Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Sheet Electronics
Uploaded by
Ayat Nabil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Answer sheet electronics(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesAnswer Sheet Electronics
Uploaded by
Ayat NabilCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Sheet 1
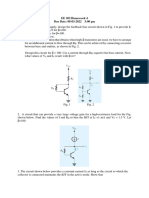
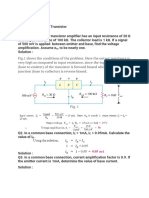
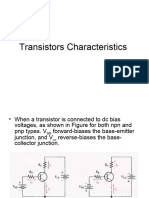
1- Assume that you wish to bias the transistor in
Figure(1) with IB=20µA. To what voltage must you
change the VBB supply? What are IC and VCE at the
Q-point, given that βDC=50?
2- Design a biased-transistor circuit using VBB=VCC=10V for a Q-point of
IC=5mA and VCE=4V Assume βDC=100. The design involves finding RB, RC,
and the minimum power rating of the transistor. (The actual power rating
should be greater.) Sketch the circuit.
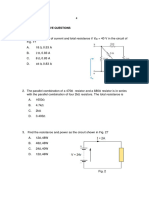
3- Determine whether the transistor in Figure(2) is
biased in cutoff, saturation, or the linear region.
Remember that . IC =βDCIB is valid only in the linear
region
4- From the collector characteristic curves and the dc
load line in
Figure(3), determine the following:
(a) Collector saturation current
(b) VCE at cutoff
(c) Q-point values of IB, IC, and VCE
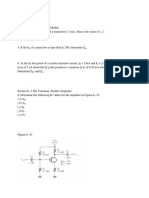
5- 14. Determine all transistor terminal voltages with
respect to ground in Figure(4).
6- (a) Determine VB in Figure(5).
(b) How is VB affected if the transistor is replaced by
one with a βDC=50?
7- Analyze the circuit in Figure(6) to determine the correct
voltages at the transistor terminals with respect to ground.
Assume βDC=100
8- Determine VB, VC, and IC in Figure(7).
9-
10-
You might also like
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5 Electronics - AnswerDocument8 pagesSheet 5 Electronics - AnswerMohamed AmgadNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- #1 Tutorial - Introduction To BJTDocument3 pages#1 Tutorial - Introduction To BJTAlbert GenceNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- UNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument14 pagesUNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorWaleed HåšhįmNo ratings yet
- BJT ProblemsDocument22 pagesBJT Problemsshobhashis nayakNo ratings yet
- BJT-BIAS - Problems & SolutionsDocument18 pagesBJT-BIAS - Problems & SolutionsJohn SantosNo ratings yet
- BJT-BIAS - Problems & SolutionsDocument18 pagesBJT-BIAS - Problems & SolutionsJohn SantosNo ratings yet
- Bjts DC BiasingDocument89 pagesBjts DC BiasingVenugopal ReddyvariNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 3Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- HW 12Document3 pagesHW 12Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 ElectronicsDocument4 pagesSheet 4 ElectronicsAhmed Abo nNo ratings yet
- SSCP2313Tutorial 7Document3 pagesSSCP2313Tutorial 7Aizzat ArfaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffDocument15 pagesSolved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffStudent HelperNo ratings yet
- Phy Transistor PracDocument5 pagesPhy Transistor PracRishabh NagdaNo ratings yet
- Transistor Characteristics Guide - Key Parameters, Regions & Ratios ExplainedDocument13 pagesTransistor Characteristics Guide - Key Parameters, Regions & Ratios Explainedpuser007No ratings yet
- Electronics I DC Biasing ExamplesDocument13 pagesElectronics I DC Biasing Examplesمحمد كاظم محمدجواد محمود -A-No ratings yet
- BJT Circuits Analysis and DesignDocument60 pagesBJT Circuits Analysis and DesignAdam MoutasemNo ratings yet
- BJT Biasing CircuitDocument40 pagesBJT Biasing Circuitfelix NizeyimanaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Package 5Document4 pagesExercise Package 5Muhammad Sohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument55 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorshuy PhamNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 Electronics - AnswerDocument7 pagesSheet 4 Electronics - AnswerOla SamirNo ratings yet
- BJT As An Amplifier: Biasing and Small Signal Model: ECE60L Lecture Notes, Spring 2002Document15 pagesBJT As An Amplifier: Biasing and Small Signal Model: ECE60L Lecture Notes, Spring 2002anon020202100% (1)
- EE 202 Homework 4Document3 pagesEE 202 Homework 4Aleyna OzenNo ratings yet
- Optimize DC Bias CircuitsDocument18 pagesOptimize DC Bias CircuitsJawad Ul Hassan Shah100% (1)
- Question Bank - Principles of ElectronicsDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank - Principles of ElectronicsADDELYN CYNTHIA ANAK TONYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5Alwani IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Module2 PDFDocument16 pagesModule2 PDFSrihari UttanurNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument46 pagesJurnalHasmar HuseinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document44 pagesLecture 8عمر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Transistors)Document9 pagesAssignment 5 (Transistors)Rajesh PathakNo ratings yet
- And I and V: BQ CQ. CEQ B C BCDocument2 pagesAnd I and V: BQ CQ. CEQ B C BCdrhammoudaNo ratings yet
- Bias Transistor1Document46 pagesBias Transistor1angel larasatiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Document23 pagesTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahageNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24: BJT Operation Regions (Active, Saturation and Cut-Off)Document3 pagesLecture 24: BJT Operation Regions (Active, Saturation and Cut-Off)Huzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- ECE 102 BJT Small Signal Analysis GuideDocument164 pagesECE 102 BJT Small Signal Analysis GuideJunice GranaNo ratings yet
- 3b BJT DC Analysis -Document24 pages3b BJT DC Analysis -Syahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- EC-1 Unit-1 Solved Part B WMRDocument31 pagesEC-1 Unit-1 Solved Part B WMRSaravanan Murugaiyan100% (1)
- Chapter 05Document40 pagesChapter 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- BJT NotesDocument110 pagesBJT NotesHardesh Chauhan100% (1)
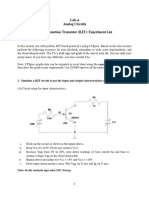
- Lab-4 Analog Circuits Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Experiment ListDocument4 pagesLab-4 Analog Circuits Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Experiment ListRAMOLIYA HARSH MADHUKANTBHAINo ratings yet
- Electronics Post Solved Problems on Transistor AmplificationDocument30 pagesElectronics Post Solved Problems on Transistor AmplificationAravind KarthikNo ratings yet
- BJT DC AnalysisDocument11 pagesBJT DC AnalysisShamganth KumarapandianNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22Document10 pagesQUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22MUHAMMAD NUR AMNI KHARIMANNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument26 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- HW 15Document3 pagesHW 15Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- BJT DCDocument19 pagesBJT DCagama1188No ratings yet
- BJ T HomeworkDocument5 pagesBJ T HomeworkDomsNo ratings yet
- TD3: Bipolar Junction Transistor common emitter and limit operationDocument2 pagesTD3: Bipolar Junction Transistor common emitter and limit operationSao SavathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transistor CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Transistor CharacteristicsHydian Genos YTNo ratings yet
- Bypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitDocument6 pagesBypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitSandesh AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- BJT DC Analysis Q-Points Load LinesDocument22 pagesBJT DC Analysis Q-Points Load Linessamsung 6000No ratings yet
- Limits of Operation:-: Versus V For A Range of Values of IDocument18 pagesLimits of Operation:-: Versus V For A Range of Values of IAns neucrossNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AecDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank AecShreyas AdkiNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuit Design ProblemsDocument17 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design ProblemsLê Hoàng ChínhNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument9 pagesBipolar TransistorJitendra DubeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityDocument14 pagesExperiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityNayyab MalikNo ratings yet
- 19 15ee201 A2 PDFDocument2 pages19 15ee201 A2 PDFYadhuvanth kumarNo ratings yet
- BJT Construction and Configurations BJT Applications: - Common Emitter - Common BaseDocument23 pagesBJT Construction and Configurations BJT Applications: - Common Emitter - Common BaseirishNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet ElectronicsDocument3 pagesAnswer Sheet ElectronicsAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3Document1 pageSheet 3Ayat NabilNo ratings yet
- Lec. 6Document6 pagesLec. 6Ayat NabilNo ratings yet
- Lec. 8Document8 pagesLec. 8Ayat NabilNo ratings yet
- Lec. 5Document12 pagesLec. 5Ayat NabilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics-LecDocument11 pagesMechanics-LecAyat NabilNo ratings yet
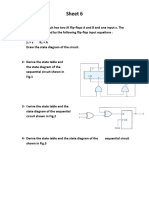
- Sheet LogicDocument2 pagesSheet LogicAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Sheet LogicDocument2 pagesSheet LogicAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Summary and Key PointsDocument20 pagesLecture 1 Summary and Key PointsAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Sheet LogicDocument1 pageSheet LogicAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Sheet LogicDocument2 pagesSheet LogicAyat NabilNo ratings yet
- Sheet LogicDocument1 pageSheet LogicAyat NabilNo ratings yet