0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views1 pageToxic Sensor Cross Sensitivities Chart
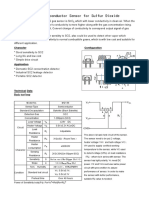
This document contains a table showing the cross-sensitivities of different toxic gas sensors when exposed to various target gases. The table lists the percentage response that each sensor provides when exposed to a known concentration of each gas. For example, the carbon monoxide sensor responds 100% to carbon monoxide but also 20% to hydrogen. The cross-interference numbers may vary over time and between sensors. The data is provided as a guide and is subject to change.
Uploaded by
S RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views1 pageToxic Sensor Cross Sensitivities Chart
This document contains a table showing the cross-sensitivities of different toxic gas sensors when exposed to various target gases. The table lists the percentage response that each sensor provides when exposed to a known concentration of each gas. For example, the carbon monoxide sensor responds 100% to carbon monoxide but also 20% to hydrogen. The cross-interference numbers may vary over time and between sensors. The data is provided as a guide and is subject to change.
Uploaded by
S RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd