Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secondary Payloads
Uploaded by
Dr Pankaj DhussaCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Secondary Payloads
Uploaded by
Dr Pankaj DhussaCopyright:
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Space Launch System
NASAfacts
Secondary Payloads
SLS Advances Science and Technology: reserved for the avionics unit that controls
CubeSat Payloads on NASA’s Artemis I the CubeSats’ deployment in deep space.
Mission
Several of the CubeSats chosen to fly
NASA’s new rocket, the Space Launch System on Artemis I are lunar-focused and were
(SLS), will launch America into a new era of proposed by programs across the agency.
exploration to destinations beyond Earth’s These missions may help the agency
orbit. In addition to demonstrating NASA’s new address Strategic Knowledge Gaps (SKGs)
heavy-lift capability and sending the Orion to inform research strategies and prioritize
spacecraft into deep space, SLS also has the technology development for human and
capability to carry CubeSats to deep space. robotic exploration.
CubeSats are small, low-cost experiments not
much larger than a shoebox. Other missions will be testing innovative
propulsion technologies, studying space
These secondary payloads may be science weather, analyzing the effects of radiation
and technology investigations or technology on organisms, and providing high-resolution
demonstrations that help pave the way for imagery of the Earth and Moon. Three
future, deep space human exploration. of these CubeSats are competing in the
Cube Quest Challenge, vying for prizes
On this first flight, known as Artemis I, SLS for accomplishing such goals as farthest
will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a communication to Earth from space.
stable orbit beyond the Moon to demonstrate
the integrated system performance of Orion
and the SLS rocket.
From the lunar vicinity, Orion will return to Earth
to demonstrate re-entry and landing prior to a
crewed flight. This mission also provides the
rare opportunity for CubeSats to reach deep
space destinations; most launch opportunities
for CubeSats are limited to low-Earth orbit.
The Artemis I flight has 10 CubeSats
manifested that are 6U in size (one U, or unit,
is 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm).
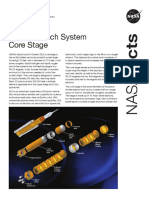
The Orion stage adapter on the Block 1 SLS
vehicle connects Orion to the upper stage
and can potentially accommodate up to 17
CubeSats in a combination of 6U or 12U sizes,
although only 10 CubeSats are riding along The completed Orion stage adapter for the SLS rocket
on the Artemis I flight. An additional slot is for the Artemis I flight, with the mounting brackets for
CubeSats in their dispensers.
Secondary payloads on SLS not only provide CubeSat
Artemis I Secondary Payload Facts
developers with an exceptional opportunity to deploy
CubeSats in deep space, they also enable NASA to
Number of manifested CubeSats: 10
engage with international partners, industry, and students.
International space agency partners are providing three
Deployment opportunities are along the upper stage
payloads, and universities are involved with five payloads.
disposal trajectory.
The CubeSats will be deployed following Orion separation
Weight Limit: 30 pounds (14 kilograms)
from the upper stage once Orion is a safe distance away.
Each payload will be ejected with a spring mechanism
Size: 6U (4.4” x 9.4” x 14.4”)
from dispensers installed on the Orion stage adapter. The
Equivalent to six 10 cm square units)
SLS program provides a secondary payload deployment
system for the CubeSats which includes the deployment
The Secondary Payload Deployment System includes
system, an avionics unit, mounting brackets for the
an avionics unit, mounting brackets, cable harnesses,
dispensers, cable harnesses, and a vibration mitigation
and a vibration mitigation system.
system.
The initial SLS rocket variant, Block 1, can launch at
least 59,525 lbs. (27 metric tons) to the Moon and will be When mission parameters allow, the SLS program
powered by twin solid rocket boosters and four RS-25 hopes to offer CubeSats, in various sizes, rideshare
engines. The next planned evolution of the SLS, Block 1B, opportunities to deep space.
will use a more powerful exploration upper stage to enable
more ambitious missions. This version will be capable
of launching more than 92,594 lbs. (42 metric tons) to
cislunar space.
Orion Stage Adapter
A later evolution, Block 2, will onramp evolved solid
Secondary Payload
rocket boosters to provide a 101,400 lb. (46 metric ton) locations
lift capacity to the Moon. These future configurations of
the vehicle will allow for larger and more varied payload
capabilities. Each SLS configuration will incorporate the
same core stage design and use four RS-25 engines.
Orion Service Module
Interim Cryogenic
Propulsion Stage
Artist concept of a CubeSat Completed Orion stage adapter
deployed in deep space. with the secondary payload Launch Vehicle
deployment system installed. Stage Adapter
For more information on SLS, visit:
Core Stage
http://www.nasa.gov/sls/
http://www.twitter.com/NASA_SLS
http://www.facebook.com/NASASLS
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
George C. Marshall Space Flight Center
Huntsville, AL 35812
www.nasa.gov/marshall
www.nasa.gov
FS-2020-05-24-MSFC
NASA Facts
You might also like
- Starship Users Guide v1Document6 pagesStarship Users Guide v1jn323iNo ratings yet
- Zubrin 1991 PDFDocument27 pagesZubrin 1991 PDFsergiobaldiNo ratings yet
- Life On MarsDocument14 pagesLife On Marscogent comityNo ratings yet
- Sls Fact SheetDocument4 pagesSls Fact SheetSaleem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Sls NasaDocument4 pagesSls NasaVíctor RivasNo ratings yet
- IAC 19, A5,4 D2.8,1, x51280Document12 pagesIAC 19, A5,4 D2.8,1, x51280pacoNo ratings yet
- A Dual Thrust Axis Lander For Mars ExplorationDocument7 pagesA Dual Thrust Axis Lander For Mars ExplorationJuan Jose Mejia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Artemis PlanDocument14 pagesThe Artemis Plan8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- NASA 136541main CEV Fs HiDocument2 pagesNASA 136541main CEV Fs HiNASAdocumentsNo ratings yet
- NASA Expands Options For Spacewalking, Moonwalking Suits, Services - NASADocument4 pagesNASA Expands Options For Spacewalking, Moonwalking Suits, Services - NASAAshkan PourkhalajiNo ratings yet
- NASA 136542main CEV FS LowDocument2 pagesNASA 136542main CEV FS LowNASAdocumentsNo ratings yet
- Forgoing Time and State - The Challenge For Cubesats On Artemis-1Document12 pagesForgoing Time and State - The Challenge For Cubesats On Artemis-1Dayanna Vargas MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10.2Document7 pagesChapter 10.2giaNo ratings yet
- MarCO - CubeSats To Mars in 2016Document7 pagesMarCO - CubeSats To Mars in 2016Ahmed FalihNo ratings yet
- Aerocubes: Delivering Large Capabilities in Small PackagesDocument2 pagesAerocubes: Delivering Large Capabilities in Small PackagesSergio Andrés UrreaNo ratings yet
- Vehiculo Espacial SEV Concept FactSheetDocument4 pagesVehiculo Espacial SEV Concept FactSheetDilan Loaiza TapieroNo ratings yet
- Space Exploration VehicleDocument4 pagesSpace Exploration VehicleAviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Launch Services Program: The LSP FleetDocument2 pagesLaunch Services Program: The LSP FleetDiengNo ratings yet
- Interplanetary CubeSatDocument30 pagesInterplanetary CubeSatDiego MV100% (1)
- Astrosat: Forthcoming SatellitesDocument5 pagesAstrosat: Forthcoming SatellitesLokesh ParganihaNo ratings yet
- 636362main - FS-2012-04-014B-JSC COTS1-pagerDocument2 pages636362main - FS-2012-04-014B-JSC COTS1-pagerJAHNo ratings yet
- NASA's SLS Core Stage: Powerhouse of Deep Space ExplorationDocument2 pagesNASA's SLS Core Stage: Powerhouse of Deep Space ExplorationHasannudin BisriNo ratings yet
- Exploration Lessons From The International Space StationDocument4 pagesExploration Lessons From The International Space StationWalt RamsNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Martian and Lunar ScienceDocument8 pagesAccelerating Martian and Lunar ScienceJunior MirandaNo ratings yet
- Space Shuttle Mission STS-6Document53 pagesSpace Shuttle Mission STS-6Aviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- The Space Almanac Q4 2020-Q1 2021Document51 pagesThe Space Almanac Q4 2020-Q1 2021Dzhozef (Zef) KonradNo ratings yet
- NASA 167413main KodiakstarDocument2 pagesNASA 167413main KodiakstarNASAdocumentsNo ratings yet
- Sceince and Tech 3Document21 pagesSceince and Tech 3charudatta kelzarkarNo ratings yet
- Starship Users Guide v2Document9 pagesStarship Users Guide v2Lucas BerthelonNo ratings yet
- Solar Electric Propulsion For Advanced Planetary MissionsDocument7 pagesSolar Electric Propulsion For Advanced Planetary MissionsShafieul mohammadNo ratings yet
- CubeSat Mission - Washinton UniversityDocument200 pagesCubeSat Mission - Washinton Universityeunsu_kimNo ratings yet
- A University Deep CubeDocument9 pagesA University Deep CubeEBEN EZERNo ratings yet
- SatellitesDocument18 pagesSatellitesSangita Gomare reddyNo ratings yet
- Starship: - Rohan BairagiDocument11 pagesStarship: - Rohan BairagiRohan BairagiNo ratings yet
- SOLAR PROBE PLUS MISSION DESIGN OVERVIEWDocument20 pagesSOLAR PROBE PLUS MISSION DESIGN OVERVIEWPrashantNo ratings yet
- Report Artemis ProgramDocument20 pagesReport Artemis ProgramBatukhan ANo ratings yet
- SRMSAT-2 Mission to Study Lunar ScienceDocument282 pagesSRMSAT-2 Mission to Study Lunar SciencePranav CVNo ratings yet
- NASA Facts Skylab Manned Orbital Scientific Space StationDocument4 pagesNASA Facts Skylab Manned Orbital Scientific Space StationBob Andrepont100% (1)
- NASA Facts Mars Science Laboratory 2010Document2 pagesNASA Facts Mars Science Laboratory 2010Bob Andrepont100% (1)
- Research Article: Vibration and Modal Analysis of Low Earth Orbit SatelliteDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Vibration and Modal Analysis of Low Earth Orbit SatelliteAmritansh RanjanNo ratings yet
- The Future of The Mars RoverDocument4 pagesThe Future of The Mars RoverJosh PillitiereNo ratings yet
- Mars 1Document20 pagesMars 1rathanNo ratings yet
- Space Shuttle Mission STS-41BDocument32 pagesSpace Shuttle Mission STS-41BAviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Advanced Solar-And Laser-Pushed Lightsail Concepts: Final ReportDocument47 pagesAdvanced Solar-And Laser-Pushed Lightsail Concepts: Final ReportNacer ItourarNo ratings yet
- NASA 133820main ESAS FactsDocument4 pagesNASA 133820main ESAS FactsNASAdocuments100% (1)
- LEIPOLDDocument6 pagesLEIPOLDkucnicamNo ratings yet
- c2 PDFDocument48 pagesc2 PDFSantiago UrgilesNo ratings yet
- Group Projet Final Report Satellite Capture and De-Orbit Mission Lead & Co-Supervisor James Campbell & Rui CardosoDocument11 pagesGroup Projet Final Report Satellite Capture and De-Orbit Mission Lead & Co-Supervisor James Campbell & Rui CardosoTaranjit SinghNo ratings yet
- NASA CubeSat Launch Initiative CandidatesDocument5 pagesNASA CubeSat Launch Initiative CandidatesRonny TelesNo ratings yet
- Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) OverviewDocument2 pagesLow-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) OverviewFernando sarriaNo ratings yet
- Artemis: The First Woman Mission To MoonDocument1 pageArtemis: The First Woman Mission To MoonSyed Wasim ul HudaNo ratings yet
- SETR 09: SpaceDocument13 pagesSETR 09: SpaceHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- 08-0255 MSL - Entry DEscent LandingoverviewDocument19 pages08-0255 MSL - Entry DEscent LandingoverviewMichel RiesNo ratings yet
- S X Isro' R 143 S L: Pace Breaks S Ecord Launches Satellites in Ingle AunchDocument21 pagesS X Isro' R 143 S L: Pace Breaks S Ecord Launches Satellites in Ingle AunchABHINAV DEWALIYANo ratings yet
- Plans For Sending Humans To MarsDocument2 pagesPlans For Sending Humans To MarsAidenJacksNo ratings yet
- Mars 2020: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument7 pagesMars 2020: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchnacenkNo ratings yet
- 77 2021 0064 - YoungDocument21 pages77 2021 0064 - Youngebooks list1No ratings yet
- Manned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969From EverandManned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969No ratings yet
- Williams SDocument3 pagesWilliams SShivam GawandNo ratings yet
- Chandrayaan 3Document12 pagesChandrayaan 3CarryNo ratings yet
- Back To Earth Non-Chronological Report Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument11 pagesBack To Earth Non-Chronological Report Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityFatma HeshamNo ratings yet
- RocketsDocument4 pagesRocketsafonsoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Space ExplorationDocument14 pagesUnit 5 Space ExplorationNOR HASNIDA BINTI HASHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- National Aeronautics and Space AdministrationDocument48 pagesNational Aeronautics and Space Administrationwatcher watchesNo ratings yet
- Spacex Falcon 9 v1.2 Data SheetDocument9 pagesSpacex Falcon 9 v1.2 Data Sheetasghar aghaNo ratings yet
- How The Soyuz Rocket Compares With The Rest - Science - In-Depth Reporting On Science and Technology - DW - 19.11.2018Document9 pagesHow The Soyuz Rocket Compares With The Rest - Science - In-Depth Reporting On Science and Technology - DW - 19.11.2018antoNo ratings yet
- Reusable RocketsDocument8 pagesReusable RocketskingsleyshilincuiNo ratings yet
- Presentation For Reading 3 - Unit 9Document14 pagesPresentation For Reading 3 - Unit 9Quinn WarcyNo ratings yet
- SpaceX's Use of Agile Methods. The Space Tech Industry Has Been Stuck - by Cliff Berg - MediumDocument8 pagesSpaceX's Use of Agile Methods. The Space Tech Industry Has Been Stuck - by Cliff Berg - MediumDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- T TP 77 Neil Armstrong Powerpoint Ver 3Document11 pagesT TP 77 Neil Armstrong Powerpoint Ver 3Yaseni ParamNo ratings yet
- Space Shuttle Columbia DisasterDocument26 pagesSpace Shuttle Columbia DisasterViet EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Intermediate b1 Tests Module 6Document5 pagesPioneer Intermediate b1 Tests Module 6Aurelia Lopez FloresNo ratings yet
- The Space Shuttle DisasterDocument1 pageThe Space Shuttle DisasterznvNo ratings yet
- AsiaSat 9 Insert - Sep 2020Document4 pagesAsiaSat 9 Insert - Sep 2020phyomauk htunNo ratings yet
- NASADocument55 pagesNASAfa faxiNo ratings yet
- NASA Artemis 1 ArticleDocument2 pagesNASA Artemis 1 Articletanzhihao0724No ratings yet
- Satsearch Sfgnyn Exoterra Halo Micro Hall Effect ThrusterDocument2 pagesSatsearch Sfgnyn Exoterra Halo Micro Hall Effect Thrustersghscribd2012No ratings yet
- Acta Astronautica: Eva Yi-Wei ChangDocument12 pagesActa Astronautica: Eva Yi-Wei ChangkemalmaqdanNo ratings yet
- Compendium of SatellitesDocument233 pagesCompendium of SatellitesRaúl InfanteNo ratings yet
- Overview of The CALLISTO ProjectDocument4 pagesOverview of The CALLISTO Projectapi-651598191No ratings yet
- Apollo 11: First Moon LandingDocument6 pagesApollo 11: First Moon LandingirfanmNo ratings yet
- Space Launch Report Falcon 9 Data SheetDocument21 pagesSpace Launch Report Falcon 9 Data Sheetasghar aghaNo ratings yet
- SpaceX - StarshipDocument1 pageSpaceX - StarshipAntonio Salas LozanoNo ratings yet
- Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro)Document9 pagesIndian Space Research Organisation (Isro)meghanpadalkarNo ratings yet
- AXM Artemis1 Orion-Stage Kit96Document11 pagesAXM Artemis1 Orion-Stage Kit96Ralph NoblejasNo ratings yet
- SoyuzRescueslidesSCLSaB Edit 2Document3 pagesSoyuzRescueslidesSCLSaB Edit 2Cornelius IntVeldNo ratings yet
- Pilgrim Bserver: Space Station Assembly InstructionsDocument8 pagesPilgrim Bserver: Space Station Assembly InstructionsJames Tiberius HenkelNo ratings yet
- Chandrayaan 3 WikipediaDocument1 pageChandrayaan 3 WikipediaOm prakash singhNo ratings yet