Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MixFx 3
Uploaded by
Sergio AquinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MixFx 3
Uploaded by
Sergio AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
Phaser (effect) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 06/10/2008LO:21AM
You can support Wikipedit by making a tax-deductibledonation.
Phaser (effect)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A phaser is an audio signal processingtechniqueused to filter a signal by
creating a series of peaks and troughs in the frequency spectrum.The position of
the peaks and troughs is typically modulated so that they vary over time, creating a
sweepingeffect. For this purpose,phasersusually include a low frequency
oscillator.
Contents Imageof a phaserguitar
stompbox.
r 1 Process
. 2 Strucfure
. 3 Usage
. 4 Similar effects
. 5 See also
r 6 External links
Process
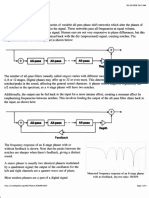
The electronic phasing effect is created by
spliaing an audio signal into two paths. One
path treatsthe signal with an all-passfilter,'
which preservesthe amplitude of the
original signal and alters the phase.The
amount of change in phasedependson the
frequency. When signals from the two paths
are mixed, the frequencies thal are out of
phasewill cancel each other out, creating
the phaser'scharacteristic notches. Spectrogramof an 8-stagephasermodulatedby a sine LFO applied
Changing the mix ratio changesthe depth of : to white noise.
the notches; the deepestnotches occur when
the mix ratio is 5A7o.
The definitionof phasertypicallyexcludessuchdeviceswherethe all-passsectionis a delayline; sucha
deviceis calleda flanger[] (http://ccrma.stanford.edu/-jos/pasp/Phasing.hrnl) . Usinga delayline createsan
unlimited seriesof equally spacednotchesand peaks.It is possibleto cascadea delayline with anothertype of
all-passfilter as in [2] (http://home.debitel.net/user/jhaible/jh-storm-tide-flanger.hfrnl)
, this combinesthe
unlimited numberof notchesfrom the flanger with the unevenspacingof the phaser.
http;I len.wikipedia.orglwiki/Phaser-%28cfrecc629 Page1 of4
You might also like
- MixFx 4Document1 pageMixFx 4Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Analyzer PDFDocument18 pagesSpectrum Analyzer PDFAgus SantosaNo ratings yet
- Ciani CookbookDocument10 pagesCiani Cookbookluca4aaronNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Transient Processing in The Phase Vocoder: IRCAM, Analysis-Synthesis Team, FranceDocument6 pagesA New Approach To Transient Processing in The Phase Vocoder: IRCAM, Analysis-Synthesis Team, FranceJamesNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Analysis and The Frequency DomainDocument16 pagesSpectrum Analysis and The Frequency DomainAhsan AmeenNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Project Description - Signal ProcessingDocument6 pagesMATLAB Project Description - Signal Processingsunshine heaven0% (1)
- 0300smith46 - The Fundamentals of Linear-Phase Filters For Digital Communications PDFDocument5 pages0300smith46 - The Fundamentals of Linear-Phase Filters For Digital Communications PDFjoe2001coolNo ratings yet
- Table Lookup Oscillators Using Generic Integrated WavetablesDocument4 pagesTable Lookup Oscillators Using Generic Integrated WavetablesPhilip KentNo ratings yet
- 3rd Int HFGW Stephenson Paper Draft 2017-02-28ADocument6 pages3rd Int HFGW Stephenson Paper Draft 2017-02-28AGary V StephensonNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 Sampling Theorem Using PAM TechniquesDocument8 pagesExperiment No 3 Sampling Theorem Using PAM TechniquesRohit GawadeNo ratings yet
- Design of Low Phase-Noise Oscillator and Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Using Microstrip Trisection Bandpass FilterDocument3 pagesDesign of Low Phase-Noise Oscillator and Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Using Microstrip Trisection Bandpass Filteranchal8singh-2No ratings yet
- Nick 2011Document4 pagesNick 2011samuelNo ratings yet
- Spring Reverb EmulationDocument8 pagesSpring Reverb EmulationsamtocieloNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument23 pagesAmplitude Shift KeyingBarnabas WendimuNo ratings yet
- Sampling: 0 Pre-Laboratory ReadingDocument10 pagesSampling: 0 Pre-Laboratory ReadingSamuel TanNo ratings yet
- Guitar Effects: ELEC-C5340 Applied Signal Processing 2016Document2 pagesGuitar Effects: ELEC-C5340 Applied Signal Processing 2016Mac MiñaNo ratings yet
- Vibrato Extraction and Parameterization PDFDocument5 pagesVibrato Extraction and Parameterization PDFGreyce OrnelasNo ratings yet
- Doma Ci Zadatak 1 Karplus-Strong Sinteza ZvukaDocument5 pagesDoma Ci Zadatak 1 Karplus-Strong Sinteza ZvukaPredrag MilićNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceMike PoznerNo ratings yet
- Bi QuadDocument5 pagesBi QuadBrian LindgrenNo ratings yet
- A Low Phase Noise Tri-Band LO Generation For Ku and E Band Radios For Backhauling Point-to-Point ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Low Phase Noise Tri-Band LO Generation For Ku and E Band Radios For Backhauling Point-to-Point ApplicationsrinsonNo ratings yet
- Additional TopicsDocument8 pagesAdditional TopicsnidharshanNo ratings yet
