near ambient pressure
the membrane used is micro pores perm selectivity for certain low molecular weight species in the feed
gas(species A)
If the membrane is dense these species are absorbed at the surface and then transported though the
membrane by one or mechanism.
Thus perm selectivity depends on both membrane adsorption and membrane transport rate.
In this process perfect separation is generally not achievable, If the difference of molecular weight of
substance is near by.
Application:
•Separation of hydrogen from methane,
• Removal of carbon dioxide,
• Removal of organic solvent from air,
• Nitrogen enrichment from air.
You might also like
- Membrane Separation in Natural Gas Processing.Document23 pagesMembrane Separation in Natural Gas Processing.CCESARPL100% (1)
- 4.0 AdsorptionDocument68 pages4.0 AdsorptionWazif ZakwanNo ratings yet
- 5B FiltrationDocument58 pages5B FiltrationWazif ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology: By: Prof. Dr. Tien R. MuchtadiDocument47 pagesMembrane Technology: By: Prof. Dr. Tien R. MuchtadiDwiMariaUlfahNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessDocument118 pagesMembrane Separation ProcessMirHamzaHamidKashmiri100% (1)
- Subtopic: Introduction To Adsorption: DefinitionDocument27 pagesSubtopic: Introduction To Adsorption: DefinitionUmmu Qurratul Aini MansorNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessesDocument52 pagesMembrane Separation Processeschie12345No ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessesDocument47 pagesMembrane Separation Processesma.junallie pomperada100% (1)
- Reverse OsmosisDocument53 pagesReverse Osmosisanabloom100% (2)
- Membrane TechnologyDocument47 pagesMembrane TechnologyDwiMariaUlfahNo ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument52 pagesMembrane SeparationJonalyn Perez - Aclan100% (1)
- Advanced Separation ProcessesDocument33 pagesAdvanced Separation Processesعمار ياسر50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Membrane Separation ProcessDocument53 pagesChapter 4 Membrane Separation ProcessCaratsSVTNo ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument24 pagesMembrane SeparationBedatrayee05100% (1)
- Membrane Technology 10.8Document37 pagesMembrane Technology 10.8Susmin SethumadhavanNo ratings yet
- Membrane Seperation (10.04.20)Document57 pagesMembrane Seperation (10.04.20)HARI PRASATHNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Membrane Manufacture MethodsDocument20 pagesUnit I: Membrane Manufacture MethodsAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM0012100% (1)
- Principles of PervaporationDocument10 pagesPrinciples of PervaporationNithya RamNo ratings yet
- Membrane Lecture 1Document16 pagesMembrane Lecture 1writtingtuNo ratings yet
- CO Absorption at Elevated Pressures Using A Hollow Fiber Membrane ContactorDocument12 pagesCO Absorption at Elevated Pressures Using A Hollow Fiber Membrane ContactorTitto Cedeño VeraNo ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument41 pagesMembrane SeparationAriadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Transport Through Polymer Membranes: G The Polymer Is in Its GlassyDocument8 pagesTransport Through Polymer Membranes: G The Polymer Is in Its Glassyeni_cristianNo ratings yet
- Advance Separation Techniques: Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocument26 pagesAdvance Separation Techniques: Pressure Swing AdsorptionJaykumar Bhupendrabhai PatelNo ratings yet
- Ultra Filteration of MilkDocument36 pagesUltra Filteration of MilkMonty KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MembranesDocument30 pagesMembranesInamullah MaitloNo ratings yet
- CE 480 - Membrane Processes - 02Document24 pagesCE 480 - Membrane Processes - 02NTEYE CHITONGENo ratings yet
- Separator SlideDocument7 pagesSeparator SlideMuhammad KasyfiNo ratings yet
- Membrane FoulingDocument8 pagesMembrane FoulingSushanta BeheraNo ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument68 pagesMembrane SeparationSaria ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Control Measures For Membrane Fouling & Concentration PolarizationDocument22 pagesUnit II: Control Measures For Membrane Fouling & Concentration PolarizationAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM0012No ratings yet
- Introduction To Membrane SeparationDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Membrane SeparationFUN GRAPHIATENo ratings yet
