Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Price Elasticity of Demand
Uploaded by
BenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Price Elasticity of Demand
Uploaded by
BenCopyright:
Available Formats
Price elasticity of demand
1. The responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. PED is calculated by %
change in quantity demanded/% change in price.
2. % change in demand = -10, % change in price = 40% PED = -0.25 it is price inelastic as
quantity doesn’t decrease relative to how price increases leaving the coefficient as between
0 and 1. Demand curve will be steep.
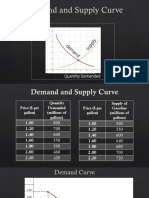
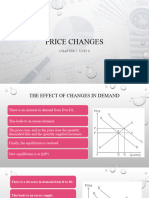
3.
Price (£) Quantity Demanded Total Revenue (£)
400 1400 560,000
500 1000 500,000
600 600 360,000
When price rises to £600 the % change in demand = -40%, % change in price = 20%, PED = -2.
When price falls to £400 the % change in demand = 40%, % change in price = -20%, PED = -2
Demand is elastic as coefficient is greater than 1. Demand curve will be shallow. The PED is elastic
which means that they should decrease prices. This increases total revenue as shown in the table
from £500,000 to £560,000.
4. PED for a normal good should be negative, this is because there is an inverse relationship
between price and quantity demanded. A steep demand curve suggests that the good is
inelastic i.e., it is relatively unresponsive to a change in price. For a good which is elastic in
nature, the percentage change in quantity demanded is more than the percentage change in
price.
You might also like
- Economics AssignmentDocument23 pagesEconomics AssignmentAqsa AnumNo ratings yet
- Section ADocument22 pagesSection AAqsa AnumNo ratings yet
- How Is Equilibrium EstablishedDocument5 pagesHow Is Equilibrium EstablishedJudy Mar Valdez, CPANo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply, and EquilibriumDocument21 pagesDemand, Supply, and Equilibriump4d2w8s5pbNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Assignment #1Document5 pagesMicroeconomics Assignment #1chloedevecseriNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ Week 3-LasDocument8 pagesApplied Econ Week 3-LasJanine CosaresNo ratings yet
- Economics SDPDocument33 pagesEconomics SDPAlcantara IanNo ratings yet
- Assignement - 2 Solution Masud RanaDocument16 pagesAssignement - 2 Solution Masud Ranaboom boomNo ratings yet
- Law of SupplyDocument26 pagesLaw of SupplyamitNo ratings yet
- Running Head: SUPPLY AND DEMAND 1Document9 pagesRunning Head: SUPPLY AND DEMAND 1klm klmNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Amrendra KumarDocument34 pagesPresented By: Amrendra Kumaramrendrakr092434No ratings yet
- L15 Price Elasticity of DemandDocument47 pagesL15 Price Elasticity of DemandNurul AzminahNo ratings yet
- Shifts in DemandDocument6 pagesShifts in DemandJyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- COBMECO Practice Set OnlyDocument5 pagesCOBMECO Practice Set OnlyAlexius Aaron LlarenasNo ratings yet
- Demandsupplyequilibriumprice1 130809232706 Phpapp02Document33 pagesDemandsupplyequilibriumprice1 130809232706 Phpapp02endangNo ratings yet
- Written Report 2Document13 pagesWritten Report 2Cindy BartolayNo ratings yet
- Assignement - 2 Solution - EditedDocument16 pagesAssignement - 2 Solution - Editedboom boomNo ratings yet
- EBA Case Solution CH 3Document4 pagesEBA Case Solution CH 3Abhinav MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis Example Excel-TemplateDocument8 pagesBreak-Even Analysis Example Excel-TemplateFernando FlorNo ratings yet
- Types of CostsDocument3 pagesTypes of CostsHaris AhnedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Demand SupplyDocument4 pagesTutorial Demand SupplyLena LeezNo ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium With ForcesDocument9 pagesMarket Equilibrium With ForcesCharlie DeltaNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument37 pagesPriceRosemarie DiquentoNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Chapter # 4Document3 pagesMicroeconomics: Chapter # 4Ghalib HussainNo ratings yet
