Professional Documents
Culture Documents
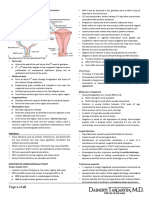
EPIDURIAL
Uploaded by
ALBERTO URIEL MONTAÑO CERVANTES0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesMédicina
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMédicina
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesEPIDURIAL
Uploaded by
ALBERTO URIEL MONTAÑO CERVANTESMédicina
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION DUE TO EPIDURAL
EXTRAMEDULLARY HAEMATOPOIESIS IN ACUTE MYELOID
LEUKEMIA: MRI FINDINGS
Güner Sönmez 1 , A. Rauf Görür 2 ,Hakan Mutlu 1 , Ersin Öztürk 1 ,
Onur Sıldıroğlu 1 , Bülent Karagöz 3
Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Haydarpasa Teaching Hospital, Departments of
Radiology 1 , Thorax Surgery 2 and Oncology 3 , İstanbul, Turkey
A 32 year-old-man with a history of acute myeloid leukemia on remission for one year presented
with sudden back pain, weakness and reduced sensation in both legs, and urinary incontinence that
had progressed over one weak. MRI of thoracic and lumbar spine was performed on a 1.5 T system
using a body coil due to his neurological symptoms. T1-weighted sequence (TR/TE: 617/15 mse)
and T2-weighted sequence (TR/TE: 4300/110 mse) on sagittal and axial images with 3 mm slice
thickness were used. Gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted axial images were obtained. Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated spinal cord compression by epidural extramedullary
hematopoietic tissue. Spinal epidural space is a very rare site for extramedullary hematopoiesis.
Key words: Acute myeloid leukemia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, spinal cord, MRI.
Eur J Gen Med 2008;5(1):42-44
INTRODUCTION legs with increased deep tendon reflexes
Extramedullary hematopoiesis is and Babinski’s sign. Abnormal laboratory
encountered in diseases with chronic findings were anemia (Hb 10.1 g/dl, RBC
overproduction of red blood cells. 3.04x106/mm3) and increased lactate
Abnormal hematopoietic tissue usually dehydrogenase blood level (558 IU/l). MRI
develops in sites involved in hematopoiesis of thoracic and lumbar spine was performed
during fetal development, such as the on a 1.5 T system using a body coil due
spleen, liver and kidney; however other to his neurological symptoms. Magnetic
locations, such as the paraspinal tissue, resonance images revealed posterior
especially in the posterior mediastinum, epidural masses extending from T1 to T11.
may be involved Spinal epidural space Vertebral marrow signal decreased on T2-
is a very rare site for extramedullary weighted images due to low fat content
hematopoiesis and most reports of this showing increased production of red
condition have been cases of thalassemia, blood cells (Figure 1A). The masses were
or myeloproliferative disorders like hyperintense on both T1 and T2-weighted
myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera images compared with spinal cord (Figure
(1,2). 1B). Axial images better delineated the
close relationship of the epidural masses
CASE with the spinal cord and nerve roots. The
A 32 year-old-man with a history of spinal cord signal was hyperintense due
acute myeloid leukemia on remission for to edema at the levels of compression
one year presented with sudden back on T2-weighted images (Figure 1C). The
pain, weakness and reduced sensation appearances suggested the diagnosis
in both legs, and urinary incontinence of extramedullary hematopoiesis. There
that had progressed over one weak. was not any characteristic MRI finding for
In neurological examination there was extramedullary hematopoiesis as thoracic
nothing special except paraparesis of the paravertebral foci of hematopoiesis or
Correspondence: Guner Sonmez, MD
Department of Radiology, GATA Haydarpasa Military
Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
Tel: 905326201560
E-mail:gunersonmez@hotmail.com
Extramedullary haematopoiesis and spinal cord 43
Figure 1A. Sagittal spin-echo T2-weighted MR image of the mid-thoracic spine shows
extensive decreased signal intensity throughout the vertebral bodies due to increased
production of red blood cells and clearly reveals posterior epidural mass. Figure 1B. The
masses are hyperintense compared with spinal cord on axial spin-echo T2-weighted MR
images. Figure 1C. On axial spin-echo T2-weighted MR image the close relationship of the
epidural masses with the spinal cord and the nerve roots is better delineated. There is also
high signal intensity in the spinal cord at the level of compression.
expansion of the posterior parts of the compression was due to extramedullary
ribs. The treatment choice was intravenous hematopoiesis caused by AML that is rarer.
prednisolone lasting for two weeks (250 Spinal cord compression secondary to
mg; 4 times in a day). His legs became extramedullary hematopoiesis commonly
stronger and he regained sensation over occurs in the mid-to-lower thoracic region
the ensuing 5 weeks. Posterior epidural possibly because of the marrow diameter
masses and cord edema disappeared on of the spinal canal in this region .
follow-up MRI of the spine. Treatment of cord compression due
to extramedullary hematopoiesis is
DISCUSSION controversial. In earlier reports, treatment
The most common sites of consisted of laminectomy alone or with
extramedullary hematopoiesis are the radiotherapy, with satisfactory responses
liver and the spleen. Paravertebral in most patients. More recently,
heterotopic marrow is less common and, radiotherapy alone has commonly been
when present, usually within the thorax carried out because of the well-known
Involvement of the spinal epidural space radiosensitivity of hematopoietic tissue
by hematopoietic tissue is rather unusual. and its accuracy in the treatment of
The rare complication of cord compression extramedullary hematopoiesis (4-6) . In
due to extramedullary hematopoiesis has our patient, by the end of the intravenous
most often been reported in patients with steroid therapy his neurological problems
thalassemia. Cord compression caused had been resolved gradually and he had
by extramedullary hematopoiesis has also not undergone additional treatment for
been reported in cases of myelofibrosis, extramedullary hematopoiesis.
sickle cell anemia and polycythemia In conclusion, extramedullary
vera (3-5) . In our case, thoracic cord hematopoiesis has to be kept in mind
44 Sönmez et al.
in the differential diagnosis of epidural 4. Pantongrag-Brown L, Suwanwela N Case
masses although there are not any typical report: chronic spinal cord compression
skeletal changes for extramedullary from extramedullary haematopoiesis in
hematopoiesis. thalassaemia MRI findings. Clin Radiol
1992;46:281-3
REFERENCES 5. Amirjamshidi A, Abbassioun K, Ketabchi
1. Aydingoz U, Oto A, Cila A. Spinal cord SE. Spinal extradural hematopoiesis in
compression due to epidural extramedullary adolescents with thalassemia. Childs Nerv
haematopoiesis in thalassaemia: MRI Syst 1991;7:223–5
Neuroradiology 1997;39:870-2 6. Guermazi A, Miaux Y, Chiras J. Imaging
2. Dibbern DA Jr, Loevner LA, Lieberman of spinal cord compression due to
AP, Salhany KE, Freese A, Marcotte PJ. thoracic extramedullary haematopoiesis in
MR of thoracic cord compression caused myelofibrosis Neuroradiology 1997;39:733–6
by epidural extramedullary hematopoiesis
in myelodysplastic syndrome. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol 1997;18:363-6
3. De Klippel, Dehou MF, Bourgain C, Schots
R, De Keyser J, Ebinger G Progressive
paraparesis due to thoracic extramedullary
hematopoiesis in myelofibrosis. J Neurosurg
1993;79:125-7
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- PHATAK'S GUIDE TO HOMEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICADocument869 pagesPHATAK'S GUIDE TO HOMEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICAminunat56% (9)
- Color Atlas of Small Animal Necropsy 1Document81 pagesColor Atlas of Small Animal Necropsy 1Sai KrupaNo ratings yet
- Syndromes Aarskog Syndrome (9p)Document10 pagesSyndromes Aarskog Syndrome (9p)M BeirutiNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal MassageDocument6 pagesLaryngeal Massageamal100% (1)
- Feu GP FGTDocument16 pagesFeu GP FGTAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Exercise-Associated Numbness and Tingling in The Legs: For Editorial Comment See Page 1509Document4 pagesExercise-Associated Numbness and Tingling in The Legs: For Editorial Comment See Page 1509herpthederpNo ratings yet
- NEUROPSYCHIATRY RADIOLOGY GUIDEDocument82 pagesNEUROPSYCHIATRY RADIOLOGY GUIDEIrham KhairiNo ratings yet
- Case Report: A Spinal Arteriovenous Fistula in A 3-Year Old BoyDocument5 pagesCase Report: A Spinal Arteriovenous Fistula in A 3-Year Old BoymanalNo ratings yet
- Causas de Isquemia Na MedulaDocument12 pagesCausas de Isquemia Na MeduladianaNo ratings yet
- Canine Choroid Plexus Tumor With Intracranial Dissemination Presenting As Multiple Cystic LesionsDocument5 pagesCanine Choroid Plexus Tumor With Intracranial Dissemination Presenting As Multiple Cystic LesionsMihai SavescuNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HypotensionDocument17 pagesIntracranial HypotensionNikhil TyagiNo ratings yet
- Plexiform Neurofibroma of The Cauda Equina Presenting As Peroneal Muscular Atrophy (Muscle & Nerve, Vol. 19, Issue 2) (1996)Document4 pagesPlexiform Neurofibroma of The Cauda Equina Presenting As Peroneal Muscular Atrophy (Muscle & Nerve, Vol. 19, Issue 2) (1996)antonioopNo ratings yet
- Thalssemia & Spinal Cord Compression in PregnancyDocument1 pageThalssemia & Spinal Cord Compression in PregnancyThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Giant Spinal Arterial Aneurysm in A Child Presenting As Quadriparesis (Case Reports, Vol. 2013, Issue Aug20 1) (2013)Document4 pagesA Giant Spinal Arterial Aneurysm in A Child Presenting As Quadriparesis (Case Reports, Vol. 2013, Issue Aug20 1) (2013)negin.safari8227No ratings yet
- DISH With SCIDocument5 pagesDISH With SCICornerstone OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Lumbar epidural hematoma case reportDocument2 pagesLumbar epidural hematoma case reportrswongym449No ratings yet
- CE (Ra1) F (SHU) PF1 (A SHU)Document5 pagesCE (Ra1) F (SHU) PF1 (A SHU)Anwesa ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientDocument3 pagesA Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)No ratings yet
- NeurosurgicalDocument5 pagesNeurosurgicalErwin WibowoNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument3 pages1 PBYudith Paula MonicaNo ratings yet
- Diag DifDocument3 pagesDiag DifJulia LemboNo ratings yet
- DD ParaparesisDocument9 pagesDD Paraparesishq_zhenNo ratings yet
- PBL 15Document27 pagesPBL 15AndiMuhYasserNo ratings yet
- Spinal Epidural Abscess in Two CalvesDocument8 pagesSpinal Epidural Abscess in Two CalvesRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- C+F-Syringomyelia and Hydro My Elia in Dogs and CatsDocument9 pagesC+F-Syringomyelia and Hydro My Elia in Dogs and Catstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- White Cord Syndrome After Cervical DecompressionDocument7 pagesWhite Cord Syndrome After Cervical DecompressionJosé A. RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Regional y Sindrome Compartamental Nov 21Document5 pagesAnesthesia Regional y Sindrome Compartamental Nov 21ema moralesNo ratings yet
- Jabot 2009Document5 pagesJabot 2009eric suNo ratings yet
- Moya Sy 2 ChildrenDocument11 pagesMoya Sy 2 Childrenthomsoon01No ratings yet
- Primary Extraskeletal Ewing Sarcoma of The Sinonasal Tract - A Rare Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument7 pagesPrimary Extraskeletal Ewing Sarcoma of The Sinonasal Tract - A Rare Case Report and Review of The LiteraturemohammadsayfooNo ratings yet
- POMES SundromeDocument5 pagesPOMES Sundromeerin_joëlNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of SpineDocument11 pagesTuberculosis of SpineSepti RahadianNo ratings yet
- 2008 TWPRMLinDocument8 pages2008 TWPRMLinVictor_id077No ratings yet
- MRI Findings in Susac SyndromeDocument6 pagesMRI Findings in Susac SyndromeLeonardoBubackNo ratings yet
