Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic#7 Managers As Leaders
Uploaded by
Tooba FarooqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic#7 Managers As Leaders
Uploaded by
Tooba FarooqCopyright:
Available Formats
Managers as
Leaders
Topic#7
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
People ask the difference between a
leader and a boss. The leader leads,
and the boss drives.
Theodore Roosevelt.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Leaders & Leadership
• Leader – someone who can influence others and who has
managerial authority.
• Leadership – the process of leading & influencing a group
to achieve goals.
• Ideally, all managers should be leaders
Although groups may have informal leaders who emerge, those are not
the leaders we’re studying.
What is an effective leader?
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Leaders & Leadership
What is an effective leader?
• Early leadership theories – traits & behavior
• Contingency theories – situational theories
• Contemporary theories - modern
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
Early 20th century.
• Leader characteristics (leader trait theories).
• Interaction of leader with his or her group members
(leadership behavior theories).
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Trait Theories
• 1920s – 1930s.
• Initial research - traits or personal
characteristics that differentiate
leaders from non-leaders –
unsuccessful.
Physical stature, appearance, social class,
emotional stability, sociability etc.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Trait Theories
• Later research – traits associated with leadership
– successful.
Seven traits – drive, the desire to lead, honesty and integrity,
self-confidence, intelligence, job-relevant knowledge, and
extraversion.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Seven Traits Associated with Leadership
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Trait Theories
• Ignored interactions of leaders and their group members as
well as situational factors.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Behavior Theories
1940s – 1960s.
➢University of Iowa Studies (Kurt Lewin)
• Autocratic style – centralized authority, dictate work methods, no
participation.
• Democratic style – Involvement, delegate authority & used feedback.
• Laissez faire style – hands-off management
Initial research showed democratic style resulted in high
performance. Later studies showed mixed results with autocratic
style.
However, democratic style always produced high employee
satisfaction – dilemma.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Behavior Theories
➢The Ohio State Studies
Two dimensions of leader behavior.
• Initiating structure – extent to which a leader defined his or her
role and the roles of group members in attaining goals – task.
• Consideration - leader’s mutual trust and respect for group
members’ ideas and feelings – people.
High-high leaders sometimes achieved high group task-
performance and satisfaction, but not always.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Behavior Theories
➢University of Michigan Studies
Two dimensions of leadership behavior.
Employee orientation - emphasizing interpersonal relationships.
Production orientation – emphasizing task accomplishment.
Leaders who were employee oriented were strongly
associated with high group-productivity and high job-
satisfaction.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Behavior Theories
➢The Managerial Grid (Blake and Mouton)
• Two dimensions – concern for people (y-axis) & concern for
production (x-axis).
• Places leadership styles in one of the five categories:
Impoverished Management (1,1), Task Management (9,1), Middle-of-
the-Road Management (5,5), Country Club Management (1,9), Team
Management (9,9).
Little evidence supported the conclusion that team
management (9,9) is the most effective style in all situations.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
The Managerial Grid
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Early Leadership Theories
➢Leadership Behavior Theories
➢Limitations
While trait and behavior theories do help us understand
leadership, an important component is missing: the
environment in which the leader exists.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
While trait and behavior theories do help us understand
leadership, an important component is missing: the
environment in which the leader exists.
If-then contingencies – situational influences.
• The Fiedler Model
• Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
• Path-Goal Model
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Fiedler Model
Fred Fiedler.
Effective group performance depends on the proper match between
leadership style and the situation.
• Define those leadership styles & different types of situations.
• Identify appropriate combinations of style & situation.
➢ Least preferred co-worker (LPC) questionnaire to identify style by
measuring whether a person is task oriented or relationship oriented –
18 pairs of contrasting adjectives like friendly-unfriendly.
Respondents were asked to think of all the co-workers they had ever had
and describe the one they least enjoyed working with.
Scale of 1 to 8 for each of 18 sets of contrasting adjectives (such as
pleasant–unpleasant, efficient–inefficient, open–guarded, supportive–
hostile)
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Fiedler Model
If the leader described the least preferred coworker in relatively
favorable terms (LPC score of 64 or above) – relationship oriented.
If the leader described the least preferred coworker in relatively
unfavorable terms (LPC score of 57 or below) – task oriented.
➢ Each leadership situation was evaluated on the basis of three
contingency dimensions – eight possible situations.
• Leader-member relations – degree of confidence and trust in the
leader (good or poor)
• Task structure – degree of structure and formalization in jobs (high or
low)
• Position power – leader’s ability to hire, fire, discipline and reward
(strong or week)
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Fiedler Model
➢ Define specific contingencies for leadership effectiveness.
Task-oriented leaders performed better in very favorable situations and
in very unfavorable situations.
Relationship-oriented leaders performed better in moderately favorable
situations.
Assumed that the leadership style remains fixed.
To improve leader effectiveness - change the leader to fit the
situation or change the situational variables to fit the
current leader.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard.
• Focuses on “followers’ readiness”
Followers can accept or reject the leader. Effectiveness of leader depends on
the followers’ response to the leader’s actions
“Readiness” is the extent to which people have the ability and willingness
to accomplish a specific task.
Task oriented vs relationship oriented – high or low – four leadership styles.
Leaders should compensate for ability and
motivational limitations in their followers.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Leadership
Theory
Four leadership styles & four stages of followers’ readiness.
Effectiveness of the leadership style depends on the follower’s
readiness.
• If followers are unable and unwilling (R1) to do a task, the
leader needs to give clear and specific directions (Telling – high
task – low relationship)
• If they are unable and willing (R2), the leader needs to display
high task orientation to compensate for followers’ lack of ability
and high relationship orientation to get them to “buy into” the
leader’s desires (Selling – high task – high relationship).
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢The Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Leadership
Theory
Leader should choose one of four leadership styles
depending on the follower’s readiness.
• If followers are able and unwilling (R3), the leader needs to use
a supportive and participative style to gain the support
(Participating – low task – high relationship)
• If they are both able and willing (R4), the leader doesn’t need to
do much (Delegating – low task – low relationship)
As the workers become more ready, the leader becomes more laissez-
faire.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢Path-Goal Model
Robert House.
Leaders provide followers with information, support, and resources to
help them achieve their goals. Leaders help clarify the “path” to the
worker’s goals.
Four leadership behaviors;
Directive leader - focuses on the work to be done. Yields greater
satisfaction when tasks are ambiguous or stressful than when they are
highly structured and well laid out.
Supportive leader – focuses on the well-being of the worker. Successful
when employees are performing structured tasks.
Participative leader – consults with employees in decision-making.
Achievement-Oriented leader – sets challenging goals & expects
followers to perform at highest level.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢Path-Goal Model
• Leadership behavior–outcome relationship is
moderated by two types of contingency
variables – environmental factors & personal
characteristics of the followers.
• Leader’s behavior won’t be effective if it’s
redundant with what the environmental
structure is providing or is incongruent with
follower characteristics.
Choose a leadership style that compensates for
shortcomings in either the employee or the work setting.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contingency Theories
➢Path-Goal Model
Predictions:
• Directive style – ambiguous & stressful tasks or in conflict & crisis.
• Supportive style – structured tasks & formal authority relationships are
more bureaucratic
• Directive style perceived as redundant when followers have higher
ability & experience.
• Participative style – followers with internal locus of control.
• Directive style – followers with external locus of control.
• Achievement-oriented style – ambiguously structured tasks.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contemporary Views
➢Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
Leaders form a special relationship with a small group of
followers: the “in-group”.
This in-group is trusted and gets more time and attention
from the leader (more “exchanges”)
All other followers are in the “out-group” and get less of the
leader’s attention and tend to have formal relationships with
the leader (fewer “exchanges”)
Leaders pick group members early in the relationship.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contemporary Views
➢Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
• Follower’s characteristics determine in-group membership.
Members have demographic, attitude, and personality
characteristics similar to those of their leader or a higher level of
competence.
Leaders and followers of the same gender tend to have closer
(higher LMX) relationships than those of different genders.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contemporary Views
➢Transformational-Transactional Leadership
➢Transactional leaders – guide or motivate followers by
exchanging rewards – social exchanges (or transactions).
Earlier view.
➢Transformational leaders – stimulates, inspires & excite
followers to achieve extraordinary outcomes (exert extra
effort).
Developed from transactional leadership.
More than charisma.
Andrea Jung of Avon.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contemporary Views
➢Charismatic-Visionary Leadership
➢Charismatic Leadership – an enthusiastic, self-confident
leader whose personality and actions influence people to
behave in certain ways.
Ideological goal – gain followers through personality rather than through
power or authority.
Martin Luther King Jr., Steve Jobs, Jeff Bezos of Amazon.com
• Characteristics - have a vision, are able to articulate the vision,
are willing to take risks to achieve the vision, are sensitive to the
environment and follower needs & exhibit out of the ordinary
behaviors.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
Contemporary Views
➢Charismatic-Visionary Leadership
➢Visionary Leadership – creates and articulates a realistic,
credible, and attractive vision of the future that improves
upon the present situation.
Michael Dell (Dell Computers) – vision of a business that
sells and delivers customized PCs directly to customers in
less than a week.
Principles of Management – Fall 2022 Sana Iqbal
You might also like
- Leadership Interpersonal Relations and CommunicationDocument60 pagesLeadership Interpersonal Relations and Communicationamila1989No ratings yet
- PPT4-Managing Communication and Being An Effective LeaderDocument75 pagesPPT4-Managing Communication and Being An Effective LeaderSofyyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 KMB101Document29 pagesUnit 5 KMB101harsh patelNo ratings yet
- Session 14Document38 pagesSession 14KANIKA GORAYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document24 pagesChapter 9Amirah RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 16Document27 pagesChapter No. 16Tayyaba FaisalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document27 pagesChapter 50054Bilal Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Early Theories of LeadershipDocument63 pagesEarly Theories of LeadershipLihthien Tang100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Leadership: OB & Analysis (MBA-532)Document33 pagesChapter 9: Leadership: OB & Analysis (MBA-532)tilahunthmNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument44 pagesLeadershipMark Angelo PagadorNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument57 pagesLeadershipFranck paulin PehnNo ratings yet
- 09 LeadershipDocument44 pages09 LeadershipMusa-ad UsmanNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument38 pagesLeadershipJosvin JoshyNo ratings yet
- Od 13Document45 pagesOd 13sneelamNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Contingency Leadership TheoriesDocument69 pagesTopic 5 Contingency Leadership Theoriesfariez79No ratings yet
- Leadership SDocument34 pagesLeadership SHarshita kumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08Document44 pagesChapter 08Mengistu NegaNo ratings yet
- Normalisation DataDocument27 pagesNormalisation DataAayush RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: How Leaders Respond To The Situation at HandDocument28 pagesChapter Five: How Leaders Respond To The Situation at Hand483-ROHIT SURAPALLINo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 LeadershipDocument29 pagesLecture 9 Leadershipannis naqilahNo ratings yet
- Basic Approaches To Leadership: TwelveDocument41 pagesBasic Approaches To Leadership: TwelveEdwinsa Auzan HashfiNo ratings yet
- THEORIES of LeadershipDocument43 pagesTHEORIES of Leadershipzephyrgreg16No ratings yet
- Basic Approaches ObDocument41 pagesBasic Approaches ObShyam PrajaptiNo ratings yet
- Ch.3.3 LeadershipDocument20 pagesCh.3.3 LeadershipChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 6 Leadership TheoriesDocument21 pagesCHAPTER - 6 Leadership TheoriesAbdi AberaNo ratings yet
- OB Lecture 12Document21 pagesOB Lecture 12Mebre WelduNo ratings yet
- Basic Approaches To Leadership TheoryDocument24 pagesBasic Approaches To Leadership TheoryKim NgânNo ratings yet
- MGT201 - CH16 - LeadershipDocument35 pagesMGT201 - CH16 - Leadershipsadmansami204No ratings yet
- 5036 - Lecture 4 - Leadership - Concepts and Theories (Double Sessions)Document48 pages5036 - Lecture 4 - Leadership - Concepts and Theories (Double Sessions)Steve100% (1)
- National University of Modern Landuage (Numl) : Presentation Topic: LeadershipDocument20 pagesNational University of Modern Landuage (Numl) : Presentation Topic: LeadershipAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: LeadershipDocument58 pagesChapter Seven: Leadershiptesfu dargeNo ratings yet
- Leadership: I Am More Afraid of An Army of 100 Sheep Led by A Lion Than An Army of 100 Lions Led by A SheepDocument21 pagesLeadership: I Am More Afraid of An Army of 100 Sheep Led by A Lion Than An Army of 100 Lions Led by A SheepSuchinda ShresthaNo ratings yet
- OB Week 11 Course SlidesDocument54 pagesOB Week 11 Course SlidesRhmano KhalilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document27 pagesChapter 12Steffi PerillaNo ratings yet
- Meaning & Theories: Presented By: Manal Manalody (Roll No.: 25) Sreena R. (Roll No.: 52)Document35 pagesMeaning & Theories: Presented By: Manal Manalody (Roll No.: 25) Sreena R. (Roll No.: 52)Pramit RastogiNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 ContingencyDocument26 pagesLecture9 Contingencymagdy elmasryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Leading: Part 1: LeadershipDocument30 pagesChapter 6: Leading: Part 1: LeadershipTuyet ThiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management - Leading - : by Dr. Gopal Iyengar Director - KIAMSDocument34 pagesPrinciples of Management - Leading - : by Dr. Gopal Iyengar Director - KIAMSAshfak ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document10 pagesChapter 17wulan.permatasariNo ratings yet
- Leadership BehaviorsDocument50 pagesLeadership BehaviorsdsravaniNo ratings yet
- Contingency Approach 2Document21 pagesContingency Approach 2api-3836390100% (1)
- Edu5816 - 1307161732.applikasi Teori Kepemimpinan DLM PendidikanDocument29 pagesEdu5816 - 1307161732.applikasi Teori Kepemimpinan DLM PendidikanSuprativ SarkarNo ratings yet
- Asli Goncu - Psy 482 - Chapter 13Document34 pagesAsli Goncu - Psy 482 - Chapter 13Swati ChamariaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour - Leadership TheoriesDocument16 pagesOrganizational Behaviour - Leadership TheoriesShivangi AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: LeadershipDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: LeadershipMoizAhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 LeadershipDocument70 pagesChapter 12 LeadershipBushra Nauman100% (3)
- LeadershipDocument43 pagesLeadershipChika KusmandarNo ratings yet
- LeadershipLeadership Theories & Styles Leadership Theories & StylesDocument21 pagesLeadershipLeadership Theories & Styles Leadership Theories & Stylesajityadav_0100% (5)
- Leadership Theories & StylesDocument21 pagesLeadership Theories & Stylesajityadav_0100% (4)
- Organizational LeadershipDocument18 pagesOrganizational LeadershipProf. Lakshman MadurasingheNo ratings yet
- Born or Made?: Dilemmas of Destiny and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesBorn or Made?: Dilemmas of Destiny and DevelopmentSamik SinghNo ratings yet
- 5036 - Lecture 4 - Leadership - Concepts and Theories (Double Sessions)Document48 pages5036 - Lecture 4 - Leadership - Concepts and Theories (Double Sessions)Thái Nguyễn PhúNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Butial, Ferlyn T. Sarmiento, Sherry AnnDocument32 pagesLeadership: Butial, Ferlyn T. Sarmiento, Sherry AnnJamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Traditional and Contingency Leadership ApproachesDocument26 pagesSession 3 Traditional and Contingency Leadership ApproachesCsec helper1No ratings yet
- Leadership in A NutshellDocument23 pagesLeadership in A NutshellSabyasachi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - LeadingDocument31 pagesChapter 6 - LeadingNaaim AzmiNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 LeadershipDocument21 pagesTopic 12 LeadershipSHI QI LEENo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document28 pagesChapter 5Ruthwik KolanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Being An Effective LeaderDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Being An Effective LeaderJeff PanNo ratings yet
- Capitalism and Civilization (Spring 2022)Document13 pagesCapitalism and Civilization (Spring 2022)Tooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- REFERENCESDocument1 pageREFERENCESTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Supply Classicals and KeynesianDocument10 pagesAggregate Supply Classicals and KeynesianTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Topic#1 Management & Organizations IntroductionDocument46 pagesTopic#1 Management & Organizations IntroductionTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Different File Types and iGil78XDocument5 pagesDifferent File Types and iGil78XTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Topic#5 Foundations of PlanningDocument27 pagesTopic#5 Foundations of PlanningTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chap 005Document40 pagesChap 005Tooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Topic#4 Managing Change - Part 1Document9 pagesTopic#4 Managing Change - Part 1Tooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Classical Macroeconomics Equilibrium Output and EmploymentDocument10 pagesClassical Macroeconomics Equilibrium Output and EmploymentTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Topic#3 Managers As Decision MakersDocument42 pagesTopic#3 Managers As Decision MakersTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Conventions of Academic Writing Sentence StructureDocument47 pagesAcademic Writing Conventions of Academic Writing Sentence StructureTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Creating A Thesis Statement1Document12 pagesCreating A Thesis Statement1Tooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Academic Paragraph StructureDocument16 pagesAcademic Paragraph StructureTooba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument12 pagesProject ReportMuhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- 01 PlantPAx 4.1 Intro To Process System For Oper and Engr LabDocument102 pages01 PlantPAx 4.1 Intro To Process System For Oper and Engr Labpisoy30392No ratings yet
- Third Generation D.O. Probes: Oxyguard Quick Guide Do ProbesDocument1 pageThird Generation D.O. Probes: Oxyguard Quick Guide Do ProbesGregorio JofréNo ratings yet
- Development of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFDocument92 pagesDevelopment of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFAjit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis Tools NIOSH Lifting EquationDocument14 pagesRisk Analysis Tools NIOSH Lifting EquationMarian RaduNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument13 pagesChapter IiEmerson CruzNo ratings yet
- Amperometric Titrations: Principle, Instrumentation and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAmperometric Titrations: Principle, Instrumentation and ApplicationsNandhanNo ratings yet
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (5)
- ProjectProposal TresMariasDocument3 pagesProjectProposal TresMariasjohnvincent.cabugnasonNo ratings yet
- Mean and Mps Pir DataDocument1 pageMean and Mps Pir DataKalixto BumiereNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7 Mineral Oil EmulsionDocument3 pagesExercise 7 Mineral Oil EmulsionFreya AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Director For GADDocument4 pagesDirector For GADSultan Kudarat State UniversityNo ratings yet
- Chilling & Freezing: Dr. Tanya Luva SwerDocument35 pagesChilling & Freezing: Dr. Tanya Luva SwerPratyusha DNo ratings yet
- Instrumenservis-Manual-Tn500-Turbidimetro PortatilDocument20 pagesInstrumenservis-Manual-Tn500-Turbidimetro PortatilFabianAndresCuervoCuervoNo ratings yet
- Pas 8811 2017Document42 pagesPas 8811 2017Mohammed HafizNo ratings yet
- Yan Li 2016Document10 pagesYan Li 2016Hendy Dwi WarmikoNo ratings yet
- Anquamine 728: Curing AgentDocument4 pagesAnquamine 728: Curing AgentGreg PanganNo ratings yet
- R Gupta - Joint CSIR-UGC NET JRF Physical Sciences (2021, Ramesh Publishing House) - Libgen - LiDocument378 pagesR Gupta - Joint CSIR-UGC NET JRF Physical Sciences (2021, Ramesh Publishing House) - Libgen - LiVasudevan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Design of Compliant Surgical Forceps With Adaptive Grasping FunctionsDocument9 pagesAutomatic Design of Compliant Surgical Forceps With Adaptive Grasping FunctionsFarjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Some Books For Stat 602XDocument1 pageSome Books For Stat 602XAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Choice TheoryDocument2 pagesChoice Theoryginabonieve100% (1)
- Course Information Booklet: FIRST SEMESTER (A.Y 2020-2021) Ged0113: The Filipino in The Contemporary WorldDocument48 pagesCourse Information Booklet: FIRST SEMESTER (A.Y 2020-2021) Ged0113: The Filipino in The Contemporary WorldcasperNo ratings yet
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- GeneratorsDocument2 pagesGeneratorsNoel GalangNo ratings yet
- SSCU3623 Lecture Note Chapter 1Document15 pagesSSCU3623 Lecture Note Chapter 1Charles A. BanguraNo ratings yet
- 105 GulletDocument8 pages105 GulletkarthiNo ratings yet
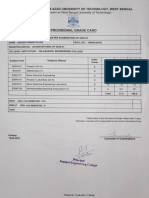
- Grade Card 1st SemDocument2 pagesGrade Card 1st SemAshish KRNo ratings yet
- Mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Sentence That Best Combines Each Pair of Sentences in The Following QuestionsDocument14 pagesMark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Sentence That Best Combines Each Pair of Sentences in The Following QuestionsPhạm Trần Gia HuyNo ratings yet
- Hight Speep Tool SteelDocument11 pagesHight Speep Tool SteelcadcamtaiNo ratings yet
- Crack The Millionaire CodeDocument32 pagesCrack The Millionaire Coderusst2100% (1)