Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SUSTAINABILITY
Uploaded by
Windy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageSustainability refers to a system's long-term ability to exist, rather than its short-term resistance to change, as defined in the 1987 Bruntland Report. Early economic models from the 1950s saw long-term growth coming from innovation rather than consumption. This view was strengthened in the 1980s by new growth theory. Thomas Malthus warned of overpopulation in 1798, though increased agricultural productivity solved this through the Green Revolution. Garret Hardin's "Tragedy of the Commons" in 1968 analyzed the exhaustion of public goods without limits.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSustainability refers to a system's long-term ability to exist, rather than its short-term resistance to change, as defined in the 1987 Bruntland Report. Early economic models from the 1950s saw long-term growth coming from innovation rather than consumption. This view was strengthened in the 1980s by new growth theory. Thomas Malthus warned of overpopulation in 1798, though increased agricultural productivity solved this through the Green Revolution. Garret Hardin's "Tragedy of the Commons" in 1968 analyzed the exhaustion of public goods without limits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageSUSTAINABILITY
Uploaded by
WindySustainability refers to a system's long-term ability to exist, rather than its short-term resistance to change, as defined in the 1987 Bruntland Report. Early economic models from the 1950s saw long-term growth coming from innovation rather than consumption. This view was strengthened in the 1980s by new growth theory. Thomas Malthus warned of overpopulation in 1798, though increased agricultural productivity solved this through the Green Revolution. Garret Hardin's "Tragedy of the Commons" in 1968 analyzed the exhaustion of public goods without limits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
SUSTAINABILITY
• Sustainability should be seen as different from stability, although at first sight the
overlap seems obvious. It considers the long-term capacities of a system to exist,
not its short-term resistance to change. A well-known definition of sustainability
comes from the Bruntland Report prepared for the United Nations in 1987.
‘Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the
ability of future generations to meet their own needs’
• The Solow-Swan model from the 1950s saw the only chance for long-term
growth in innovations, rather than consumption.
• In the 1980s another powerful theory of Paul Romer and Robert Lucas
strengthened this way of thinking (called the new growth theory).
• The pioneer was Thomas Malthus, who published in 1798 a book on the grim
consequences of a rising population. The solution was found in increased
productivity of agriculture, which culminated in the Green Revolution.
• In 1968 Garret Hardin wrote his famous work 'Tragedy of the commons', which
analyzed how public goods got exhausted by actors in a free market economy.
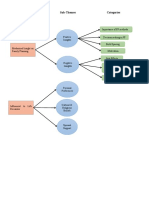
• Figure 48.1 Top 20 of the highest public debt ratio (% to GDP)
You might also like
- FOUNDATION CONCEPTS: What Is SustainabilityDocument12 pagesFOUNDATION CONCEPTS: What Is SustainabilityPost Carbon Institute100% (14)
- Economic Heresies Some Old Fashioned Questions in Economic Theory PDFDocument167 pagesEconomic Heresies Some Old Fashioned Questions in Economic Theory PDFWashington Quintero100% (1)
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument7 pagesContemporary World ReviewerAnzelle Armonio100% (2)
- ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT - TheoryDocument26 pagesECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT - TheoryChristine Leal-EstenderNo ratings yet
- Towards A Sustainable WorldDocument60 pagesTowards A Sustainable WorldDominic Manguerra AtienzaNo ratings yet
- The Boy Who Fed The NightmaresDocument4 pagesThe Boy Who Fed The NightmaresWindyNo ratings yet
- SUSTAINABLE ECONOMIC SYSTEMS, Contemporary World, by Sebastian PóciennikDocument19 pagesSUSTAINABLE ECONOMIC SYSTEMS, Contemporary World, by Sebastian PóciennikAubrey Illurimo70% (10)
- Capitalism and Its Economics: A Critical HistoryFrom EverandCapitalism and Its Economics: A Critical HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- TCWD Week 15-Sustainable DevelopmentDocument3 pagesTCWD Week 15-Sustainable DevelopmentKATHLEEN ANGELA RODULFONo ratings yet
- Contemp RevDocument9 pagesContemp RevNubskie 314No ratings yet
- Capitalism and Degrowth An Impossibility Theorem Monthly ReviewDocument6 pagesCapitalism and Degrowth An Impossibility Theorem Monthly ReviewlahgritaNo ratings yet
- Socialforum DKDocument6 pagesSocialforum DKagbogbemanou4No ratings yet
- Economics Steady StateDocument8 pagesEconomics Steady StateRizwana NourNo ratings yet
- Degrowth - Overview - Sadhbh Juarez BourkeDocument8 pagesDegrowth - Overview - Sadhbh Juarez BourkeSadhbh SaifNo ratings yet
- Sustanable DevelopmentDocument10 pagesSustanable Developmentsushant dawaneNo ratings yet
- Cowen and ShentonDocument4 pagesCowen and ShentonpepeNo ratings yet
- Capitalism and DegrowthDocument8 pagesCapitalism and DegrowthSercanNo ratings yet
- BrundtlandDocument28 pagesBrundtlandMalick HaiderNo ratings yet
- Approaches To GlobalizationDocument35 pagesApproaches To GlobalizationEr LiNo ratings yet
- Challenges To Globalism - Change and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesChallenges To Globalism - Change and DevelopmentDon Zian EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Rostow Development Model 1960Document21 pagesRostow Development Model 1960Mia SamNo ratings yet
- Contem World NotesDocument13 pagesContem World NotesslacsonNo ratings yet
- A Degrowth Response To An Ecomodernist ManifestoDocument21 pagesA Degrowth Response To An Ecomodernist ManifestoRj SuNo ratings yet
- Gaining Perspective On Sustainability and Sustainable Manufacturing PracticesDocument19 pagesGaining Perspective On Sustainability and Sustainable Manufacturing PracticesPromodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document10 pagesChapter 11I change my name For no reasonNo ratings yet
- Theories On Society: Manuelito S. UyDocument18 pagesTheories On Society: Manuelito S. UyManuelito UyNo ratings yet
- Population Resources 2023Document57 pagesPopulation Resources 2023sancallonandez.95No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Globalization 11Document42 pagesMODULE 2 Globalization 11Gerald MagaitaNo ratings yet
- Green Growth, Smart Growth: A New Approach to Economics, Innovation and the EnvironmentFrom EverandGreen Growth, Smart Growth: A New Approach to Economics, Innovation and the EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- 3-2 Bullard and MullerDocument20 pages3-2 Bullard and MullermufasashulizeeNo ratings yet
- Globalization Lecture PDFDocument29 pagesGlobalization Lecture PDFniqueisreal0227No ratings yet
- Política EconómicaDocument34 pagesPolítica EconómicaCarlosMuñozNo ratings yet
- Modernization PDFDocument12 pagesModernization PDFalice caulfieldNo ratings yet
- RODRIK, Dani - Understanding Economic Policy ReformDocument36 pagesRODRIK, Dani - Understanding Economic Policy ReformAndré Gonçalves OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Welfare - Joseph Stiglitz - FINAL PDFDocument31 pagesWelfare - Joseph Stiglitz - FINAL PDFRoosevelt InstituteNo ratings yet
- Indecs2007 pp151 160Document10 pagesIndecs2007 pp151 160Dániel TokodyNo ratings yet
- Assignment IOSDocument24 pagesAssignment IOSᘉᓋᘻᗗᘙ ᘉᓋᙏᓲ ᖽᐸᗁᕠᘘNo ratings yet
- Klein The Second Great TransformationDocument24 pagesKlein The Second Great TransformationAristóteles De Almeida SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ruggie Taking Embedded Liberalism GlobalDocument38 pagesRuggie Taking Embedded Liberalism GlobalgabrielalgarroboNo ratings yet
- Treadmill of Production TheoryDocument24 pagesTreadmill of Production TheoryLANKA ADARSHNo ratings yet
- Dinescu - The Future of Globalization 3Document6 pagesDinescu - The Future of Globalization 3lhinjohn maglasangNo ratings yet
- Globalisation A Converging Commanality CS 3Document2 pagesGlobalisation A Converging Commanality CS 3Bolang chaiNo ratings yet
- THE Contemporary WorldDocument22 pagesTHE Contemporary WorldSteven Claude TanangunanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development - What Is It? Definition, History, Evolution, Importance and ExamplesDocument8 pagesSustainable Development - What Is It? Definition, History, Evolution, Importance and ExamplesqwertyNo ratings yet
- Introducing Sustainable Development IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntroducing Sustainable Development IntroductionEureka KingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer The Development Theories ECODEVDocument2 pagesReviewer The Development Theories ECODEVShiene SalamidaNo ratings yet
- The Official Definition of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument3 pagesThe Official Definition of Sustainable DevelopmentWico SyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Historical Development of Envirionmental EconomicsDocument13 pages1 - Historical Development of Envirionmental EconomicsGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Neoliberal Collapse Markets Are Not The Answer FADocument7 pagesThe Neoliberal Collapse Markets Are Not The Answer FAveroNo ratings yet
- 697-Article Text-4430-1-10-20190919Document15 pages697-Article Text-4430-1-10-20190919Family SulitNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Architecture in PhilippinesDocument7 pagesSustainable Architecture in PhilippinesVu ʕ·ᴥ·ʔNo ratings yet
- Practical Utopians PrintDocument6 pagesPractical Utopians PrintFrancine NunesNo ratings yet
- TCWD PrelimDocument7 pagesTCWD PrelimcalibraelleNo ratings yet
- Abundance On TrialDocument19 pagesAbundance On TrialRajagopal KombiyilNo ratings yet
- Global Stratification 1Document9 pagesGlobal Stratification 1Katkat FilomeraNo ratings yet
- AssigDocument16 pagesAssigMelikteNo ratings yet
- Dresner - 2002 - Principles of Sustainability - CH 3Document9 pagesDresner - 2002 - Principles of Sustainability - CH 3Arundhati DuttaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lesson 1 B. History of GlobalizationDocument18 pagesPrelim Lesson 1 B. History of GlobalizationJANETH SATRAINNo ratings yet
- AsdfghjkmnDocument15 pagesAsdfghjkmnLaila GoldeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Human+development+report+1999+-+chapter+5Document18 pages2.1 Human+development+report+1999+-+chapter+5Alexis Vásquez LópezNo ratings yet
- Ignition and Burning Rate of Sheanut Shell Briquettes Produced at Moderate Temperature and Die PressureDocument6 pagesIgnition and Burning Rate of Sheanut Shell Briquettes Produced at Moderate Temperature and Die PressureWindyNo ratings yet
- 1251 ChordsDocument2 pages1251 ChordsWindyNo ratings yet
- Theme Sub-Themes CategoriesDocument1 pageTheme Sub-Themes CategoriesWindyNo ratings yet
- Windy Salinda - Ncm116assignment1Document2 pagesWindy Salinda - Ncm116assignment1WindyNo ratings yet
- REVIEW OF RELATedDocument5 pagesREVIEW OF RELATedWindyNo ratings yet
- RRL SampleDocument1 pageRRL SampleWindyNo ratings yet
- TriageDocument6 pagesTriageWindyNo ratings yet
- Article TitleDocument1 pageArticle TitleWindyNo ratings yet
- The EMERGENCY SEVERITY INDEXDocument4 pagesThe EMERGENCY SEVERITY INDEXWindyNo ratings yet
- Annex 5Document3 pagesAnnex 5WindyNo ratings yet
- Rizal's ReflectionDocument10 pagesRizal's ReflectionWindyNo ratings yet
- The EMERGENCY SEVERITY INDEXDocument6 pagesThe EMERGENCY SEVERITY INDEXWindyNo ratings yet
- Movie AnalysisDocument3 pagesMovie AnalysisWindyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StatisticsDocument15 pagesChapter 1 StatisticsWindyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document15 pagesChapter 4WindyNo ratings yet
- Chapters 2 and 3pptxDocument12 pagesChapters 2 and 3pptxWindyNo ratings yet