- Follicular Carcinoma of Thyroid Presenting As Brain MetastasisDocument3 pagesFollicular Carcinoma of Thyroid Presenting As Brain MetastasisArif Susilo RahadiNo ratings yet
- Yuh2009 Article ImagingOfEpendymomasMRIAndCTDocument11 pagesYuh2009 Article ImagingOfEpendymomasMRIAndCTHuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Signal Abnormality with Enhancement: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord Signal Abnormality with Enhancement: A Case ReportGabriel PinillaNo ratings yet
- A Sinister Cause For Recurrent Syncope: Metastatic Parapharyngeal Space TumorDocument4 pagesA Sinister Cause For Recurrent Syncope: Metastatic Parapharyngeal Space TumorasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument22 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeNUR ZAMZAM AZIZAHNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of A Drop Foot Developed After Common Femoral Artery Cannulation For Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane OxygenationDocument4 pagesA Case Report of A Drop Foot Developed After Common Femoral Artery Cannulation For Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane OxygenationAnon0123No ratings yet
- Jhua16000143 PDFDocument3 pagesJhua16000143 PDFsamiratumananNo ratings yet
- Hood2000 PDFDocument4 pagesHood2000 PDFFiorella GNo ratings yet
- Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Review ArticleDocument10 pagesSpinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Review ArticleMeiriyani LembangNo ratings yet
- Decreased Consciousness Bithalamic InfarcDocument3 pagesDecreased Consciousness Bithalamic InfarcshofidhiaaaNo ratings yet
- 03 PrezentaredecazDocument21 pages03 PrezentaredecazKarina TeodoraNo ratings yet
- Maus 2012Document29 pagesMaus 2012211097salNo ratings yet
- DR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's HospitalDocument152 pagesDR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's Hospitalagnes trianaNo ratings yet
- Gomez 2023 Dissecting A Radiculomedullary ArteDocument4 pagesGomez 2023 Dissecting A Radiculomedullary ArteLuis Alejandro Garcia RairanNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Multiple Spinal Extradural Arachnoid Cysts Occurring in A ChildDocument4 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Multiple Spinal Extradural Arachnoid Cysts Occurring in A ChildRafael Mujica OreNo ratings yet
- InvestigationsDocument28 pagesInvestigationsAndrei BulgariuNo ratings yet
- Skeik Et Al 2015 - CirculatoryDocument5 pagesSkeik Et Al 2015 - Circulatorymattlight07No ratings yet
- Pituitaria SEMINARSDocument12 pagesPituitaria SEMINARSNathaly CantorNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Anatomy and Pathology: Pictorial ReviewDocument10 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Anatomy and Pathology: Pictorial Reviewbdalcin5512No ratings yet
- Boroumand 2016Document3 pagesBoroumand 2016Winston FontesNo ratings yet
- Leukodystrophies and MucopolysacridosisDocument78 pagesLeukodystrophies and MucopolysacridosisMobin Ur Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- Spinal Epidural Cavernous Hemangiomas in The 2024 International Journal of SDocument3 pagesSpinal Epidural Cavernous Hemangiomas in The 2024 International Journal of SRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome About A Series of Four CasesDocument9 pagesPopliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome About A Series of Four CasesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Electrodiagnosis of Cervical RadiculopathyDocument12 pagesElectrodiagnosis of Cervical RadiculopathywutariNo ratings yet
- Lesion Del Tracto Cortico - Espinal InglesDocument14 pagesLesion Del Tracto Cortico - Espinal InglesCarolina Andrea Daza CharrisNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging of Spinal Canal StenosisDocument17 pagesNeuroimaging of Spinal Canal Stenosisrulitoss_41739No ratings yet
- Cauda Equina Syndrome Review: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesCauda Equina Syndrome Review: Diagnosis and Treatmentabelinda100% (1)
- Electrodiagnosisofcervical Radiculopathy: Kevin Hakimi,, David SpanierDocument12 pagesElectrodiagnosisofcervical Radiculopathy: Kevin Hakimi,, David Spanierkashif mansoorNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Epidermoid Cyst with HemorrhageDocument3 pagesIntracranial Epidermoid Cyst with HemorrhageWildaHanimNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar Hemangioblastoma-A Rare EntityDocument10 pagesCerebellar Hemangioblastoma-A Rare EntityJay LeheriNo ratings yet
- WakeMed Non-Hemorrhagic Stroke-TIA Admission Orders Rev 12-07iDocument3 pagesWakeMed Non-Hemorrhagic Stroke-TIA Admission Orders Rev 12-07iNafilah SyellaNo ratings yet
- Implant Retained Overdenture: Splint Approach Using Copy DenturesDocument9 pagesImplant Retained Overdenture: Splint Approach Using Copy DenturesSorabh JainNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Periapical ConditionsDocument31 pagesPulp and Periapical ConditionsmythaiuNo ratings yet
- Management of The Urologic Sepsis SyndromeDocument10 pagesManagement of The Urologic Sepsis SyndromeNur Syamsiah MNo ratings yet
- Position Paper: A B C D e F G H CDocument11 pagesPosition Paper: A B C D e F G H CNico IonaşcuNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Bedside Ultrasound BookDocument274 pagesBedside Ultrasound Bookbilly thomas0% (1)
- NCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesNCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- Preeklampsia Update - Layanan Primer - BPJSDocument50 pagesPreeklampsia Update - Layanan Primer - BPJSansyNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Inhaler 20201203Document29 pagesAsthma and Inhaler 20201203松山內科部No ratings yet
- The Iraqi Doctor With Highest Academic Rank According To International StandardsDocument1 pageThe Iraqi Doctor With Highest Academic Rank According To International StandardsAamir Jalal Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic SurgeryDocument16 pagesLaparoscopic SurgeryHuda A LatifNo ratings yet
- Sok Case Study 2Document21 pagesSok Case Study 2Mohammad Onupom RahmanNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Oncology Study QuestionsDocument18 pagesOrthopaedic Oncology Study QuestionsFasa RoshadaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Screening Results and InterpretationDocument2 pagesLipid Screening Results and InterpretationsureshNo ratings yet
- Arthritis and Rheumatism: Seminars inDocument8 pagesArthritis and Rheumatism: Seminars inAnuj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Galeazzi FractureDocument14 pagesCase Study - Galeazzi FractureRio Cornell Golo50% (2)
- Me A S L E S: Aka Rubeola/ MorbilliDocument20 pagesMe A S L E S: Aka Rubeola/ MorbilliDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Local AnestheticsDocument50 pagesClassification of Local AnestheticsHelen Reyes HallareNo ratings yet
- The Following Rules Must Always Be Observed by The Physician in The Examination of WoundsDocument4 pagesThe Following Rules Must Always Be Observed by The Physician in The Examination of WoundsMondrich GabrienteNo ratings yet
- The Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelyDocument11 pagesThe Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelypriyankaNo ratings yet
- AUB CompiledDocument72 pagesAUB CompiledDinesha PaniselvamNo ratings yet
- 1990 ITE ExamDocument73 pages1990 ITE ExamTawona Dhlakama100% (1)
- Neuroimaging Clinics - Imaging of Head TraumaDocument184 pagesNeuroimaging Clinics - Imaging of Head TraumaSimion Iulian100% (1)
- W2-11 Neurological Issues in Women - LectureDocument47 pagesW2-11 Neurological Issues in Women - LectureNanjit SharmaNo ratings yet