Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Practical Chromatography0001
Chemistry Practical Chromatography0001
Uploaded by
Sattwik Manna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesChemistry Practical Chromatography0001
Chemistry Practical Chromatography0001
Uploaded by
Sattwik MannaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Experiment - 20
Aim:
To separate the pigments present in leaves and
flowers by paper chromatography and
determine their Rf values.
Theory:
Paper chromatography is essentially a partition chromatography. In
paper chromatography the stationary phase is paper. Paper contains
22% of water molecules absorbed on about 78% of cellulose.
‘The separation of the components of the mixture takes place by
partitioning of the components between the stationary phase and
mobile phase. The mobile phase travels through the paper by capillary
action. Based upon the ways the solvent travels on the paper there are
three types of chromatography
1, Ascending Paper Chromatography
2, Descending Paper Chromatography
3. Circular Paper Chromatography
‘The distribution occurs in a definite ratio which represents the
characteristic distribution coefficient of the solution.
‘The Rr coefficient ration is given by
_ Distance travelled by the pigments from the point of application
«Distance travelled by the solvent from the original distance
Different substances possess different Rr values. Rr depends upon a
number of factors.
+ Nature of the substance
+ Nature of the solvent
+ Temperature
+ Presence of impurities
+ Quality of the filter paper
If the compound is coloured, it cam be easily located on the
chromatographic paper. if the substance is colourless, however, a
reagent may be used to treat it, which gives it a characteristic colour.
‘The name developer is given to this reagent. Iodine is the most
frequently used paper chromatography developer.
Glass rod
Paper clip
Jar
— Strip of filter
paper
‘Spot of ink
Strip of filter
paper
Line drawn
by pencil Water
Spot of ink
(a> (b)
Materials Required:
1, Whatman’s filter paper
2. Extract of leaves and extract of flowers
3. Chloroform /acetene
4, Methanol/Acetone
5. Rubber cork fixed with hook in the centre
6. Glass jar
7. Rubber cork fixed with hook in the centre
8. Test tubes
9. Distilled water
10. Petroleum ether
Procedure:
1. Take the whatman filter paper and draw a line with the help of a
pencil above 4cm from one end.
2. Grind the leaves and flowers in a motor and transfer the paste
into a test tube.
3. This crushed material add acetone or methanol, shake well and
filter the mixture.
4. The filtrate is collected in a test tube for performing experiments.
5. Using a capillary put one drop of the filtrate on the filter paper
and allow it to dry.
6. Now hang the filter paper in a jar containing 20ml of petrolem.
ether and chloroform.
7. Keep this jar till the mobile phase rises up to 2/3th of the length
of the paper.
8. Remove the filter paper from the jar mark the solvent front.
9. Outline the spots with the help of pencil and make the filter
paper to dry.
20. Measure the distance between the solvent front and the ceatre
of different spots in relation to the reference line as indicated
11, Determine the number of pigments in the leaves and flowers
extract.
12. Using the expression, calculate the Rr value of different spots.
Observations and Inference:
S.No Name ofthe Colour Distance Distance Rr Values
extract and of the travelled by travelled
colour spot the spotfrom by the =a/xX
the original solvent
Hne.{A} from the
original
Hine (&)
1 Chlorophyll Green 3cm 12cm 0.25
2 Xanthophyll Yellow 4cm 12 cm 0.33
3 Carotene Red 10 cm i2em 0.83
Precautions:
1, Always make use of a fine capillary tube.
2. Do not allow spots to spread while spotting the test solution on
the paper.
3. Use the capillary finely drawn to place the spot on the paper.
4. Do not disturb the jar once the experiment is set as long as the
chromatogram is developed.
5. Before developing the spots, make the paper strip perfectly dry.
6. Carefully handle organic solvents.
Experiment - 21
AIM : Separate Cu” and Ca ions Present
in the Given Mixture by Using Ascending
Paper Chromatography and Determine
their R; Values:
Apparatus
Gas jar, glass rod, filter paper strip (What man No. 1 filter paper), jar
cover, fine capillary tube.
Chemicals Requirement
Sample solution containing cobalt (11) and nickel (7) ions, acetone,
concentrated aqueous ammonia, Rubeanic acid spray reagent.
Procedure
1. Take a What man filter paper strip (20 x 2 em) and draw 4 line with
pencil above 3 cm from one end. Draw another Hine lengthwise
from the centre of the paper as shown in Fig.
Chromatographic
paper
Original line about
4 om above the edge
Point to put the
spot of the mixture
Fig. Spotting of the mixture.
2. With the help of fine capillary tube, put a drop of the mixture of
yed and blue inks at the point P. Let it dry in air. Put another drop
Fea' he same spot and dry again. Repeat 2-3 times, so that the spot
is rich in mixture.
3. Suspend the filter paper vertically in a gas Jer containing the
srtont (eluent) with the help of glass rod in such « way that the
pencil ne (and the spot) remains about 2 em cabove the solvent
jewel (50% alcohol + distilled water}.
4. Cover the jar and keep it undisturbed. Notice the rising solvent
along with the mixture of red and bine inks. After the solvent has
Sisen about 15 cm you will notice two different spots of blue and
red colours on the filter paper.
5. Take the filter paper out of the jar and mark the distanes that the
solvent has risen on the paper with a pencil. This is called the
solvent front.
6. Dry the paper. Put pencil marks in the centre of the blue and red
spots.
17, Measure the distance of the two spots from the original line and
the distance of the solvent from the original line.
8. Calculate the Rewalnes of the bine and red inks by using the
formula : ;
We eacetrevlled by the Ble o rod ink fom the point of applceto
ae =e travelled by the solvent from the original ine
After elution and drying, place the paper in a large, dry, covered beaker
containing a smaller beaker of concentrated aqueous ammonia. After
Shout two minutes, remove the paper and spray it on both sides with
ccbeanic acid reagent. Allow it to dry. Nickel becomes visible as blue
we band while cobalt becomes visible as yellow orange band.
Evaluate Rrvalues of the two ions.
Observations and Calculations:
Colour ofthe | Distance Distance Rvalues = A/K
spot travelled by travelled by
different solvent (%)
component (A}
Black 4.0 em 5.3om 0.75
component
{Ca}
|
Yellow 45cm 5.3cm 0.85
component
{Ca?"}
The above experiment can be carried by using a mixture of
(@} Tron (11) and cobalt (1) (i) Iron (i) and nickel (H}
Precautions:
1, Always make use of a fine capillary tube.
o pereue altow spots to spread while spotting the test solution on
the paper.
3, Use the capillary finely drawn to place the spot om the paper,
S De aot disturb the jar once the experiment is set as long es the
chromatogram is developed.
§. Before developing the spots, make the paper strip perfectly dry.
&. Carefully handle organic solvents.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 3-4 Autotransformer and Three Phase ConnectionDocument9 pages3-4 Autotransformer and Three Phase ConnectionSattwik MannaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (AC Circuit)Document23 pagesModule 2 (AC Circuit)Sattwik MannaNo ratings yet
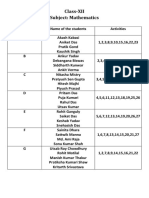
- XII Math ActivitiesDocument1 pageXII Math ActivitiesSattwik MannaNo ratings yet
- Organic Practical0001Document7 pagesOrganic Practical0001Sattwik MannaNo ratings yet