- Examen de Speaking: IntegrantesDocument3 pagesExamen de Speaking: IntegrantesBriseida Alvarado GuerraNo ratings yet
- Price DeterminationDocument8 pagesPrice DeterminationIruoluwaniosi OwolabiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Quantity Per PeriodDocument12 pagesAnswers: Quantity Per PeriodghaliaNo ratings yet
- W4 NewProductLaunch SensitivityAnalysisDocument6 pagesW4 NewProductLaunch SensitivityAnalysisChip choiNo ratings yet
- Exposición SpeakingDocument3 pagesExposición SpeakingBriseida Alvarado GuerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unit 6Document13 pagesChapter 2 Unit 6Fatima KabirNo ratings yet
- Excel WorkBookDocument60 pagesExcel WorkBookArnavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibriumfinn mertensNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Trading-1Document6 pagesSupply and Demand Trading-1CRYPTO BEGINNERSNo ratings yet
- Group Exercise On Demand and Elasticity (13354)Document7 pagesGroup Exercise On Demand and Elasticity (13354)AprvaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles o F Demand and Suppl Y: "Supply"Document30 pagesBasic Principles o F Demand and Suppl Y: "Supply"Albert LlagunoNo ratings yet
- 06a) Price Elasticity of DemandDocument4 pages06a) Price Elasticity of DemandMohamed Yasser50% (2)
- Part A. Multiple ChoicesDocument4 pagesPart A. Multiple ChoicesJessica FeliciaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: How Markets WorkDocument59 pagesSupply and Demand: How Markets WorkGayathri22394No ratings yet
- Price and The Interaction of Demand and SupplyDocument51 pagesPrice and The Interaction of Demand and SupplyRose Jeannie Nabong0% (2)
- Course Material - Demand and Supply Analysis 2Document14 pagesCourse Material - Demand and Supply Analysis 2JAMES CRISTOFER TARROZANo ratings yet
- 2.5 Marks: Step-By-Step ExplanationDocument5 pages2.5 Marks: Step-By-Step ExplanationMUHAMMAD AZAM50% (2)
- Mba Economics Presentation On SupplyDocument30 pagesMba Economics Presentation On Supplysourav kumar rayNo ratings yet
- ECO Assignment - 1Document10 pagesECO Assignment - 1Nilesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Break Even PointDocument8 pagesBreak Even Pointrachma diniNo ratings yet
- Case Keeping TimeDocument3 pagesCase Keeping TimeMaybelle Bernal33% (3)
- Chapter ElasticityDocument33 pagesChapter ElasticityIsya LolaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 AnswersDocument6 pagesTutorial 5 AnswersJohn TomNo ratings yet
- The Price Theory Complete by Kongnso Rene 674729925Document87 pagesThe Price Theory Complete by Kongnso Rene 674729925kinsodaddy1No ratings yet
- SS12 Answered Problem SetsDocument23 pagesSS12 Answered Problem SetsMark DonesNo ratings yet
- Chartbook of The IGWT20 Gold Conquering New Record HighsDocument68 pagesChartbook of The IGWT20 Gold Conquering New Record HighsTFMetals100% (1)
- Basic Economics Task Performance (Prelims)Document1 pageBasic Economics Task Performance (Prelims)godwill oliva0% (1)
- Applied Economics: Application of Demand and SupplyDocument19 pagesApplied Economics: Application of Demand and SupplyBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- Econ 102: Supply, Demand, and Competitive EquilibriumDocument24 pagesEcon 102: Supply, Demand, and Competitive EquilibriumNecromancerNo ratings yet
- Price DeterminationDocument29 pagesPrice DeterminationGatik BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Supply Curve: No. of Jeans ('000)Document9 pagesSupply Curve: No. of Jeans ('000)Nilesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document39 pagesSession 2Akshit GaurNo ratings yet
- LEAP AWE NPP - FinalDocument1 pageLEAP AWE NPP - Finalvikyraj0420No ratings yet
- 8 August Inventory 2010Document1 page8 August Inventory 2010Jason IngleNo ratings yet
- 07a) Income Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pages07a) Income Elasticity of DemandBenNo ratings yet
- Economics Edexcel As Macro 2016Document169 pagesEconomics Edexcel As Macro 2016BenNo ratings yet
- 10a) Price Elasticity of SupplyDocument2 pages10a) Price Elasticity of SupplyBenNo ratings yet
- Income Elasticity of DemandDocument1 pageIncome Elasticity of DemandBenNo ratings yet