Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Car
Uploaded by
SzsbxbhxdhdhdOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Car
Uploaded by
SzsbxbhxdhdhdCopyright:
Available Formats
Car
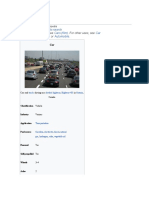
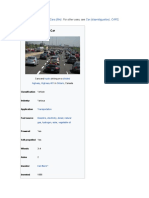
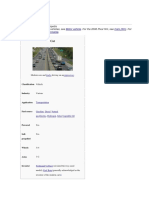
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars say that they run
primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead
of goods. Cars became widely available during the 20th century. One of the first cars affordable by
the masses was the 1908 Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars
were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriages and carts. In Europe
and other parts of the world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II. The
car is considered an essential part of the developed economy.
Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and a variety of lights. Over the decades,
additional features and controls have been added to vehicles, making them progressively more
complex. These include rear-reversing cameras, air conditioning, navigation systems, and in-car
entertainment. Most cars in use in the early 2020s are propelled by an internal combustion engine,
fuelled by the combustion of fossil fuels. Electric cars, which were invented early in the history of the
car, became commercially available in the 2000s and are predicted to cost less to buy than gasoline
cars before 2025. The transition from fossil fuels to electric cars features prominently in most climate
change mitigation scenarios, such as Project Drawdown's 100 actionable solutions for climate
change.
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs to the individual include acquiring the vehicle,
interest payments, repairs and maintenance, fuel, depreciation, driving time, parking fees, taxes, and
insurance. The costs to society include maintaining roads, land use, road congestion, air pollution,
public health, healthcare, and disposing of the vehicle at the end of its life. Traffic collisions are the
largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide.
Personal benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility, independence, and convenience.
There are around one billion cars in use worldwide. Car usage is increasing rapidly, especially in
China, India, and other newly industrialized countries.
Etymology
The English word car is believed to originate from Latin / "wheeled vehicle" or Middle English carre
"two-wheeled cart", both of which in turn derive from Gaulish karros "chariot". It originally referred
to any wheeled horse-drawn vehicle, such as a cart, carriage, or wagon.
"Motor car", attested from 1895, is the usual formal term in British English. "Autocar", a variant
likewise attested from 1895 and literally meaning "self-propelled car", is now considered archaic.
You might also like
- WkiDocument1 pageWkiAle IlovanNo ratings yet
- Cars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiesDocument5 pagesCars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiestjasaNo ratings yet
- მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობDocument1 pageმანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- Recarch CarDocument1 pageRecarch CarBhupender AswalNo ratings yet
- Citation NeededDocument1 pageCitation NeededDexterNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSuryansh RajputNo ratings yet
- Rise of Motorized VehiclesDocument2 pagesRise of Motorized VehiclesMauyrNo ratings yet
- CarDocument2 pagesCarSimran Singh KotlaNo ratings yet
- Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument1 pageCar Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDerrick BaltimoreNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Flexible-Fuel VehiclesDocument1 pageEthanol Flexible-Fuel VehicleslatchanyananaNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument2 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Cars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument3 pagesCars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orAndrei SlabakovNo ratings yet
- Modern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntarioDocument2 pagesModern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntariosudinorangeNo ratings yet
- A Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsDocument2 pagesA Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsAlin VoicuNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarssaleha3695No ratings yet
