Professional Documents
Culture Documents
House
Uploaded by
SzsbxbhxdhdhdOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
House
Uploaded by
SzsbxbhxdhdhdCopyright:
Available Formats
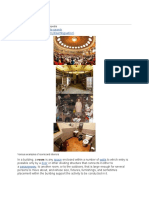
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a
complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical,
and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Houses use a range of different roofing
systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have
doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or
other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more
bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate
dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North
America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such
as chickens or larger livestock may share part of the house with humans.
The social unit that lives in a house is known as a household. Most commonly, a household is a family
unit of some kind, although households may also be other social groups, such as roommates or, in a
rooming house, unconnected individuals. Some houses only have a dwelling space for one family or
similar-sized group; larger houses called townhouses or row houses may contain numerous family
dwellings in the same structure. A house may be accompanied by outbuildings, such as a garage for
vehicles or a shed for gardening equipment and tools. A house may have a backyard or a front yard
or both, which serve as additional areas where inhabitants can relax or eat.
Etymology
The English word house derives directly from the Old English hus
You might also like
- List of House TypesDocument14 pagesList of House Typespankaj sahu0% (1)
- Popular Types of HousesDocument5 pagesPopular Types of HousesVeronNo ratings yet
- Garden Secrets for Attracting Birds, Second Edition: A Bird-by-Bird Guide to Favored PlantsFrom EverandGarden Secrets for Attracting Birds, Second Edition: A Bird-by-Bird Guide to Favored PlantsNo ratings yet
- Bahay Na BatoDocument7 pagesBahay Na BatoClaris Cainto50% (6)
- Types of HousesDocument23 pagesTypes of HousesMaria Riza Maaya LaurdausNo ratings yet
- House & Home DefinedDocument33 pagesHouse & Home DefinedMaria Riza Maaya Laurdaus100% (1)
- House: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument24 pagesHouse: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchKevinViriaWinataNo ratings yet
- Types of Vernacular BuildingsDocument13 pagesTypes of Vernacular BuildingsnathrshaNo ratings yet
- HousesDocument1 pageHousesMaddie0No ratings yet
- Una CasaDocument2 pagesUna CasaMarlon Josue Orellana LainezNo ratings yet
- House: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 pagesHouse: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterNo ratings yet
- Single-Family Detached Home - WikipediaDocument20 pagesSingle-Family Detached Home - WikipediaDamilare Daniel OlaniyiNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is A HouseDocument17 pages1 What Is A HouseBiruk AlemuNo ratings yet
- Major Categories: Single-Family Detached House In,, USA. A Photograph of Townhouses inDocument3 pagesMajor Categories: Single-Family Detached House In,, USA. A Photograph of Townhouses inJohnhusainNo ratings yet
- FitsumDocument12 pagesFitsumAbel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Typologies of Residential BuildingsDocument7 pagesTypologies of Residential BuildingsMai NieverasNo ratings yet
- Housing PortfolioDocument18 pagesHousing PortfolioDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Major Categories in North America and Europe: 'Single-Family Detached Home'Document2 pagesMajor Categories in North America and Europe: 'Single-Family Detached Home'Shashank ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeLittle SpidermanNo ratings yet
- Housing 1Document21 pagesHousing 1Ako Si Jeje ÜNo ratings yet
- Types of HousesDocument14 pagesTypes of Houses19BCO637 Prabhavathi SNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See and - For The Front Page of The Wikipedia Site, See - For The Structure, SeeDocument6 pagesFor Other Uses, See and - For The Front Page of The Wikipedia Site, See - For The Structure, SeeKANCHANAMUNINo ratings yet
- House: Dear Wikipedia Readers: We Are The Small Non-Profit That Runs The #5 Website in The World. We HaveDocument21 pagesHouse: Dear Wikipedia Readers: We Are The Small Non-Profit That Runs The #5 Website in The World. We Havecjcute91No ratings yet
- Real Estate: Navigation SearchDocument3 pagesReal Estate: Navigation SearchLGNo ratings yet
- Text RiportDocument3 pagesText RiportmarshaNo ratings yet
- HousingDocument5 pagesHousingMiska KubaščíkováNo ratings yet
- Bahay KuboDocument2 pagesBahay KuboAubrey Cueto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Independent HousesDocument14 pagesIndependent Housesgaurav1972No ratings yet
- Types of HousesDocument10 pagesTypes of HousesMarius StarNo ratings yet
- History of Real EstateDocument3 pagesHistory of Real EstateElano JeffersonNo ratings yet
- HousingDocument16 pagesHousingY YNo ratings yet
- BuildingsDocument1 pageBuildingsSingly DoublyNo ratings yet
- ScrjksadhfkjasDocument1 pageScrjksadhfkjasSem RanNo ratings yet
- Description of Houses and Their InteriorsDocument88 pagesDescription of Houses and Their InteriorsmikijisterNo ratings yet
- Soul, Space and Symmetry Art: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesSoul, Space and Symmetry Art: Learning OutcomesKristel Kate SottoNo ratings yet
- Architecture AsignmentDocument40 pagesArchitecture AsignmentMuaz HararNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter2Document19 pages11 Chapter2Asha SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design: Comparative Analysis of ChenesDocument18 pagesTropical Design: Comparative Analysis of ChenesHerald PadillaNo ratings yet
- Home VocabularyDocument19 pagesHome VocabularyAsya JustNo ratings yet
- Types of Houses in The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesTypes of Houses in The PhilippinesBiezer WoodNo ratings yet
- ResidenceDocument31 pagesResidenceDipti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Work SearchDocument2 pagesWork SearchARIADNA LAGUNES RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Text 2 British House: Ou 1trDocument1 pageText 2 British House: Ou 1trОлінька СтецюкNo ratings yet
- A Britain House PDFDocument1 pageA Britain House PDFОлінька СтецюкNo ratings yet
- Local Intern. Case StudyDocument5 pagesLocal Intern. Case Studyjerome espirituNo ratings yet
- House Is Not A HomeDocument21 pagesHouse Is Not A HomeRamsrajNo ratings yet
- Dineing RomDocument9 pagesDineing RomKevinViriaWinataNo ratings yet
- Writesonic Chatsonic 1680837032992Document1 pageWritesonic Chatsonic 1680837032992Jein Graceilyn L. CabangonNo ratings yet
- Citizenship atDocument1 pageCitizenship atmarc justineNo ratings yet
- Buildings Where People Live or Stay: Adobe Apartment Block Apartment Building Back-To-BackDocument25 pagesBuildings Where People Live or Stay: Adobe Apartment Block Apartment Building Back-To-BackjmblouNo ratings yet
- Doors: Door Floor Plan SymbolsDocument4 pagesDoors: Door Floor Plan Symbolsdaryll_05No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Name of StudentDocument16 pagesAcknowledgement: Name of StudentAnonymous hV05BMNo ratings yet
- Danny ArchDocument99 pagesDanny Archelnan1etNo ratings yet
- LOI - Where We Are in Place and TimeDocument5 pagesLOI - Where We Are in Place and TimeSowmya KarthikNo ratings yet
- 5 - q3 - c2 - l1 Parts of The HouseDocument21 pages5 - q3 - c2 - l1 Parts of The HouseHan Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Housing (Theory) 3Document2 pagesHousing (Theory) 3ashitha bodduNo ratings yet
- Leaving Certificate Social and Scientific Home Design and Management ElectiveDocument33 pagesLeaving Certificate Social and Scientific Home Design and Management Electivepete carl anthone abrenicaNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Keeping Rabbits on a Smallholding - A Selection of Classic Articles on Housing, Feeding, Breeding and Other Aspects of Rabbit ManagementFrom EverandA Guide to Keeping Rabbits on a Smallholding - A Selection of Classic Articles on Housing, Feeding, Breeding and Other Aspects of Rabbit ManagementNo ratings yet
- Beauty SalonDocument1 pageBeauty SalonSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- CakeDocument1 pageCakeSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- Football SportDocument1 pageFootball SportSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- SportDocument1 pageSportSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet