Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Symbolism - 10
Uploaded by
Izash Ahamed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesRhizobium bacteria form a mutualistic relationship with leguminous plants where they reside in root nodules and convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form the plant can use for growth, and in return receive nutrients and shelter from the plant. Cuscuta is a parasitic plant that grows on other plants through haustoria and withdraws water and nutrients from the host, weakening it. Lichens represent a mutualism between fungi and algae where the algae produces food for the fungi through photosynthesis and the fungi provides shelter and absorbs minerals and water for the algae.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRhizobium bacteria form a mutualistic relationship with leguminous plants where they reside in root nodules and convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form the plant can use for growth, and in return receive nutrients and shelter from the plant. Cuscuta is a parasitic plant that grows on other plants through haustoria and withdraws water and nutrients from the host, weakening it. Lichens represent a mutualism between fungi and algae where the algae produces food for the fungi through photosynthesis and the fungi provides shelter and absorbs minerals and water for the algae.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesSymbolism - 10
Uploaded by
Izash AhamedRhizobium bacteria form a mutualistic relationship with leguminous plants where they reside in root nodules and convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form the plant can use for growth, and in return receive nutrients and shelter from the plant. Cuscuta is a parasitic plant that grows on other plants through haustoria and withdraws water and nutrients from the host, weakening it. Lichens represent a mutualism between fungi and algae where the algae produces food for the fungi through photosynthesis and the fungi provides shelter and absorbs minerals and water for the algae.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
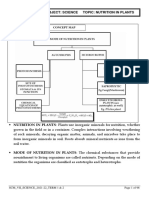
10.
Symbolism association in root nodules of of leguminous plants, Cuscuta on host,
Lichens.
In nature animals, plants and microbes do not and cannot live in islation but interact in various
ways. When two different species interact with ecah other and are in close association. With
each other in suc away that at least one species is benefited while for other species the
relationship may be positive, negative or neutal such association is called symbiotic relationsip.
1. Rhizobium in root nodules of leguminous plant (Mutualism)
i. Rhizobium bacteria are present in root nodules of leguminous plant and form a
symbiotic relationshp, mutualism, where both are benefited from each other.
ii. Rhizobium can convert atmosperic nitrogen to ammonia tat can be used by pea plant for
growth and development.
iii. Bacteteria receive nutrients and suitable place to grow from plant.
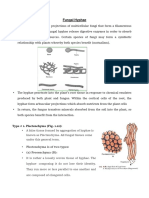
2. Cuscuta on host (Parasitism)
i. Cuscuta commonly called dodder or amerbel and live as stem ectoparasite on other
plants.
ii. Cuscuta has no fully expanded form of leaves (scale like leaves are present) and has no
chloropyll and cannot make its own food by photosynthesis.
iii. Instead, it grows on other plants, using their nutrients for its growth and weakening the
host plant
iv. Haustoria forms direct connection to the vascular bundles of the host and withdraw
water, carbohydrates and other solutes.
3. Lichens (Mutualism)
i. Lichens are composite organisms representing a symbiotic association (Mutualism)
between fungus and algae.
ii. The algal component is known as phycobiot and fungal component is known as
mycobiont.
iii. Algae prepare food for fungi and fungi provide shelter and absorb mineral, nutrients and
water for its partner.
iv. They grow on lands, rocks, tree trunks and walls of houses, like dry vegetation.
You might also like
- Growing Wild MushroomsDocument50 pagesGrowing Wild Mushroomsviki90% (10)
- Chapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andNantha KumaranNo ratings yet
- Soil Food WebDocument3 pagesSoil Food WebJosh BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Xii - Bio Exp - 10 & 11 by DDKDocument4 pagesXii - Bio Exp - 10 & 11 by DDKYaishnave R75% (8)
- The Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsFrom EverandThe Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Notes + Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 4Document9 pagesForm 2 Science Notes + Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 4Kelvin100% (4)
- Experiment No-15Document6 pagesExperiment No-15hdgsefseaNo ratings yet
- Revised Exp 16Document2 pagesRevised Exp 16yugakrisNo ratings yet
- Myco AssignmentDocument12 pagesMyco AssignmentBalmes, Wyvrn F.No ratings yet
- Cuscuta, Nodule, LichenDocument2 pagesCuscuta, Nodule, LichenSelva moorthyNo ratings yet
- BGFHFDocument4 pagesBGFHFManpreet SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Science SCMDocument98 pagesScience SCMKoustavi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Fungi Classification and Animal KingdomDocument11 pagesFungi Classification and Animal KingdomsdsaylenvallejoNo ratings yet
- Fungi. What Are TheyDocument4 pagesFungi. What Are TheyFabrizio MVNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Biotic Relationships: Positive Interaction ObjectivesDocument8 pagesActivity 8 Biotic Relationships: Positive Interaction ObjectivesJoshua BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument3 pagesNutrition in Plantsridhamjain860No ratings yet
- Spotting Practical Symbiotic AssociationDocument1 pageSpotting Practical Symbiotic AssociationChatan ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Chap21worksheet FungiDocument3 pagesChap21worksheet FungiJashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument20 pagesCh1 Nutrition in Plantsshyam123gNo ratings yet
- PLP4653C Basic FunGal Course NotesDocument2 pagesPLP4653C Basic FunGal Course NotesYonatan DogzNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - Kingdom FungiDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Kingdom FungiMSNo ratings yet
- Ecology of FungiDocument3 pagesEcology of FungiSafitri Rya AngrainiNo ratings yet
- Under-Ground Interplay of Opportunistic Fungi, Nematode and PlantDocument7 pagesUnder-Ground Interplay of Opportunistic Fungi, Nematode and PlantEzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 BiologyDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Biologylilithescuela14No ratings yet
- Diversity of Living Things Kingdom Fungi, and PlantaeDocument4 pagesDiversity of Living Things Kingdom Fungi, and Plantaeakabiru831No ratings yet
- Soil FungiDocument22 pagesSoil Fungidwana148100% (1)
- 3.3 The Fungus KingdomDocument5 pages3.3 The Fungus KingdomAverey MeloNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPradip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Nutrition in Plants .PMDDocument16 pages1 Nutrition in Plants .PMDvivek tripathiNo ratings yet
- FUNGI - GR 7 Lesson NotesDocument2 pagesFUNGI - GR 7 Lesson Notesclairehong08No ratings yet
- Fungi NotesDocument1 pageFungi NotesRIVALS〆toxicNo ratings yet
- Ecology of FungiDocument4 pagesEcology of FungiAugustine CrystalNo ratings yet
- 72 FungiDocument8 pages72 FungietNo ratings yet
- Fungal Hyphae: Type # 1. Plectenchyma (Fig. 1.12)Document5 pagesFungal Hyphae: Type # 1. Plectenchyma (Fig. 1.12)vineetvishal73No ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungiwebpixel servicesNo ratings yet
- BioreportDocument8 pagesBioreportAbigail CostalesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesNutrition in PlantsroopamsNo ratings yet
- Fungal SymbiosisDocument37 pagesFungal Symbiosisbhima.135591No ratings yet
- ThesisDocument25 pagesThesisapi-608954316No ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition LAS Q4 Week 2Document4 pagesAnimal Nutrition LAS Q4 Week 2Roland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Soil Microorganisms and Their Interactions - Positive and Negative Interactions.Document10 pagesLecture 1. Soil Microorganisms and Their Interactions - Positive and Negative Interactions.VIGNESH VICKY100% (2)
- General Features of AlgaeDocument6 pagesGeneral Features of AlgaeSreeja RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Nutrition in PlantsDocument14 pagesChapter - 1: Nutrition in Plantsfgh ijkNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4Document30 pagesBiology Unit 4Kayleen PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Biome VocabularyDocument2 pagesBiome VocabularyDog BotNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals NotesDocument6 pagesNutrition in Animals NotesSeema Singh SengarNo ratings yet
- 3.11.20-Plants and Their FoodDocument3 pages3.11.20-Plants and Their FoodMilliNo ratings yet
- Protist PDFDocument14 pagesProtist PDFlyn100% (1)
- Hyphae: Indian Pipe, Ghost Plant, or Corpse Plant (Monotropa Uniflora) Is A Holoparasitic Plant With An EvenDocument3 pagesHyphae: Indian Pipe, Ghost Plant, or Corpse Plant (Monotropa Uniflora) Is A Holoparasitic Plant With An EvenHalil Onur AltayNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument21 pagesNutrition in PlantsRavinder Sutari100% (1)
- Nutrition in Plants NotesDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Bio-Fertilizers: Dr. Kathirvelu SambandanDocument8 pagesBio-Fertilizers: Dr. Kathirvelu SambandanSambandhan Kathirvelu100% (1)
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument4 pagesNutrition in PlantsAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Microorganism SDocument30 pagesEukaryotic Microorganism Smarvin candorNo ratings yet
- 0969d5da 1619498709723Document6 pages0969d5da 1619498709723AGNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Tropical Plant Types: The Commonwealth and International Library: Biology DivisionFrom EverandTropical Plant Types: The Commonwealth and International Library: Biology DivisionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity ADocument7 pagesChapter 15 Biodiversity AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues ADocument6 pagesChapter 16 Environmental Issues AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Organism and Population ADocument15 pagesChapter 13 Organism and Population AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem ADocument15 pagesChapter 14 Ecosystem AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- 12 Ex. 8.1 Q.no.1-5Document8 pages12 Ex. 8.1 Q.no.1-5Izash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Applications of Biotechnology ADocument9 pagesChapter 12 Applications of Biotechnology AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 Human Health and Diseases ADocument4 pagesChapter 08 Human Health and Diseases AIzash AhamedNo ratings yet
- Oil SpillDocument9 pagesOil SpillIzash AhamedNo ratings yet