- The Evolution of CarsDocument1 pageThe Evolution of CarsmikkelNo ratings yet
- AutomobileDocument1 pageAutomobileschoolemail bellaNo ratings yet
- Reference:WikipediaDocument1 pageReference:Wikipediagnoble30No ratings yet
- Accident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportDocument40 pagesAccident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportAlmubeenNo ratings yet
- CARSDocument8 pagesCARSRajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- FDFXDocument1 pageFDFXMahmoud Al NuaimiNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarinbawNo ratings yet
- Auto Part 1Document1 pageAuto Part 1paul.benstarckNo ratings yet
- Test 7Document8 pagesTest 7Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- The World of AutomobilesDocument3 pagesThe World of AutomobilesAmogus MogusNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesDocument88 pagesTata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesParth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- All About CarsDocument16 pagesAll About Carsapi-255581071No ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andDocument5 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andbluesparkles013No ratings yet
- Safari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Document1 pageSafari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Santosh J Yadav's FriendNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of AutomobilesDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Automobilesrjn46189nezidcomNo ratings yet
- Car ReviewDocument3 pagesCar Reviewerwand21No ratings yet
- Scientific PaperDocument9 pagesScientific Paperapi-317125318No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Cars Over TimeDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Cars Over TimediogoNo ratings yet
- Describe The Car IndustryDocument3 pagesDescribe The Car IndustryLillian KobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Rahuman BBA ProjectDocument82 pagesRahuman BBA ProjectjithuNo ratings yet
- Automobile Industry - Marketing MixDocument35 pagesAutomobile Industry - Marketing MixmupadeNo ratings yet
- Car IndustryDocument32 pagesCar IndustryMohammad HagigiNo ratings yet
- Tata To Kia ProjectDocument44 pagesTata To Kia Projectbaskar rNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument56 pagesINTRODUCTIONkoolvansh692No ratings yet
- Automotive Industry AnalysisDocument31 pagesAutomotive Industry AnalysisSaif Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The History of The Automobile 1Document42 pagesThe History of The Automobile 1Sharma KawalNo ratings yet
- Mahindra and MahindraDocument58 pagesMahindra and MahindraMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- The Future of Cars: Special ReportDocument5 pagesThe Future of Cars: Special ReportWild Billy Barker GahanNo ratings yet
- Automobile Industry: Idustry HistoryDocument2 pagesAutomobile Industry: Idustry HistoryFatma MusallamNo ratings yet
- Cars StudyDocument2 pagesCars StudyFfkfj djdjfjNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electric and Hybrid Cars - A History BookDocument39 pages1 - Electric and Hybrid Cars - A History BookHubert CelisNo ratings yet
- Title The Automobile Revolution A JDocument2 pagesTitle The Automobile Revolution A JromohacNo ratings yet
- English Cars EssayDocument5 pagesEnglish Cars EssayShannon ChoiNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument12 pagesSwot Analysispoonamy09No ratings yet
- Introduction About Automobiles IndustryDocument12 pagesIntroduction About Automobiles IndustrybasavtejaNo ratings yet
- AugustinianheraldDocument2 pagesAugustinianheraldHello Its MeNo ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andDocument4 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andewbNo ratings yet
- POM SC045 Study ReportDocument6 pagesPOM SC045 Study ReportRushikesh PatilNo ratings yet
- What Was The Original Problem (S) That The Automobile Was Supposed To Solve?Document9 pagesWhat Was The Original Problem (S) That The Automobile Was Supposed To Solve?Angel LagmayNo ratings yet
- Automotive IndustryDocument6 pagesAutomotive IndustryPankaj KansalNo ratings yet
- GEO EssayDocument12 pagesGEO EssaywisamNo ratings yet
- The Car: The Rise and Fall of the Machine that Made the Modern WorldFrom EverandThe Car: The Rise and Fall of the Machine that Made the Modern WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 4Document1 page4noneofyourbusinessNo ratings yet
- Online WordpadDocument1 pageOnline Wordpadmovieexclusive02No ratings yet
- Beauty SalonDocument1 pageBeauty SalonSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- HouseDocument1 pageHouseSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- CakeDocument1 pageCakeSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- Football SportDocument1 pageFootball SportSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- SportDocument1 pageSportSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- SportDocument1 pageSportSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- Audit WikiDocument7 pagesAudit WikiWilfreddo Quispe MaytaNo ratings yet
- Sagem d30t AnglaisDocument64 pagesSagem d30t AnglaisZENASNI BOUCIFNo ratings yet
- BNI Taplus Muda - Group8 - Tourism CDocument27 pagesBNI Taplus Muda - Group8 - Tourism CsayudeviNo ratings yet
- Shri Krishnam HDFCDocument10 pagesShri Krishnam HDFCSimi AroraNo ratings yet
- Placement Report For The A Y 2018-20 - NewDocument5 pagesPlacement Report For The A Y 2018-20 - Newallabout beingsmartNo ratings yet
- INFO-6078 - Lab 2 - OSI Model - Layers 2 & 3Document3 pagesINFO-6078 - Lab 2 - OSI Model - Layers 2 & 3Minh Phuc LưNo ratings yet
- Suplly Chain ManagementDocument24 pagesSuplly Chain ManagementFerryStyawanNo ratings yet
- New Jeevan Anand Plan 815Document6 pagesNew Jeevan Anand Plan 815Anonymous YakppP3vAnNo ratings yet
- Techgrains - Ecommerce Portfolio v1.1Document17 pagesTechgrains - Ecommerce Portfolio v1.1infoNo ratings yet
- Thomas Anderson: Myoffice Inc, Boston Oct 2005 - PresentDocument2 pagesThomas Anderson: Myoffice Inc, Boston Oct 2005 - PresentUltrapure AnalytichemNo ratings yet
- TA DA RulesDocument2 pagesTA DA RulesYogen Ji100% (1)
- Class Presentation On Startup:OLA: Presented To:-Asst. Prof. Dr. Praveen AronkarDocument14 pagesClass Presentation On Startup:OLA: Presented To:-Asst. Prof. Dr. Praveen AronkarKushagra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Name Shehnila Azam Registration No# 45736 Course Cost and Management Accounting DAY Sunday Timing 3 To 6 Practice#1Document6 pagesName Shehnila Azam Registration No# 45736 Course Cost and Management Accounting DAY Sunday Timing 3 To 6 Practice#1yousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- ACC 225 Week 6 Problem 6-1ADocument6 pagesACC 225 Week 6 Problem 6-1APraveen SudarsanNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 - BankingDocument92 pagesUnit 12 - BankingNhung Cẩm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document25 pagesChap 4Dharmesh MistryNo ratings yet
- Qikpod GhuDocument6 pagesQikpod GhuAkhil RajNo ratings yet
- The Journey of Reforms by Integrating ICT: Case of KNH - Connected Kenya - Richard LesiyampeDocument22 pagesThe Journey of Reforms by Integrating ICT: Case of KNH - Connected Kenya - Richard LesiyampeICT AUTHORITYNo ratings yet
- HDFC Standard Life InsuranceDocument120 pagesHDFC Standard Life InsuranceAyush PathakNo ratings yet
- NAVDocument27 pagesNAVSai PrintersNo ratings yet
- Auditing-Non Profit Entities and HospitalsDocument12 pagesAuditing-Non Profit Entities and HospitalsVirgie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Co Operative Accounting of CampusDocument5 pagesQuestion Paper Co Operative Accounting of CampusJagadeesha Mohan60% (5)
- Master DataDocument32 pagesMaster DataAshwini KanranjawanePasalkarNo ratings yet
- Health Care Internal AuditDocument5 pagesHealth Care Internal Auditmark gmNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 - Intra Group Transactions - Illustrative ExamplesDocument4 pagesTopic 12 - Intra Group Transactions - Illustrative ExamplesMiss SlayerNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Installment LiquidationDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 7 Installment LiquidationJethro Ephraim San Miguel67% (9)
- Profile Van de BogartDocument6 pagesProfile Van de BogartMariyam AkmalNo ratings yet
- 543 Abdulelah Presentation DatabaseDocument12 pages543 Abdulelah Presentation Databaseapi-529533386No ratings yet
- Ambreen Raza: Ex - Senior Associate - Deloitte PakistanDocument2 pagesAmbreen Raza: Ex - Senior Associate - Deloitte PakistanMurtaza JangdaNo ratings yet
- Safetynet Credit Facility An Explanation of Your Running Account Credit AgreementDocument8 pagesSafetynet Credit Facility An Explanation of Your Running Account Credit AgreementLiliana IonNo ratings yet