Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hakdog
Uploaded by
Mica De Guzman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOriginal Title
hakdog
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesHakdog
Uploaded by
Mica De GuzmanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
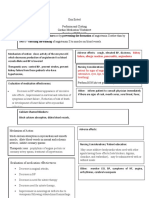
List the effects of Alpha 1 Adrenergic receptors.
Eye - pupil dilation What are Beta-Adrenergic Adverse Effects?
Blood vessels - vasoconstriction CNS - tremors, headaches,
(increased BP) nervousness, dizziness
Bladder - bladder relaxes (less pressure Cardiovascular - Palpitations,
= less need to pee); constriction of tachycardia, dysrhythmia, angina
bladder sphincter Other - sweating, nausea, vomiting,
List the effects of Beta 1 Adrenergic receptors. muscle cramps
Heart - increased heart rate to pump
more blood, increased conduction What are Alpha 1 Adrenergic Adverse Effects?
through AV node, increased force of CNS - headache, restlessness,
contraction excitement
Kidney - secretes renin to retain water Cardiovascular - Palpitations,
List the effects of Beta 2 Adrenergic receptors. tachycardia, hypertension,
Smooth muscle of lungs – dysrhythmias
bronchodilation Other - necrosis (death of cells in
What are the other names for Adrenergic tissue/organ) if IV infiltrates
drugs? Patient Education for Adrenergic Drugs
Adrenergic agonists & Do NOT stop abruptly
Sympathomimetics (because they All other medications require
mimic the SNS) prescriber's approval due to high risk of
bad interactions
Mechanism of action and adverse effects for
Direct-acting sympathomimetic vs. Indirect Alpha-Blockers (Flomax).
acting sympathomimetic Decreased vasoconstriction &
Direct-acting = binds directly onto the decreased prostatic capsule
specific receptor to cause a response contraction (decreased
Indirect-acting = stimulates the resistance to urinary flow).
presynaptic neuron to release Adverse Effects: dizziness, first dose syncope,
neurotransmitters, which then bind to orthostatic hypotension, impotence.
the specific receptor to cause a
response Effects of Beta-blockers (atenolol/metoprolol)
and adverse effects.
Decreased demand for myocardial
What is Anaphylaxis and how is it treated? oxygen (decreased angina).
Sever allergic reaction that leads to Decreased heart rate.
shock, decreased BP, increased heart Decreased force of contraction (lowers
rate, and bronchoconstriction. hypertension).
Adverse effects = bradycardia, rebound
Managed with EpiPen that injects myocardium excitation (BLACKBOX),
epinephrine and stimulates all bronchoconstriction, hypoglycemia.
adrenergic receptors; only lasts 10-
20mins so must go to hospital still! Nursing implications/Patient education for
Beta-Blockers.
Assess pulse/BP before giving What happens during a Cholinergic Crisis? What
meds; do not give if patient is the antidote?
already has bradycardia (below Bronchoconstriction (shortness of
60). breath), hypotension, cardiac
Avoid hot tubs to prevent hypotension arrest (bradycardia); Atropine
and passing out. (anticholinergic)
Change positions slowly due to decreased BP. Mechanism of action of Anticholinergic Drugs
(atropine, tolterodine).
Mechanism of action of Cholinergic Drugs and Block/inhibit the actions of
other names for them. acetylcholine by blocking the
Stimulate parasympathetic muscarinic receptors in the
nervous system by mimicking PSNS; blocks cholinergic effect
acetylcholine (ACh). Effects of Anticholinergic Drugs.
Also known as Cholinergic agonists & Dilated pupils
Parasympathomimetics. Increased heart rate
Bronchodilation/decreased
Direct-acting Cholinergics vs. Indirect-acting bronchial secretions
Cholinergics. Relaxed bladder
Direct-acting = bind directly to Decreased sweating
cholinergic receptors. Indications to use Anticholinergic Drugs:
Indirect-acting = increases available ACh by Atropine/Tolterodine
inhibiting acetylcholinesterase enzyme. Symptomatic Bradycardia
Overactive Bladder
Adverse Effects of Anticholinergic Drugs.
Effects of Cholinergic Drugs. Dilated pupils, tachycardia,
Increased gastric secretions dysrhythmias, constipation,
Relaxation of bladder sphincter decreased sweating
Pupil constriction What is the antidote for atropine
Decreased heart rate/force of (anticholinergic) overdose?
contraction Physostigmine
Bronchoconstriction
Sweating
Indications to use Cholinergic Drug:
Bethanechol
Post-Op Urinary Retention =
causes contraction of bladder
detrusor muscle and relaxation
of bladder sphincter.
What happens during Cholinergic poisoning?
S.L.U.D.G.E - salivation,
lacrimation, urinary
incontinence, diarrhea, GI
cramps, Emesis (vomiting)
You might also like
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument23 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AgentsCarlo GaradoNo ratings yet
- Alpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHDocument21 pagesAlpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHKaylee LengNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System: 1 AlazarDocument55 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System: 1 Alazarsiltanu awokeNo ratings yet
- ANS2Document16 pagesANS2yaya mohaNo ratings yet
- WK 5 Pharma Cns Drugs B Adrenergic Blockers - Cholenergic and Blockers Motion SicknessDocument83 pagesWK 5 Pharma Cns Drugs B Adrenergic Blockers - Cholenergic and Blockers Motion SicknessKryza B. CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Cholinergic (2017 - 11 - 01 22 - 03 - 49 UTC)Document2 pagesAdrenergic and Cholinergic (2017 - 11 - 01 22 - 03 - 49 UTC)Kimberly WhitesideNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic& Antiadrengeic DrugsDocument39 pagesAdrenergic& Antiadrengeic DrugsAsif Ali LashariNo ratings yet
- PNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.Document6 pagesPNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.rqu3l0% (1)
- ANS PharmacologyDocument24 pagesANS PharmacologySOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Drenergic AND Anti Adrenergic Drugs: Shabib AkhtarDocument21 pagesDrenergic AND Anti Adrenergic Drugs: Shabib AkhtarDeepa ShaiekhNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Medications TemplateDocument5 pagesCardiac Medications TemplateErinNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medications: Hamdan Al HarbiDocument7 pagesEmergency Medications: Hamdan Al Harbijohn72decNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesDrugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemjisooNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument82 pagesNervous SystemEdgardo TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocument7 pagesAutonomic Nervous System DrugsLucañas PringelNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsDocument12 pagesEpinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsChristina SantosNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic DrugsDocument7 pagesAnesthetic DrugsAJ DalawampuNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic & Antiadrenergic DrugsDocument54 pagesAdrenergic & Antiadrenergic DrugsUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug ChartDocument20 pagesDrug Chartstarobin100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument14 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AgentsRhenier S. Ilado100% (1)
- OoasuhsDocument23 pagesOoasuhsNicole RomeroNo ratings yet
- DR: Samah Gaafar Al-ShaygiDocument22 pagesDR: Samah Gaafar Al-Shaygiكسلان اكتب اسميNo ratings yet
- Application of Drugs Acting On Autonomic Nervous System in HospitalsDocument58 pagesApplication of Drugs Acting On Autonomic Nervous System in HospitalsTama Fara ChiNo ratings yet
- Ing GrisDocument9 pagesIng GrisKaerud ZamanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide PNS and CNSDocument7 pagesStudy Guide PNS and CNSsquicciariniNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenDocument33 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenHendra EfendiNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document15 pagesCH 19Emmanuel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Prototype Drug - Adrenergic AgonistDocument1 pagePrototype Drug - Adrenergic Agonistshiloh Paradis100% (1)
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerEinstein MKNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyPregielyn RancheNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - MidtermDocument35 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - MidtermHeizmaebrizNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument28 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsolswnhNo ratings yet
- Drug StudypppDocument42 pagesDrug Studyppp2022106284No ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document27 pagesLesson 3Dipika Rani sahuNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument120 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Agentscoosa liquors100% (1)
- 05-Adrenergic Agonists DR Hala 2020Document30 pages05-Adrenergic Agonists DR Hala 2020مشاعرمبعثرةNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Module For FinalsDocument11 pagesPharmacology Module For FinalsCarlo GaradoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudySocial BaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesDrugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemJah SuNo ratings yet
- 2020 Feb Answer KeyDocument27 pages2020 Feb Answer KeyAjitha boopathiNo ratings yet
- Internet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid ReferenceDocument1 pageInternet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid Referenceian porterNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and VasopressorsDocument63 pagesInotropes and VasopressorsCraig DuHaney50% (2)
- Drugs On RespiratoryDocument17 pagesDrugs On RespiratoryIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsDocument7 pagesNorepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsJohn denver FloresNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- SympathomimeticDocument56 pagesSympathomimeticvarish0% (1)
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemPranalosaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The ANS: Clinical Pharmacist: Dr. Fatima Bani SalamaDocument144 pagesDrugs Acting On The ANS: Clinical Pharmacist: Dr. Fatima Bani SalamaNada AlhaririNo ratings yet
- Drug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYDocument71 pagesDrug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Pharm QuestionsDocument5 pagesPharm Questionsvaroon525No ratings yet
- Drug Study Sir MarkDocument5 pagesDrug Study Sir MarkKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous Systembaby laine100% (2)
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- NURS320 Quiz 4Document5 pagesNURS320 Quiz 4Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Practice 8Document6 pagesNURS320 Practice 8Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Presentation 5Document5 pagesNURS320 Presentation 5Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Practice Problems 10Document5 pagesNURS320 Practice Problems 10Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Lab Report 4Document5 pagesNURS320 Lab Report 4Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Assignment 7Document5 pagesNURS320 Assignment 7Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Info 5Document3 pagesNURS320 Info 5Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- EthDocument3 pagesEthMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Doc 5Document5 pagesNURS320 Doc 5Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NURS320 Demo 6Document6 pagesNURS320 Demo 6Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CHN QuizzDocument8 pagesCHN QuizzMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxiclavMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CHN QuizDocument4 pagesCHN QuizMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pols273 Exam 2Document5 pagesPols273 Exam 2Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pols273 Essay 6Document6 pagesPols273 Essay 6Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pols273 Essay 6Document6 pagesPols273 Essay 6Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Demonstration 1Document4 pagesPOLS273 Demonstration 1Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Answers 9Document4 pagesPOLS273 Answers 9Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Demonstration 1Document4 pagesPOLS273 Demonstration 1Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Analysis 4Document6 pagesPOLS273 Analysis 4Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pols273 Exam 2Document5 pagesPols273 Exam 2Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Worksheet 1Document3 pagesPOLS273 Worksheet 1Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Answers 9Document4 pagesPOLS273 Answers 9Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Answers 5Document4 pagesPOLS273 Answers 5Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Response 1Document4 pagesPOLS273 Response 1Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Soultions 3Document2 pagesPOLS273 Soultions 3Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- POLS273 Presentation 7Document5 pagesPOLS273 Presentation 7Mica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocument28 pagesHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Varaah KavachDocument7 pagesVaraah KavachBalagei Nagarajan100% (1)
- Ultimate GuideDocument33 pagesUltimate GuidemrosamusicNo ratings yet
- Mercedez-Benz: The Best or NothingDocument7 pagesMercedez-Benz: The Best or NothingEstefania RenzaNo ratings yet
- Schneider Modicon M580 CatalogueDocument268 pagesSchneider Modicon M580 CatalogueKhaerul Imam HermanNo ratings yet
- S.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Document532 pagesS.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Gianpiero Boccato0% (1)
- Indigo Airlines - Final ReportDocument22 pagesIndigo Airlines - Final Reportanand_lihinarNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Objective Questionsmohammad shaqib100% (4)
- Disa Match: A Match You Can Count OnDocument8 pagesDisa Match: A Match You Can Count OngNo ratings yet
- The Failed Rotator CuffDocument307 pagesThe Failed Rotator Cufforthofitness2017No ratings yet
- Transfer Case Electrical RMDocument51 pagesTransfer Case Electrical RMDaniel Canales75% (4)
- The Ecological Effects of Eucalyptus PDFDocument97 pagesThe Ecological Effects of Eucalyptus PDFgejuinaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorDocument14 pagesCalculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorWeiKiat Goh67% (3)
- InTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument20 pagesInTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesM VetriselviNo ratings yet
- TA308 616configurationDocument1 pageTA308 616configurationJesus AvilaNo ratings yet
- Earth Bonding LeadsDocument2 pagesEarth Bonding LeadsrocketvtNo ratings yet
- Avionic ArchitectureDocument127 pagesAvionic ArchitectureRohithsai PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Document2 pagesMobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Shirley RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Calabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1Document5 pagesCalabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1MarkJasperCalabanoNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesMagneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Subject: Digital System Design Faculty: Mr. P.Jayakrishna Unit-5 Assignment 5 Set 1Document2 pagesSubject: Digital System Design Faculty: Mr. P.Jayakrishna Unit-5 Assignment 5 Set 1Jayakrishna CharyNo ratings yet
- TA1515VDocument4 pagesTA1515VLeo LeiNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++Document5 pagesPolynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++wlsvieiraNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Document326 pagesAnnual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Gaurav DurejaNo ratings yet
- Study of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderDocument3 pagesStudy of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderAnonymous AkoNo ratings yet
- Iloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2006-010Document4 pagesIloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2006-010Iloilo City CouncilNo ratings yet
- Acer AIO Z1-752 System DisassemblyDocument10 pagesAcer AIO Z1-752 System DisassemblySERGIORABRNo ratings yet
- Stokerchapter25lipidmetabolism 160320032037Document29 pagesStokerchapter25lipidmetabolism 160320032037Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet