Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Genetics and Evolution
Uploaded by
Tulika BholaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Genetics and Evolution
Uploaded by
Tulika BholaCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Give any one reason why Mendel used a true breeding line of garden pea plants in his experiments.
1
2. What are the codons ‘AUG’ and ‘UAA’ referred to as? 1
3. Why are color blindness and thalassemia categorized as Mendelian disorders? 1
4. Why did Morgan and his group attribute the terms linkage and recombination with respect to position of genes on
a chromosome? 2
5. Name a genetic disorder where a human female is always a carrier yet rarely suffers from the disorder. Explain. 3
6. Give three reasons to justify why between the two nucleic acids, DNA is considered to be the better one. 3
7. What constitutes an operon? Explain the role of repressor in lac operon. 3
8. a. What would happen if oxygen was present among the other gases in miller’s experiment? 3
b. why was an electric discharge created in a closed flask?
c. Write the conclusion drawn by him at the end of his experiment.
9. a. Name the types of Ribo nucleic acids and mention their functions. 5
b. Describe the process of transcription in prokaryotes.
10. What are fossils? Explain how paleontological evidence shows that evolution of life forms has indeed taken place
on Earth. 5
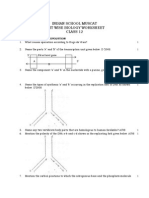
11. British geneticist R.C. Punnett developed a graphical representation of a genetic cross
called “Punnett Square”. Mention the possible result this representation predicts of the
genetic cross carried. 1
12. State the two principal outcomes of the experiments conducted by Louis Pasteur on
origin of life. 1
13. How would the gene flow or genetic drift affect the population in which either of them
happen to take place ? 2
14. Compare in any three ways the chromosomal theory of inheritance as proposed by3
Sutton and Bovery with that of experimental results on pea plant presented by Mendel.
15. (a) Explain linkage and recombination as put forth by T.H. Morgan based on his 3
observations with Drosophila melanogaster crossing experiment.
(b) Write the basis on which Alfred Sturtevant explained gene mapping.
16. . Explain the mechanism of DNA replication with the help of a replication fork. What 3
role does the enzyme DNA-ligase play in a DNA replication fork ?
17. Construct and label a transcription unit from which the RNA segment given below has 3
been transcribed. Write the complete name of the enzyme that transcribed this RNA.
18. (a) Write two differences between Homo erectus and Homo habilis. 3
(b) Rearrange the following from early to late geologic periods :
Carboniferous, Silurian, Jurassic.
19. Differentiate between incomplete dominance and co-dominance. Substantiate your 5
answer with one example of each.
20. (a) Write the contributions of the following scientists in deciphering the genetic code. 4+1
Georce Gamow ; Hargobind Khorana ; Marshall Nirenberg ; Severo Ochoa
(b) State the importance of a Genetic code in protein biosynthesis.
21. State Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment. 1
22. Write one example each of organisms exhibiting (i) male heterogamety, and (ii) female heterogamety.1
23. Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness more in human males than in females? Explain. 2
24. How is polygenic inheritance different from pleiotropy? Give one example of each. 3
OR
Explain the Hardy-Weinberg principle with the help of an algebraic equation.
25. What is adaptive radiation? How did Darwin explain it? 3
26. Explain the role of regulatory gene in a lac operon. Why is regulation of lac operon called as negative
regulation ? 3
27. Compare the processes of DNA replication and transcription in prokaryotes. 5
OR
(a) Explain Griffith’s ‘transforming principle’ experiment.
(b) In the above experiment, ‘‘heat which killed one type of bacteria, did not destroy the properties of genetic
material.’’ Justify.
28. Name a human genetic disorder due to the following : 1
(a) An additional X-chromosome in a male
(b) Deletion of one X-chromosome in a female 2
OR
State what does aneuploidy lead to.
29. Mention one example each from plants and animals exhibiting divergent evolution. 2
A segment of DNA molecule comprises of 546 nucleotides. How many cytosine nucleotides would be present in
it if the number of adeninenucleotides is 96 ?
30. (a) How does mutation occur ? 3
(b) Differentiate between point mutation and frameshift mutation.
31. ‘‘Use of heavy isotope of nitrogen by Meselson and Stahl demonstrated semi-conservative mode of
replication of a DNA molecule.’’ Explain how did they arrive at this conclusion. 3
OR
Explain the mechanism of translation that occurs in the ribosomes in a prokaryote.
32. According to Darwinian theory of natural selection the rate of appearance of new forms is 3
linked to the life-cycle or the life-span of an organism. Explain with the help of an example.
33. Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having yellow and round seeds with another pea 5
plant bearing green and wrinkled seeds. He found that in some of the F2 population new combination of parental
characters were observed.
How will you explain the appearance of a new combination of parental characters in F2-offsprings ? Support your
answer with the help of Punnett square.
OR
Describe S.L. Miller’s experiment. Comment on the observations he made and his contribution towards the origin
of life on Earth.
34. British geneticist R.C. Punnett developed a graphical representation of a genetic cross called 2 “Punnett
Square”. Mention the possible result this representation predicts of the genetic cross carried.
35. Explain the mechanism of DNA replication with the help of a replication fork. What role does the 3 enzyme
DNA-ligase play in a DNA replication fork ?
OR
Construct and label a transcription unit from which the RNA segment given below has been transcribed. Write the
complete name of the enzyme that transcribed this RNA.
You might also like
- Selective Breeding: Carla Daniela Granada Ana María Cardona Mariana Rivera Amador María José HurtadoDocument16 pagesSelective Breeding: Carla Daniela Granada Ana María Cardona Mariana Rivera Amador María José Hurtadodaniela granadaNo ratings yet
- 100 Past QuestionsDocument37 pages100 Past QuestionsNasif Basher0% (1)
- Class XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionDocument10 pagesClass XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionMohamad Qulam Zaki100% (1)
- Shomus MOD 3 NOTEDocument96 pagesShomus MOD 3 NOTEvishalNo ratings yet
- Essential Cell BiologyDocument7 pagesEssential Cell BiologyKyle Broflovski0% (2)
- Test Bank For Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition William S KlugDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition William S KlugPhilip Yarbrough100% (34)
- Structural and Evolutionary Genomics: Natural Selection in Genome EvolutionFrom EverandStructural and Evolutionary Genomics: Natural Selection in Genome EvolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- (Cambridge Introductions To Philosophy and Biology 4) Paul Griffiths, Karola Stotz - Genetics and Philosophy - An Introduction (2013, Cambridge University Press)Document279 pages(Cambridge Introductions To Philosophy and Biology 4) Paul Griffiths, Karola Stotz - Genetics and Philosophy - An Introduction (2013, Cambridge University Press)Yerson Ariel Vasquez Valdés100% (3)
- 6 BIO462 Chapter 6Document21 pages6 BIO462 Chapter 6Syafiqah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Evo E3Document15 pagesEvo E3shahzebNo ratings yet
- CSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperDocument17 pagesCSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperManu Mallahalli ShanthappaNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document3 pagesBio 2BoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 SolutionsDocument12 pagesChapter 01 Solutionsjeanmarie20150% (1)
- Galaxy - Unit Test - 1 - BiologyDocument4 pagesGalaxy - Unit Test - 1 - BiologyMani VannanNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution Unit NotesDocument19 pagesGenetics and Evolution Unit NotesJames OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Biology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010Document4 pagesBiology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010gggtdyfhuuoNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND MOLECULAR BASISDocument2 pagesGENETICS - PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND MOLECULAR BASISSouparna GhoshNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.Document2 pagesClass 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.joshan jayapaul pandiyan100% (1)
- Some Midterm Free ResponsesDocument4 pagesSome Midterm Free Responsesjenh191No ratings yet
- Assignment Unit - 7, Genetics and EvolutionDocument1 pageAssignment Unit - 7, Genetics and EvolutionNikhil MishraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SAQsDocument37 pagesBiochemistry SAQscarolinegatwiri08No ratings yet
- 12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Document6 pages12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Mubashshir Al NahyanNo ratings yet
- Fred Review 16Document8 pagesFred Review 16Justin HsuNo ratings yet
- BIO Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesBIO Model Question PaperPrithwish DaluiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Theory) : STD: XIIDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY (Theory) : STD: XIIReena csbNo ratings yet
- Unit C ExamDocument18 pagesUnit C Examapi-199149636No ratings yet
- Solution 648974Document4 pagesSolution 648974ArpitNo ratings yet
- Biology Pyqs 2023Document15 pagesBiology Pyqs 2023Zara KNo ratings yet
- PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION, January 2015 Class XII Biology (044) : G.G.N. Public School, Rose Garden, LudhianaDocument5 pagesPRE-BOARD EXAMINATION, January 2015 Class XII Biology (044) : G.G.N. Public School, Rose Garden, LudhianaSamita BhallaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper BIOLOGY (044) CLASS XII (2013-14)Document17 pagesSample Question Paper BIOLOGY (044) CLASS XII (2013-14)api-243565143No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceMahesh T MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Chapters 10, 11,12 AnswersDocument5 pagesHomework 4 Chapters 10, 11,12 AnswersButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2013 Question Paper Set 1Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2013 Question Paper Set 1Medhya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Why Gene Cloning and DNA Analysis are CrucialDocument11 pagesWhy Gene Cloning and DNA Analysis are CrucialharichandanaaravindNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument106 pagesCombine PDFМөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2013-1-0Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2013-1-0Manish kumar 13702No ratings yet
- University of Texas BIO 325 ExamDocument6 pagesUniversity of Texas BIO 325 ExamGeetika InstaNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Biology 12th - PDF QuestionsDocument69 pagesXam Idea Biology 12th - PDF QuestionsDeepa SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Biology Xii PyqDocument16 pagesChapter - Biology Xii Pyqalina jamalNo ratings yet
- GenesDocument4 pagesGeneseReader.LeaderNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Asm 2022-23Document33 pagesUnit-Ii Asm 2022-23AnshnuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by KlugDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by Klugminhkhoit8cua3No ratings yet
- Third-Quarter-Exam_Science-10-Carnation-GreenDocument8 pagesThird-Quarter-Exam_Science-10-Carnation-GreenGabriel HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Gene TikaDocument5 pagesGene Tikaluluk.farichaNo ratings yet
- Bio1a03 Practice Test 3Document10 pagesBio1a03 Practice Test 3QforQANo ratings yet
- Genetic Linkage Is A Term Which Describes The Tendency of Certain Loci or Alleles To BeDocument34 pagesGenetic Linkage Is A Term Which Describes The Tendency of Certain Loci or Alleles To BeHabibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Biology SQP MergedDocument15 pagesBiology SQP Mergedvipulkrishna045No ratings yet
- G.D. GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL BIOLOGY EXAM PAPERDocument5 pagesG.D. GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL BIOLOGY EXAM PAPERDevdutt sharmaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 ReviewerDocument22 pagesQuiz 2 ReviewerPia CastilloNo ratings yet
- Answerkey ExamI 13Document10 pagesAnswerkey ExamI 13waldo625No ratings yet
- Genetics Unit Test ReviewDocument3 pagesGenetics Unit Test ReviewvexelleNo ratings yet
- (B) Explain How The Biochemnical Characterization (Nature) of Transforming Principle 'WasDocument3 pages(B) Explain How The Biochemnical Characterization (Nature) of Transforming Principle 'WasBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Minireview: Ancient DNA and The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument4 pagesMinireview: Ancient DNA and The Polymerase Chain ReactiontaufiqNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1st Edition Benjamin A PierceDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1st Edition Benjamin A PierceJesus Yu100% (32)
- CLASS XII 2018 QUESTION PAPER BiologyDocument4 pagesCLASS XII 2018 QUESTION PAPER BiologyAnonymous f2rVBHlSuNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Biology Worksheet 2Document3 pagesClass Xii Biology Worksheet 2AksharaNo ratings yet
- L8 Biol261F2014DNA StrfunctDocument36 pagesL8 Biol261F2014DNA StrfunctjdazuelosNo ratings yet
- RNA SilencingDocument4 pagesRNA SilencingVictor JavierNo ratings yet
- BIS101 Study Questions AnswersDocument8 pagesBIS101 Study Questions Answerskkk13whyNo ratings yet
- Botany Paper SolvedDocument5 pagesBotany Paper SolvedUmair ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Molecular Biology of The Gene 6th Edition 9780805395921Document36 pagesSolutions Manual To Accompany Molecular Biology of The Gene 6th Edition 9780805395921antjwfgarza100% (9)
- Daniel Dwyer Biology 103 Module 8 Exam 2, Part 2 EssaysDocument4 pagesDaniel Dwyer Biology 103 Module 8 Exam 2, Part 2 EssaysDaniel DwyerNo ratings yet
- Remediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaDocument6 pagesRemediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaFlozieNo ratings yet
- Psychology CH 5 Class 12Document25 pagesPsychology CH 5 Class 12Tulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Preboard 2Document1 pageGrade 12 Preboard 2Tulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychological DisordersDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Psychological DisordersTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Flow ChartDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Flow ChartTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 FlowDocument2 pagesChapter 5 FlowTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology ApplicationsDocument38 pagesBiotechnology ApplicationsTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Lead NitrateDocument3 pagesLead NitrateTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Indus Universal School Physics Theory QuestionsDocument2 pagesIndus Universal School Physics Theory QuestionsTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Indus Universal School Biology Exam GuideDocument3 pagesIndus Universal School Biology Exam GuideTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project DraftDocument4 pagesPhysics Project DraftTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument43 pagesBiotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnushka LimbuNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Inv - Project Certificate.Document1 pageClass 12 Chemistry Inv - Project Certificate.Tulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Sexual ReproductionDocument1 pageFlowering Plant Sexual ReproductionTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles - ProcessesDocument11 pagesBiotechnology Principles - ProcessesTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Evolution Chap NotesDocument12 pagesEvolution Chap NotesTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- X-Rays Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesX-Rays Investigatory ProjectTulika BholaNo ratings yet
- Career Preference Record Intro For Class 12Document2 pagesCareer Preference Record Intro For Class 12Tulika Bhola50% (4)
- VA1Document4 pagesVA1Tulika BholaNo ratings yet
- G12 DR BiologyDocument196 pagesG12 DR BiologyAli RahimiNo ratings yet
- People v. KlingerDocument8 pagesPeople v. KlingerKennethQueRaymundoNo ratings yet
- Branches of Genetics: Classical to PsychiatricDocument3 pagesBranches of Genetics: Classical to Psychiatrickevin maravillaNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic Acids Test ResultsDocument2 pagesHydrolysis of Nucleic Acids Test ResultsDanilo ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities and DysmorphologyDocument5 pagesCongenital Abnormalities and DysmorphologyNaliaka WafulaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Document7 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Bing Sepe CulajaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Mutagenesis PDFDocument5 pagesUnit 10 - Mutagenesis PDFvuivevuiveNo ratings yet
- BIOL1090 W'23 Lecture 1-MitosisDocument49 pagesBIOL1090 W'23 Lecture 1-Mitosisateez photo-dumpNo ratings yet
- 01sex LinkageDocument26 pages01sex LinkageAehronCatilocNo ratings yet
- Case Study Genome Edited Human EmbryosDocument2 pagesCase Study Genome Edited Human EmbryosDivya Dharshini RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - NeoplasiaDocument23 pagesChapter 7 - NeoplasiaAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Simulation Activity: Maria Maureen Sado, Aimee George, Julianne Maniago, Kelly NovakDocument16 pagesMitosis Simulation Activity: Maria Maureen Sado, Aimee George, Julianne Maniago, Kelly NovakJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science Curriculum Map Final DraftDocument5 pages7th Grade Science Curriculum Map Final Draftapi-455790872No ratings yet
- Earth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Document4 pagesEarth Science Gr. 11 Module 2Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Draft of Comprehensive Data Privacy BillDocument64 pagesDiscussion Draft of Comprehensive Data Privacy BillRuss LatinoNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument6 pagesGenetic Engineeringsarguss14100% (1)
- Reverse TranscriptionDocument9 pagesReverse TranscriptionzahraNo ratings yet
- Wbi11 01 Que 2023101we30Document28 pagesWbi11 01 Que 2023101we30Amal AbuelfotouhNo ratings yet
- Ethan Antoninich - NaturalSelection Intro SHODocument7 pagesEthan Antoninich - NaturalSelection Intro SHONelson AbdulNo ratings yet
- Fisher y LErman DGGEDocument5 pagesFisher y LErman DGGEErik Estrada SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Co DominanceDocument10 pagesCo DominanceMaxxxxWillsNo ratings yet
- BP605T Unit 4-6Document482 pagesBP605T Unit 4-6Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet
- Biological Database 1Document50 pagesBiological Database 1Muhammad uzairNo ratings yet
- Revisión 2021 Genética Niemann Pick.Document22 pagesRevisión 2021 Genética Niemann Pick.patricia.rtorreshotmail.comNo ratings yet
- In Fruit FliesDocument3 pagesIn Fruit FliesNicole WehbieNo ratings yet
- Información Del Producto EZ-Vision™Document5 pagesInformación Del Producto EZ-Vision™Fabian Andres CortesNo ratings yet
- How To Design PrimersDocument14 pagesHow To Design PrimersDeepak RawoolNo ratings yet