Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 1111@dth 14775
Uploaded by
dermatom dervenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 1111@dth 14775
Uploaded by
dermatom dervenCopyright:
Available Formats
Received: 14 August 2020 Revised: 11 December 2020 Accepted: 30 December 2020
DOI: 10.1111/dth.14775
LETTER
Amlodipine-induced generalized fixed drug eruption clinically
mimicking mycosis fungoides
Dear Editor, occasionally been reported.6 Here in, we report a case of generalized
Fixed drug eruption (FDE) is an adverse drug reaction characterized fixed drug eruption due to amlodipine clinically mimicking mycosis
by the development of well circumscribed, round, dusky erythematous fungoides.
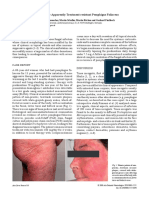
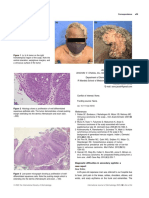
macules and plaques on cutaneous and mucosal surfaces.1 Drugs A 73-year-old male patient presented with red-brown rash on
which most commonly cause FDE include sulfonamides, tetracyclines, trunk and legs for 8 months. On dermatologic examination, there
dapsone, ampicillin, acetaminophen, aspirin, other NSAIDs, pseudo- were sharp limited, brown-erythematous plaques ranging in diameter
ephedrine, anticonvulsants and oral contraceptives.2 from 2 to 10 cm (Figure 1). He was taking amlodipine for 9 months
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine-derived selective calcium- for hypertension. On physical examination, there was no cervical
channel blocker that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions lymphadenopathy or hepatomegaly. Laboratory test results revealed
into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle. Its direct and selective no peripheral blood eosinophilia, normal renal and liver enzymes. He
action on arteriolar smooth muscles leads to a reduction in peripheral had an aortic aneurysm operation. A punch biopsy was taken from the
vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure3. Both allergic and plaque in the abdomen. In the differential diagnosis, mycosis
non-allergic adverse drug reactions (ADRs) have been reported, such fungoides, parapsoriasis and drug eruption were considered.
as flushing, gingival hyperplasia, gynaecomastia and also cutaneous Histopathologic examination revealed; orthokeratosis on surface,
ADRs.4,5 Serious adverse events such as anaphylaxis, Steven-Johnson focal parakeratosis on epidermis, diffuse basal cell vacuolization and
syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) have rare single cell keratinization (Figures 2 and 3). Perivascular edema
and lymphohistiocytic infiltration were observed in dermis. Immuno-
histochemical staining was positive for CD3-CD4-CD8 and CD68.
Histopathological findings showed features of lichenoid dermatitis.
The patient was diagnosed with drug eruption with clinical and histo-
pathological findings. Amlodipine, which suspicious drug, was changed
to another antihypertensive drug by Cardiology Department. Topical
clobetasol propionate was started twice daily. The lesions were
completely regressed after 2 months.
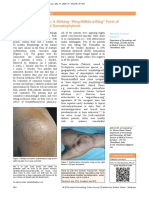
F I G U R E 2 Focal parakeratosis, basal vacuolization in the
F I G U R E 1 Sharp limited, brown-erythematous plaques ranging in epidermis and lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the superficial
diameter from 2 to 10 cm on trunk dermis. (HE ×40)
Dermatologic Therapy. 2021;34:e14775. wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/dth © 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC. 1 of 2
https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.14775
2 of 2 LETTER
CONFLIC T OF INT ER E ST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
DATA AVAILABILITY STAT EMEN T
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the
corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Tubanur Çetinarslan1
Aylin Türel Ermertcan2
Peyker Temiz3
1
Department of Dermatology, Manisa City Hospital, Manisa, Turkey
2
Department of Dermatology, Manisa Celal Bayar University, Faculty of
Medicine, Manisa, Turkey
F I G U R E 3 Focal parakeratosis, basal vacuolization in the 3
Department of Pathology, Manisa, Turkey
epidermis and lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis.