- Gas Separation: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesGas Separation: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediabekku100% (1)
- Membrane Separation FinalDocument49 pagesMembrane Separation FinalCester Avila DucusinNo ratings yet
- MembranesDocument30 pagesMembranesmiraziey100% (1)
- Plasma Technology in TextilesDocument49 pagesPlasma Technology in TextilesKeshav Dhawan100% (2)
- Polymer: Norman R. Horn, D.R. PaulDocument9 pagesPolymer: Norman R. Horn, D.R. Paulpoint_far_artNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Pore Size DistributionDocument36 pagesSurface Area and Pore Size DistributionWanderson MoraesNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Osmosis and DiffusionDocument3 pagesDifference Between Osmosis and DiffusionNebojsa MirkovicNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument39 pagesSeminar ReportJazz DhimmerNo ratings yet
- MicrofiltrationDocument6 pagesMicrofiltration2k17che 26No ratings yet
- MembranesDocument6 pagesMembranesWan SamiraNo ratings yet
- Membrane 1Document41 pagesMembrane 1Abhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocument5 pagesVacuum Pressure Swing Adsorptionumesh deshpandeNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsis: Date of RegistrationDocument9 pagesProject Synopsis: Date of RegistrationAdeep KhahNo ratings yet
- 5.membrane Based Bioseparation-PurificationDocument55 pages5.membrane Based Bioseparation-Purificationobs6732100% (1)
- Dialysis Methods For Protein ResearchDocument5 pagesDialysis Methods For Protein Researchanon_482210535No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Adsorption 1. OverviewDocument13 pagesAn Introduction To Adsorption 1. OverviewSupriya ChumberNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer: AdsorptionDocument21 pagesSimultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer: AdsorptionSyed Irtaza Haider NaqviNo ratings yet
- LAB SOLAHmembrane SeparationDocument22 pagesLAB SOLAHmembrane SeparationSo Lah Musa100% (1)
- Module-3 Membrane ModuleDocument120 pagesModule-3 Membrane ModuleRimeli RoychoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Thermal Evaporation NotesDocument8 pagesThermal Evaporation NotesMrunalNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phase (A Liquid or A Gas) - The Mobile Phase Flows Through The StationaryDocument9 pagesMobile Phase (A Liquid or A Gas) - The Mobile Phase Flows Through The StationarySudip TikaitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vacuum Science and Technology: Thin Film Fabrication ProcessesDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Vacuum Science and Technology: Thin Film Fabrication Processes1MM1R HL'No ratings yet
- Phases Separated by A MembraneDocument37 pagesPhases Separated by A Membranelata sinsinwarNo ratings yet
- ARTIAN OTK SeninDocument4 pagesARTIAN OTK SeninSapnaNo ratings yet
- Separation Assignment MembraneDocument4 pagesSeparation Assignment MembraneQilah KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Document9 pagesJurnal Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Pemisahan Kimia Pembuatan Membran Polysulfon (PSF)Rizki AuNo ratings yet
- Membrane Emulsification - A Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesMembrane Emulsification - A Literature ReviewAsteriaA.SusantoNo ratings yet
- Granular Materials at Meso-scale: Towards a Change of Scale ApproachFrom EverandGranular Materials at Meso-scale: Towards a Change of Scale ApproachNo ratings yet
- Be Civil Regulation 2021Document154 pagesBe Civil Regulation 2021KrishNo ratings yet
- Exam CoursesDocument1 pageExam CoursesKrishNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledKrishNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Heat CapacitiesDocument8 pagesAppendix C Heat CapacitiesKrishNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Time Table.Document1 pageChemical Engineering Time Table.KrishNo ratings yet
- Technical QuestionsDocument19 pagesTechnical QuestionsKrishNo ratings yet
- Technical Question AnswersDocument4 pagesTechnical Question AnswersKrishNo ratings yet
- BIOCOLOURS The New Generation Additives-1 (Final)Document20 pagesBIOCOLOURS The New Generation Additives-1 (Final)KrishNo ratings yet
- Jet EnginesDocument11 pagesJet EnginesKrishNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL PROCES-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageCHEMICAL PROCES-WPS OfficeKrishNo ratings yet
- The filtration-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesThe filtration-WPS OfficeKrishNo ratings yet