- Week-8 Analysis by SynthesisDocument5 pagesWeek-8 Analysis by SynthesisMacloud KamulaNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Measurement and Monitoring On Rotating MachineDocument5 pagesPartial Discharge Measurement and Monitoring On Rotating MachineWagdy KhaterNo ratings yet
- Frequency Multipliers PDFDocument22 pagesFrequency Multipliers PDFduymanhhusNo ratings yet
- Assig 4 2023Document1 pageAssig 4 2023Baochen TianNo ratings yet
- Phaser Block - Fractal Audio WikiDocument8 pagesPhaser Block - Fractal Audio WikiNikko Rafael NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Spectral Mutation in SoundHackDocument10 pagesSpectral Mutation in SoundHackJuli?n r?osNo ratings yet
- Blind Paper SpineDocument5 pagesBlind Paper SpineJoao PauloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4Manwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Aaip hw2 0151902Document5 pagesAaip hw2 0151902Hsuian ManNo ratings yet
- Paper For The IMSDocument5 pagesPaper For The IMSmiguelgarciagarciaNo ratings yet
- Lab01 FiltersDocument19 pagesLab01 Filtersjosh.ee11No ratings yet
- Synchronizing Renewable Energy Sources in Distributed Generation SystemsDocument5 pagesSynchronizing Renewable Energy Sources in Distributed Generation SystemsRehan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chen1993 tecnicaPulso-ecoBandaAnchaDocument5 pagesChen1993 tecnicaPulso-ecoBandaAnchaFabian Torres RoblesNo ratings yet
- Physics - IJPR - Sugato Pulse Act On Circular Rydberg Atoms - Sugato GhoshDocument6 pagesPhysics - IJPR - Sugato Pulse Act On Circular Rydberg Atoms - Sugato GhoshTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document4 pagesLab 6Aneeqa YasinNo ratings yet
- FMDocument25 pagesFMankit1819444602No ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation Practical File: Group 1 Ice - 3 Semester 7Document26 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation Practical File: Group 1 Ice - 3 Semester 7Prabhav SinghNo ratings yet
- RB Hyperfine StructureDocument3 pagesRB Hyperfine StructureKapila Wijayaratne100% (1)
- Ut AscanDocument7 pagesUt AscanEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNo ratings yet
- Active Control of Fan Noise: Nobuhiko YAMASAKI and Hirotoshi TAJIMADocument7 pagesActive Control of Fan Noise: Nobuhiko YAMASAKI and Hirotoshi TAJIMAManouel Cem CebiogluNo ratings yet
- Predobro Za Konctrukciju FilteraDocument8 pagesPredobro Za Konctrukciju FilteraElvir Čolak Ope-PastuhNo ratings yet
- Effects of Sampling and Aliasing On The Conversion of Analog Signals To Digital FormatDocument2 pagesEffects of Sampling and Aliasing On The Conversion of Analog Signals To Digital FormatBeny StephenNo ratings yet
- ConclusionsDocument3 pagesConclusionsMalik JaanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Break-Lock Conditions For Effective Jamming in Missile Borne Monopulse ReceiversDocument7 pagesEstimation of Break-Lock Conditions For Effective Jamming in Missile Borne Monopulse ReceiversIJERDNo ratings yet
- Optical Cavities As Amplitude Filters For Squeezed FieldsDocument9 pagesOptical Cavities As Amplitude Filters For Squeezed FieldsSasa TopicNo ratings yet
- Characterization of A High-Power Erbium-Doped Fiber LaserDocument4 pagesCharacterization of A High-Power Erbium-Doped Fiber Laserwarse1No ratings yet
- Oscillator Noise Analysis:: (T) Be A Noisy Signal. It Can Be Separated Into A N (T)Document12 pagesOscillator Noise Analysis:: (T) Be A Noisy Signal. It Can Be Separated Into A N (T)deepakvaj25No ratings yet
- WolaDocument51 pagesWolaSidharth MahotraNo ratings yet
- Butterworth Filter DesignDocument12 pagesButterworth Filter DesignVannyMeiSariNo ratings yet
- Reloj AtomicoDocument8 pagesReloj AtomicogcarreongNo ratings yet
- 5GHz VCODocument5 pages5GHz VCOnavinrkNo ratings yet
- Chap11 - Sampling & Pulse ModulationDocument59 pagesChap11 - Sampling & Pulse ModulationVijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Prediction of Phase Noise In: Resonators and OscillatorsDocument32 pagesAnalysis and Prediction of Phase Noise In: Resonators and OscillatorsDimNo ratings yet
- Tests of Backscatter Coefficient Measurement Using Broadband PulsesDocument5 pagesTests of Backscatter Coefficient Measurement Using Broadband PulsesMostafa AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Influence of RF Oscillators On An Ofdm SignalDocument12 pagesInfluence of RF Oscillators On An Ofdm SignalLi ChunshuNo ratings yet
- A 1.6-GHz 3.3-MW 1.5-MHz Wide Bandwidth Fractional-N PLL With A Single Path FIR Phase Noise FilteringDocument4 pagesA 1.6-GHz 3.3-MW 1.5-MHz Wide Bandwidth Fractional-N PLL With A Single Path FIR Phase Noise FilteringSuyog DhakneNo ratings yet
- Burt 2006Document8 pagesBurt 2006Zhenyu YangNo ratings yet
- MixFx 6Document1 pageMixFx 6Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- MixFx 5Document1 pageMixFx 5Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- MixFx 2Document1 pageMixFx 2Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- MixFx 10Document1 pageMixFx 10Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- MixFx 11Document1 pageMixFx 11Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet
- MixFX 1Document1 pageMixFX 1Sergio AquinoNo ratings yet