(HE ×100)
Correspondence
Dr. Tubanur Çetinarslan, Department of Dermatology, Manisa City
Hospital, Uncubozkoy Mah. 5501 Sok. 29/5 Manisa, Turkey.
Drug eruptions can mimic many dermatological diseases. In such
Email: t_sarmis@windowslive.com
cases, histopathology and drug history are helpful in differential diag-
nosis. The lichenoid tissue reaction is characterized by epidermal basal
OR CID
cell damage that is associated with a band-like infiltrate of mononu-
Tubanur Çetinarslan https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2847-9127
clear cells in the papillar dermis.7 Cases of MF in which prior biopsy
Aylin Türel Ermertcan https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7720-5491
specimens had been diagnosed as “lichenoid dermatitis” have been
reported. In the presence of a lichenoid pattern, histopathologic clues
RE FE RE NCE S
helpful in identifying MF are basal epidermotropism, nuclear atypia,
1. Rho YK, Yoo KH, Kim BJ, Kim MN, Song KY. A case of generalized
and, frequently eosinophils and plasma cells in the dermal infiltrate.8 fixed drug eruption due to a piroxicam plaster. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;
Previous studies of ADRs associated with antihypertensive drugs 35(2):204-205.
have shown that CCBs were the most common cause of ADRs, 2. Gupta R. Fixed drug eruption due to ornidazole. Indian J Dermatol.
2014;59(6):635.
followed by diuretics and β-blockers. These reactions are generally
3. Ioulios P, Charalampos M, Efrossini T. The spectrum of cutaneous reac-
not serious and regress with discontinuation of the drug. It is impor-
tions associated with calcium antagonists: a review of the literature and
tant to keep in mind that some patients may develop serious skin the possible etiopathogenic mechanisms. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:6.
reactions from CCBs.6 4. Stern R, Khalsa JH. Cutaneous adverse reactions associated with cal-
We present a case of generalized fixed drug eruption induced by cium channel blockers. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:829-832.
5. Kitamura K, Kanasashi M, Suga C, Saito S, Yoshida S, Ikezawa Z. Cuta-
an anti-hypertensive drug amlodipine which is a selective calcium-
neous reactions induced by calcium channel blocker: high frequency of
channel blocker. Although FDE usually occurs as a single lesion, it psoriasiform eruptions. J Dermatol. 1993;20:279-286.
should be kept in mind that in rare cases, it may occur as multiple 6. Khurshid F, Aqil M, Alam MS, Kapur P, Pillai KK. Monitoring of adverse
lesions in generalized form. The drug history should be questioned. To drug reactions associated with antihypertensive medicines at a univer-
sity teaching hospital in New Delhi. Daru: J Faculty Pharm. 2012;20:34.
the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of generalized fixed
7. Pinkus H. Lichenoid tissue reaction. Arch Dermatol. 1973;107:840-846.
drug eruption due to amlodipine in the literature. It should be consid- 8. Guitart J, Peduto M, Caro WA, Roenigk HH. Lichenoid changes in
ered that drug eruptions may mimic many dermatological diseases. mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:417-422.
You might also like
- 7 Best Natural Remedies For Lymph DetoxDocument17 pages7 Best Natural Remedies For Lymph Detoxrajib100% (1)
- Blood Morphometry or Blood Film CommentDocument103 pagesBlood Morphometry or Blood Film CommentYangnuu TitusNo ratings yet
- Conversion DisorderDocument8 pagesConversion DisorderMaria Von ShaftNo ratings yet
- Gopu.R:::: Patient Age / Sex 30 Y / Male BranchDocument1 pageGopu.R:::: Patient Age / Sex 30 Y / Male BranchGopu RNo ratings yet
- African Holistic Health PDFDocument16 pagesAfrican Holistic Health PDFMilaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Vs Nephritic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNephrotic Vs Nephritic SyndromeSS100% (1)
- Apoptosis in Selected Skin Diseases PDFDocument9 pagesApoptosis in Selected Skin Diseases PDFDiana Gabriela GutuerrezNo ratings yet
- Is Dermal Melasma A Phototoxic Reaction? A Case: AbbrevationsDocument2 pagesIs Dermal Melasma A Phototoxic Reaction? A Case: AbbrevationsTika Renwarin Tua ElNo ratings yet
- 2022 37 1 145 147 EngDocument3 pages2022 37 1 145 147 EngAri Tri UtamiNo ratings yet
- Darier-White Disease: A Rare Genetic DisorderDocument4 pagesDarier-White Disease: A Rare Genetic Disorderanis utamiNo ratings yet
- Journal Tinea IncognitoDocument3 pagesJournal Tinea Incognitochindy sulistyNo ratings yet
- Acquired Cutaneous Lymphangiectasias Secondary ToDocument3 pagesAcquired Cutaneous Lymphangiectasias Secondary ToAndrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Bizkova 2009Document8 pagesBizkova 2009mario256No ratings yet
- Acad Dermatol Venereol - 2019 - Nowak - Rosacea Fulminans Coincidence of The Disease With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument2 pagesAcad Dermatol Venereol - 2019 - Nowak - Rosacea Fulminans Coincidence of The Disease With Inflammatory Bowel DiseasecamilabettiomatosNo ratings yet
- Estudio MetronidazolDocument8 pagesEstudio Metronidazolluis beltranNo ratings yet
- Erythema Dyschromicum Perstans A Case Report 2376 0427 1000266Document3 pagesErythema Dyschromicum Perstans A Case Report 2376 0427 1000266Batra MourinhoNo ratings yet
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Paradigm of Critical IllnessDocument10 pagesToxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Paradigm of Critical IllnessViolett LiebeNo ratings yet
- A Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With AcitretinDocument3 pagesA Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With Acitretindr_RMNo ratings yet
- Erythroderma: A Clinico-Etiological Study of 58 Cases in A Tertiary Hospital of North IndiaDocument5 pagesErythroderma: A Clinico-Etiological Study of 58 Cases in A Tertiary Hospital of North IndiaAditya FmfNo ratings yet
- 8 - Reversal of Atopic Dermatitis With Narrow-Band UVB Phototherapy and Biomarkers - Tintle ShemerDocument15 pages8 - Reversal of Atopic Dermatitis With Narrow-Band UVB Phototherapy and Biomarkers - Tintle ShemerSandrine SinsoulieuNo ratings yet
- (Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) Dermoscopy Case of The Month PDFDocument5 pages(Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) Dermoscopy Case of The Month PDFArya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Epidermodysplasia-Verruciformis YmjdDocument1 pageEpidermodysplasia-Verruciformis YmjdAndrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis: A Rare Case Report of Dermatological Manifestation of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesInterstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis: A Rare Case Report of Dermatological Manifestation of Rheumatoid ArthritisFurgu TenzinNo ratings yet
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis A Case ReportDocument3 pagesToxic Epidermal Necrolysis A Case ReportResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s40257 017 0309 6Document3 pages10.1007@s40257 017 0309 6shf.mxlikNo ratings yet
- Vano Galvan2008Document2 pagesVano Galvan2008Laura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Causes of Nonblanching Skin LesionsDocument5 pagesTop 5 Causes of Nonblanching Skin LesionsCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Agep Poster EadvDocument1 pageAgep Poster EadvAhmet KayaaltıNo ratings yet
- Eritem PolimorfDocument3 pagesEritem PolimorfMădălina ŞerbanNo ratings yet
- Eitema Nodoso LeprosoDocument4 pagesEitema Nodoso LeprosoGuada SosaNo ratings yet
- Lichen Amyloidosis With Combined Topical Therapy: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesLichen Amyloidosis With Combined Topical Therapy: A Case ReportmutmainnahNo ratings yet
- BDJ Paper On DentalDocument5 pagesBDJ Paper On DentalZihao WuNo ratings yet
- Tiwari 2013Document8 pagesTiwari 2013Stella SunurNo ratings yet
- Httpsinnovareacademics Injournalsindex Phpijppsarticledownload2221213586Document3 pagesHttpsinnovareacademics Injournalsindex Phpijppsarticledownload2221213586Gusti Ayu Sattwika PramitaNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.04.015Document11 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.04.015Tuis PreviyantiNo ratings yet
- Ashy Dermatosis and Lichen PlanusDocument27 pagesAshy Dermatosis and Lichen PlanusAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Pathogenesis of ErythrodermaDocument20 pagesGroup 5 - Pathogenesis of Erythrodermaachmad billy hakiemNo ratings yet
- Tinea Pseudoimbricata A StrikingDocument2 pagesTinea Pseudoimbricata A Strikingibnu annafiNo ratings yet
- Stevens Johnson SyndromeDocument13 pagesStevens Johnson SyndromeMimi SyakilaNo ratings yet
- 3.TPD 45 149Document4 pages3.TPD 45 149YuyumNo ratings yet
- Therapy Selection For Tinea Corporis and Cruris With CommorbidityDocument9 pagesTherapy Selection For Tinea Corporis and Cruris With CommorbidityShimie Shimie KokobopNo ratings yet
- TPD 47 127 enDocument2 pagesTPD 47 127 enNur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Fde CedDocument2 pagesFde CedmdpavlovicNo ratings yet
- Bilgili2011 Nonsteroidal Anti-InflammatoryDocument5 pagesBilgili2011 Nonsteroidal Anti-InflammatoryShelaMaretaNo ratings yet
- Psoriais PDF NemDocument14 pagesPsoriais PDF NemFabiola VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Isotretinoin Treatment For Folliculitis Decalvans: A Retrospective Case-Series StudyDocument4 pagesIsotretinoin Treatment For Folliculitis Decalvans: A Retrospective Case-Series Studyabdulmunim hanyNo ratings yet
- HAPP-PICO Tissue Pathology Journal ResearchDocument4 pagesHAPP-PICO Tissue Pathology Journal ResearchArlynn MartinezNo ratings yet
- Document - 119 - 322how To Download Dermatology For Advanced Practice Clinicians 1St Edition Ebook PDF Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument36 pagesDocument - 119 - 322how To Download Dermatology For Advanced Practice Clinicians 1St Edition Ebook PDF Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapterdoug.wiggins940100% (25)
- Neagu 2021Document40 pagesNeagu 2021meenakshi.r.agrawalNo ratings yet
- Short CommunicationDocument2 pagesShort CommunicationmarissapuenteshernandezNo ratings yet
- Joost Schalkwijk., 2010 PDFDocument11 pagesJoost Schalkwijk., 2010 PDFInna LiashenkoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KulitDocument8 pagesJurnal Kulitzak bearNo ratings yet
- M: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - BrazilDocument2 pagesM: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - Brazilpruebaprueba321765No ratings yet
- Jurnal PruritusDocument4 pagesJurnal Pruritusdvunsrat agt2021No ratings yet
- 2024-Article Text-6560-1-10-20230128Document4 pages2024-Article Text-6560-1-10-20230128Adniana NareswariNo ratings yet
- Tinea Incognito Hidden Under Apparently Treatment-Resistant Pemphigus FoliaceusDocument2 pagesTinea Incognito Hidden Under Apparently Treatment-Resistant Pemphigus FoliaceusdayangNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Interdigital Erythrasma in Southern Region of TurkeyDocument5 pagesThe Prevalence of Interdigital Erythrasma in Southern Region of TurkeyJennifer JaneNo ratings yet
- Management of Pearly Penile Papules: A Review of The LiteratureDocument7 pagesManagement of Pearly Penile Papules: A Review of The LiteratureMeta SakinaNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Steroid Induced Acneiform EruptionsDocument3 pagesA Case Report On Steroid Induced Acneiform EruptionsVidini Kusuma AjiNo ratings yet
- Volltext PDFDocument5 pagesVolltext PDFJhonnie Gaona CardonaNo ratings yet
- Slide Eritroderma 2Document7 pagesSlide Eritroderma 2Anonymous QqGJk2jK5No ratings yet
- Congenital Scalp Tumor With Ulceration: Jeremy Udkoff MA, MAS - Ralph E. Holmes MD - Magdalene A. Dohil MDDocument2 pagesCongenital Scalp Tumor With Ulceration: Jeremy Udkoff MA, MAS - Ralph E. Holmes MD - Magdalene A. Dohil MDAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Dermatologica Sinica: Demet Kartal, Salih L. Ç Inar, Sibel Ak In, Ayten Ferahbas, Murat BorluDocument5 pagesDermatologica Sinica: Demet Kartal, Salih L. Ç Inar, Sibel Ak In, Ayten Ferahbas, Murat BorlulalaNo ratings yet
- Int J Dermatology - 2022 - Iwasawa - Diagnostic Difficulties in Secondary Syphilis A Case ReportDocument3 pagesInt J Dermatology - 2022 - Iwasawa - Diagnostic Difficulties in Secondary Syphilis A Case ReportArmando NogueraNo ratings yet
- Tape-Strip Proteomic Profiling of Atopic Dermatitis On Dupilumab Identifies Minimally Invasive BiomarkersDocument9 pagesTape-Strip Proteomic Profiling of Atopic Dermatitis On Dupilumab Identifies Minimally Invasive BiomarkersAlexis PaivaNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used DrugsDocument7 pagesCommonly Used DrugsJarvin SantosNo ratings yet
- Micro Q Final 2Document45 pagesMicro Q Final 2Rashed Aiman Sameer Alsayyed AlalqamawiNo ratings yet
- PDF Muestra - Kafka and The Travelling Doll IngDocument12 pagesPDF Muestra - Kafka and The Travelling Doll IngPritam Singha0% (1)
- Evaluation of Pallor in ChildrenDocument23 pagesEvaluation of Pallor in ChildrenFlorie Lei BulosNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption Syndrome: By:-Ms. Sarungbam Sarju Devi Asst. Professor RinpsDocument27 pagesMalabsorption Syndrome: By:-Ms. Sarungbam Sarju Devi Asst. Professor RinpsShitaljit IromNo ratings yet
- KanMend NMCDDocument32 pagesKanMend NMCDSincerely ReynNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Course 1Document57 pagesParasitology: Course 1anaNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument11 pagesTESTANKITA YADAVNo ratings yet
- "And The Band Played On" AnalysisDocument5 pages"And The Band Played On" Analysisalarea monaéNo ratings yet
- Iris Guideline 6Document3 pagesIris Guideline 6saurav.das2030No ratings yet
- 4 BollousDocument172 pages4 Bollousmedicina garridoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Assessment of The Musculoskeletal System: A Guide For Medical Students and Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument40 pagesClinical Assessment of The Musculoskeletal System: A Guide For Medical Students and Healthcare ProfessionalsChristine Joy Molina100% (1)
- IGNOU Block 4 Unit 1 Epidemiology of Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument12 pagesIGNOU Block 4 Unit 1 Epidemiology of Non-Communicable Diseaseserice.researchNo ratings yet
- Cath Lab Case Study Aortic StenosisDocument22 pagesCath Lab Case Study Aortic StenosisRajeev Kumar100% (1)
- Appendicitis Introduction AppendicitisDocument4 pagesAppendicitis Introduction AppendicitisShiba AmpaNo ratings yet
- Buteyko Breathing Technique: A Golden Cure For AsthmaDocument9 pagesButeyko Breathing Technique: A Golden Cure For AsthmaGerry KrikhoffNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Managing Chronic Abdominal Bloating and Distension - Mayo ClinicDocument1 pageUnderstanding and Managing Chronic Abdominal Bloating and Distension - Mayo ClinicmarieclownNo ratings yet
- CL2018 65Document5 pagesCL2018 65Ron loyolaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6Document4 pagesBahasa Inggris Kelas 6Nia Asih KurniasariNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Document5 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument21 pagesRheumatic Heart Diseaseram krishnaNo ratings yet
- Fisioterapi Ppok EngDocument7 pagesFisioterapi Ppok EngEi lessonNo ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Document41 pagesDiffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Mary Joy BernasolNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMaria MarquezNo ratings yet