Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What is a capacitor
Uploaded by
Juan CruzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a capacitor
Uploaded by
Juan CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a capacitor?
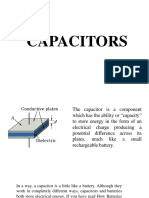
A capacitor is a device used to store electric charge. Capacitors have applications ranging from
filtering static out of radio reception to energy storage in heart defibrillators. Typically,
commercial capacitors have two conducting parts close to one another, but not touching, such
as those in Figure 1. (Most of the time an insulator is used between the two plates to provide
separation—see the discussion on dielectrics below.) When battery terminals are connected to
an initially uncharged capacitor, equal amounts of positive and negative charge, +Q and –Q, are
separated into its two plates. The capacitor remains neutral overall, but we refer to it as storing
a charge Q in this circumstance.
What is a dielectric?
How does a dielectric increase capacitance?
Microscopically, how does a dielectric increase capacitance? Polarization of the insulator is
responsible. The more easily it is polarized, the greater its dielectric constant κ. Water, for
example, is a polar molecule because one end of the molecule has a slight positive charge and
the other end has a slight negative charge. The polarity of water causes it to have a relatively
large dielectric constant of 80. The effect of polarization can be best explained in terms of the
characteristics of the Coulomb force. Figure 5 shows the separation of charge schematically in
the molecules of a dielectric material placed between the charged plates of a capacitor. The
Coulomb force between the closest ends of the molecules and the charge on the plates is
attractive and very strong, since they are very close together. This attracts more charge onto the
plates than if the space were empty and the opposite charges were a distance d away.
Figure 5. (a) The molecules in the insulating material between the plates of a capacitor are
polarized by the charged plates. This produces a layer of opposite charge on the surface of the
dielectric that attracts more charge onto the plate, increasing its capacitance. (b) The dielectric
reduces the electric field strength inside the capacitor, resulting in a smaller voltage between the
plates for the same charge. The capacitor stores the same charge for a smaller voltage,
implying that it has a larger capacitance because of the dielectric.
You might also like
- 4th WeekDocument7 pages4th WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Worktext in Electromagnetism For Teachers 4Document8 pagesWorktext in Electromagnetism For Teachers 4Xein BangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 CapacitanceDocument49 pagesChapter 26 Capacitancewaelabood51No ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument21 pagesCapacitorhetmaNo ratings yet
- L5 Electricity and MagnetismDocument37 pagesL5 Electricity and Magnetismbussanmugwati2004No ratings yet
- Capacitors and DielectricsDocument16 pagesCapacitors and DielectricsMahadi HasanNo ratings yet
- Passive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorDocument3 pagesPassive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorRenielDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and DielectricsDocument5 pagesCapacitors and DielectricsRae RedillasNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument98 pagesCapacitorklprasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting CapacitanceDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting CapacitanceKrati PandeyNo ratings yet
- Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument48 pagesCapacitor and CapacitanceDave Serapion50% (2)
- LAS BE 10 MELC 1-2 Week 1-2-StudentDocument10 pagesLAS BE 10 MELC 1-2 Week 1-2-StudentKrissa Leigh TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricDocument3 pagesCapacitance and DielectricKazuki KazehayaNo ratings yet
- Let's Begin: Module 3. Capacitance, Current and Resistance Capacitors and CapacitanceDocument40 pagesLet's Begin: Module 3. Capacitance, Current and Resistance Capacitors and CapacitanceSam TabujaraNo ratings yet
- Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectrics ExplainedDocument16 pagesParallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectrics ExplainedMelissa A. BernardoNo ratings yet
- Capacitors, Capacitance, and DielectricsDocument57 pagesCapacitors, Capacitance, and DielectricseemylNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Capacitive CircuitsDocument39 pagesLecture 5-Capacitive CircuitsMAENYA BRUCE OYONDINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Its ApplicationsDocument3 pagesCapacitors and Its ApplicationsadeelNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument5 pagesPhysics ProjectPrajvi0% (1)
- Electrical CapacitorsDocument20 pagesElectrical CapacitorsVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Capacitive CircuitsDocument38 pagesLecture 4-Capacitive CircuitsBen MachariaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance: Ref Book: Fundamentals of Physics - D. Halliday, R. Resnick & J. Walker (10 Ed.)Document58 pagesCapacitance: Ref Book: Fundamentals of Physics - D. Halliday, R. Resnick & J. Walker (10 Ed.)kuber bdNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIA AS A BIOLOGICAL CELL CAPACITORDocument150 pagesMITOCHONDRIA AS A BIOLOGICAL CELL CAPACITORBhargavNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjDocument19 pagesPhy Projselavathy1937No ratings yet
- Lecture: Capacitance: Ref Book: Fundamentals of Physics - D. Halliday, R. Resnick & J. Walker (10 Ed.)Document52 pagesLecture: Capacitance: Ref Book: Fundamentals of Physics - D. Halliday, R. Resnick & J. Walker (10 Ed.)GlitchNo ratings yet
- The Parallel Plate Capacitor - Construction, Principle, Videos and ExamplesDocument5 pagesThe Parallel Plate Capacitor - Construction, Principle, Videos and ExamplesBharat BhushanNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Their CircuitsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and Their CircuitsPrince JairoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsVenkatesh VenkiNo ratings yet
- 10 - CapacitorsDocument5 pages10 - Capacitorschie CNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Constant KitDocument12 pagesDielectric Constant KitNeha AgarwallaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Revision NotesDocument29 pagesCapacitors Revision NotesSabrin OmarNo ratings yet
- Capacitor: Jump ToDocument22 pagesCapacitor: Jump ToRakesh GroverNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides 7 CapacitorDocument79 pagesLecture Slides 7 CapacitorTawsif ahmedNo ratings yet
- TLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateDocument6 pagesTLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateNoli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Electrostatics Lecture 12: Conductors and DielectricDocument9 pagesModule 2: Electrostatics Lecture 12: Conductors and DielectricEviVardakiNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument14 pagesElectricalRomel PanisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorsxpNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and CapacitanceDocument9 pagesCapacitors and CapacitanceSrushti ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Document37 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Noli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- 1 CapacitorDocument37 pages1 CapacitorHeri Ardana SilaenNo ratings yet
- Phys502 Lect 5Document8 pagesPhys502 Lect 5MaissaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Project 30Document30 pagesPHYSICS Project 30SAHILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument27 pagesChapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. Boylestadakankshag_13No ratings yet
- Krati XII-B Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesKrati XII-B Physics ProjectKrati PandeyNo ratings yet
- 04 CapacitanceDocument27 pages04 Capacitanceade saputraNo ratings yet
- UP2 Ch8. CapacitanceDocument40 pagesUP2 Ch8. CapacitanceFatuhu Abba dandagoNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument86 pagesCapacitorsarunNo ratings yet
- Conductors, Insulators, and CapacitorsDocument3 pagesConductors, Insulators, and Capacitorsmanzoor10No ratings yet
- Capacitor Construction: Factors Affecting CapacitanceDocument10 pagesCapacitor Construction: Factors Affecting CapacitanceGolam Robbani RabbiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction Project ReportDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Project ReportT VpNo ratings yet
- EXPT 7-CapacitanceDocument8 pagesEXPT 7-Capacitance예지No ratings yet
- Introduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Capacitor BasicsDocument11 pagesCapacitor BasicsTuppada VeereshNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 12TH - Reyansh TomarDocument17 pagesPhysics Project 12TH - Reyansh TomarT VpNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQ Guide on Capacitors and Electric CircuitsDocument7 pagesPhysics MCQ Guide on Capacitors and Electric CircuitsEhtisham KhattakNo ratings yet
- Informe Final DielectricosDocument9 pagesInforme Final DielectricosVanesa Alberto DamianNo ratings yet
- 4th Qa PhysicsDocument88 pages4th Qa PhysicsEarl Clyde BañezNo ratings yet
- Mutual Inductance-ModuleDocument1 pageMutual Inductance-ModuleJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- BVPDocument1 pageBVPJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Fields of Rings and Coils-ModuleDocument1 pageFields of Rings and Coils-ModuleJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Philippines Monsoons - Amihan & HabagatDocument2 pagesPhilippines Monsoons - Amihan & HabagatJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- ThunderstormsDocument4 pagesThunderstormsJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument1 pageWeather and ClimateJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Jumbled WordsDocument1 pageJumbled WordsJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Identify The Parts of A MicroscopeDocument11 pagesIdentify The Parts of A MicroscopeJuan CruzNo ratings yet