Professional Documents
Culture Documents
მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობ
Uploaded by
dachi apkhazavaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობ
Uploaded by
dachi apkhazavaCopyright:
Available Formats
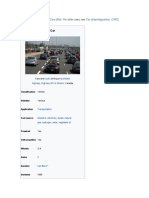
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels.
Most definitions of cars say
that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and
mainly transport people (rather than goods).[1][2]
Cars were invented in 1886, when German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz
Patent-Motorwagen.[3][4][5] Cars became widely available during the 20th century.
One of the first cars affordable by the masses was the 1908 Model T, an American
car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US,
where they replaced horse-drawn carriages.[6] In Europe and other parts of the
world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II.[7] The car
is considered an essential part of the developed economy.
Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and a variety of
lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls have been added to
vehicles, making them progressively more complex. These include rear-reversing
cameras, air conditioning, navigation systems, and in-car entertainment. Most cars
in use in the early 2020s are propelled by an internal combustion engine, fuelled
by the combustion of fossil fuels. Electric cars, which were invented early in the
history of the car, became commercially available in the 2000s and are predicted to
cost less to buy than gasoline cars before 2025.[8][9] The transition from fossil
fuels to electric cars features prominently in most climate change mitigation
scenarios,[10] such as Project Drawdown's 100 actionable solutions for climate
change.[11]
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs to the individual include
acquiring the vehicle, interest payments (if the car is financed), repairs and
maintenance, fuel, depreciation, driving time, parking fees, taxes, and insurance.
[12] The costs to society include maintaining roads, land use, road congestion, air
pollution, noise pollution, public health, and disposing of the vehicle at the end
of its life. Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths
worldwide.[13] Personal benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility,
independence, and convenience.[14] Societal benefits include economic benefits,
such as job and wealth creation from the automotive industry, transportation
provision, societal well-being from leisure and travel opportunities, and revenue
generation from taxes. People's ability to move flexibly from place to place has
far-reaching implications for the nature of societies.[15]
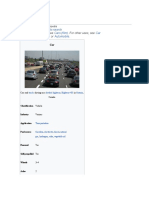
There are around one billion cars in use worldwide. Car usage is increasing
rapidly, especially in China, India, and other newly industrialized countries.[16]
You might also like
- Recarch CarDocument1 pageRecarch CarBhupender AswalNo ratings yet
- WkiDocument1 pageWkiAle IlovanNo ratings yet
- Citation NeededDocument1 pageCitation NeededDexterNo ratings yet
- Cars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiesDocument5 pagesCars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiestjasaNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSuryansh RajputNo ratings yet
- Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument1 pageCar Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDerrick BaltimoreNo ratings yet
- Rise of Motorized VehiclesDocument2 pagesRise of Motorized VehiclesMauyrNo ratings yet
- CarDocument2 pagesCarSimran Singh KotlaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Flexible-Fuel VehiclesDocument1 pageEthanol Flexible-Fuel VehicleslatchanyananaNo ratings yet
- Cars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument3 pagesCars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orAndrei SlabakovNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- A Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsDocument2 pagesA Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsAlin VoicuNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument2 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarinbawNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarssaleha3695No ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andDocument5 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andbluesparkles013No ratings yet
- Modern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntarioDocument2 pagesModern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntariosudinorangeNo ratings yet
- AutomobileDocument1 pageAutomobileschoolemail bellaNo ratings yet
- CARSDocument8 pagesCARSRajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Accident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportDocument40 pagesAccident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportAlmubeenNo ratings yet
- FDFXDocument1 pageFDFXMahmoud Al NuaimiNo ratings yet
- Safari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Document1 pageSafari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Santosh J Yadav's FriendNo ratings yet
- Reference:WikipediaDocument1 pageReference:Wikipediagnoble30No ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument30 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orLeonard IonutNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesDocument88 pagesTata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesParth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of CarsDocument1 pageThe Evolution of CarsmikkelNo ratings yet
- All About CarsDocument16 pagesAll About Carsapi-255581071No ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4noneofyourbusinessNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument56 pagesINTRODUCTIONkoolvansh692No ratings yet
- Etymology: Source - WikipediaDocument3 pagesEtymology: Source - WikipediaWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- History of CarsDocument21 pagesHistory of CarsGayle OmisolNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument5 pagesCarsPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Automotive IndustryDocument6 pagesAutomotive IndustryPankaj KansalNo ratings yet
- POM SC045 Study ReportDocument6 pagesPOM SC045 Study ReportRushikesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industry Crisis of 2008-2010: Team MembersDocument8 pagesAutomotive Industry Crisis of 2008-2010: Team MembersMaged M.W.No ratings yet
- Tata To Kia ProjectDocument44 pagesTata To Kia Projectbaskar rNo ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andDocument4 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andewbNo ratings yet
- Title The Automobile Revolution A JDocument2 pagesTitle The Automobile Revolution A JromohacNo ratings yet
- Natural SciencesDocument13 pagesNatural Sciencesxxmahnoor21No ratings yet
- Project Report OnDocument61 pagesProject Report OnVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Car HistoryDocument15 pagesCar HistoryprakashNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of AutomobilesDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Automobilesrjn46189nezidcomNo ratings yet
- Tentang Motor HybridDocument8 pagesTentang Motor HybridRudi HutagaolNo ratings yet
- Page SemiDocument39 pagesPage SemiBallon DopeNo ratings yet
- Lucas TVS ProjectDocument58 pagesLucas TVS ProjectSourav Roy0% (1)
- Car ReviewDocument3 pagesCar Reviewerwand21No ratings yet
- Cars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaDocument24 pagesCars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Cars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument9 pagesCars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourShrinivas_shprNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Wheels Roads Seat Wheels People Cargo Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot François Isaac de RivazDocument163 pagesMotor Vehicle Wheels Roads Seat Wheels People Cargo Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot François Isaac de Rivazshrimati.usha.sharmaNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industry AnalysisDocument31 pagesAutomotive Industry AnalysisSaif Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- How To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyDocument3 pagesHow To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyDeangelo ParkhursterNo ratings yet
- The World of AutomobilesDocument3 pagesThe World of AutomobilesAmogus MogusNo ratings yet
- Automobile Industry - Marketing MixDocument35 pagesAutomobile Industry - Marketing MixmupadeNo ratings yet
- Mahindra and MahindraDocument58 pagesMahindra and MahindraMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument12 pagesSwot Analysispoonamy09No ratings yet
- Car IndustryDocument32 pagesCar IndustryMohammad HagigiNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engine: Recent Developments Characteristics History Engine TypesDocument4 pagesAutomotive Engine: Recent Developments Characteristics History Engine TypesMARCELA LA QUE SE MEANo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Cars Over TimeDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Cars Over TimediogoNo ratings yet
- Ali's CareerDocument2 pagesAli's CareeradadNo ratings yet
- TysonDocument1 pageTysondachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- გერმანიაDocument1 pageგერმანიაdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- ტურკეტიDocument2 pagesტურკეტიdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- სასომხეთDocument1 pageსასომხეთdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- მაშინაებატDocument1 pageმაშინაებატdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- KMG Profile 202306013-WHDocument43 pagesKMG Profile 202306013-WHThương VuNo ratings yet
- SMRC Project Report 1Document59 pagesSMRC Project Report 1anil100% (1)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6 SD Sekolah DasarDocument7 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6 SD Sekolah DasarNaufal AdiprasetyoNo ratings yet
- FAJASDocument891 pagesFAJASCecilia GilNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 186312 June 29, 2010 Spouses Dante Cruz and Leonora Cruz, Petitioners, SUN HOLIDAYS, INC., RespondentDocument47 pagesG.R. No. 186312 June 29, 2010 Spouses Dante Cruz and Leonora Cruz, Petitioners, SUN HOLIDAYS, INC., RespondentAngelica Joyce DyNo ratings yet
- Atlas-350MHE en CompressedDocument11 pagesAtlas-350MHE en CompressedHala100% (1)
- Car Series A, C,& D, Practice QuestionsDocument26 pagesCar Series A, C,& D, Practice QuestionsVijaya shelarNo ratings yet
- Duronto Express Sleeper Class (SL) : WL WLDocument2 pagesDuronto Express Sleeper Class (SL) : WL WLSchool AppNo ratings yet
- New Flyer - Xcelsior SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNew Flyer - Xcelsior SpecificationspandiyarajmechNo ratings yet
- The 'Union Moon' and 'Stena Feronia' at BelfastDocument3 pagesThe 'Union Moon' and 'Stena Feronia' at Belfastmihalikj2190No ratings yet
- 03 Evs Ws Ch12 Means of Transport 02 KVDocument4 pages03 Evs Ws Ch12 Means of Transport 02 KVChandra BabuNo ratings yet
- Mca Formula SheetDocument4 pagesMca Formula SheetBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Drill Requirements.Document2 pagesDrill Requirements.Imam Saja DechNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Growth of Indian Domestic Aviation Industry During Pre-Privatization EraDocument28 pagesChapter-3 Growth of Indian Domestic Aviation Industry During Pre-Privatization EraMohammed BilalNo ratings yet
- Bomb Threat Stand-Off Distances: UnclassifiedDocument1 pageBomb Threat Stand-Off Distances: UnclassifiedShyam PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Brake Rendering TestDocument1 pageBrake Rendering TestSukhvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Kerala PDFDocument22 pagesKerala PDFAlthaf BackerNo ratings yet
- Safety Fi RST: The Airbus Safety MagazineDocument52 pagesSafety Fi RST: The Airbus Safety MagazineJamesNo ratings yet
- MPTO Charts566662Document25 pagesMPTO Charts566662andres ortizNo ratings yet
- Student Driver ArticleDocument2 pagesStudent Driver Articleapi-588922852No ratings yet
- RDSO Guidelines G-33 Rev.1Document29 pagesRDSO Guidelines G-33 Rev.1Ashish Goswami86% (7)
- Motor - Assist - Booklet (Done Excel, Done CC) PDFDocument52 pagesMotor - Assist - Booklet (Done Excel, Done CC) PDFCK AngNo ratings yet
- BIOBASE Deep Freezer BDF-40V268 '362 User Manual 202008Document18 pagesBIOBASE Deep Freezer BDF-40V268 '362 User Manual 202008Eliana Arroyo MedinaNo ratings yet
- A. Identify The Relevant FactsDocument2 pagesA. Identify The Relevant FactsQuỳnh LêNo ratings yet
- 1 BIJ TO BAG - MergedDocument10 pages1 BIJ TO BAG - MergedSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- SSA AUS Safesmart - Edge Protection Brochure 12 Pager 06 - 20Document12 pagesSSA AUS Safesmart - Edge Protection Brochure 12 Pager 06 - 20notengofffNo ratings yet
- Suzuki V Strom DL 250Document2 pagesSuzuki V Strom DL 250FelipeNo ratings yet
- Kiwi Experience: Mark ColgateDocument16 pagesKiwi Experience: Mark ColgateNitish Shah100% (1)
- PNQ 17:30 BLR 19:00: Pune To BengaluruDocument3 pagesPNQ 17:30 BLR 19:00: Pune To BengaluruSwarali JoshiNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions: PART NUMBER: 22-547Document10 pagesInstallation Instructions: PART NUMBER: 22-547kilofome05No ratings yet