Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
Mehak KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
Mehak KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
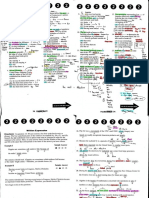
Kinematics - motion Forces
Connected Particles
Variable Acceleration -53
l
Constant Speed Constant Acceleration Method
Equilibrium
l l
a
-
-
O
• ,
, , ,
} F¥mmaa} equation of
f f standat rest forces are balanced 1)
-
motion
- - - -
T
- - - - -
- -
- - - - -
- -
- - - - - - -
- -
- - -
- -
It dist speed -
-
+ time
I Fo V= utat 1 SIK on the
point ofslipping timing equilibrium ←
= -7
r 2)
③ ¥, ( L dat §
t T
Fa s
-
wttzat
' l
Sdt constant speed T =L 3) fin Equations
751¥"wm"
-
, ooo
.
×
t
IT ' ' ate
4) SWAT
'
"
kmph ms ut Eat find after string breaks
qv yoga
f
en s -
f
v → u
-
ut
-
, a ,
\ ' after particle hitsfloor
I
Ms
"
.s kmph
+60×60 I
en V' = u 't 2.as
I fat , Vector forces •
E ,
t Eet E, =D at T T 5) New acceleration, Teo
.
b)
T
zlutvlt
n
12=51
'
Fr I a t
s More SWAT and will be
-_
\ use new a u
l m
's ,
f from before
- - -
f
-
Dynamics
- - -
- - -
- - - - -
-
-
-
- - - - -
-
- - - - -
-
said I seed Trapezium thatb) hi seed F-ma v .
§ I mg
yr
foil
,
n '
l l dist
-
at + IS!vdt/ If of the above it is mutual
.mg/deukralihg
R
dart
f
-
⇐ none
Bl
a t
v , L
, , a
R=2Tws(9029)
"
JB
"
Resolve
of 's
'
f-ma in the direction
¥µ¥me
' '
i
'
motion
using
#
l
dist i
,
.
y n ao
i'
l l
ftp.nnis.gs?g
l Te a
Te
.
'
I
' Vectors, use E-me where E is the resultant
, E ← is ka
time time "
'
,
t ,
1
E=E,tEztE, ⑤
m's
mid
negative
l l 1-
↳ area
,
\ distance travelled =
area under the line .
'
t
acceleration -_ gradient of the line -
- - -
-
Friction
T
-
- - - - -
-
- - - - - - - -
g
- - - -
'
E- at Et
fly Always the direction of motion titis about lomoveih
Rigid Bodies uniform weight acts at centre
opposes
uniform
I d
z
§¥
i
Idt
Tat
It
ja
'
E- Iot f- eotutttzat l
I tf static, Frank non :
weight doesn't act at centre
pas
i -
fast It
,
> '
l '
fat
l E- Iot et tat If limiting eguilibn.am/dynauneFr--mR
us
on the point
of
-
tg t
'
tilting about A : 12,3=0
'
l
OEM # 4 ish A
I
< B
Projectiles /
1-
'
I
Vector Motion On slopes MT
(3) 1=1423)
"
"
the direction Imax it will
my
mgtih%EF.mn
in > move down
n l yer Mgm
tugging Fry
'
, it will remain at rest
.in ,
Kl !) I
"
' "
is north-east of
the E- 18 N←
µ¥t
origin rt
T
, , o
l
↳ i.
comp comp T.fr y
tw
→x
Forces Basic
q ly
hying
> i -
i + Diagrams -
1=-1 I I
Resolving
'
→¥÷gTF"
F
-
\
-
no
'
Horizontal Motion Vertical Motion ,
W
X E
→ er
a- -
O a= -
g i N Tension ma > a ma Moments
I I Thrust Mac Mh moment -_ force perp dist / perp force
!
> x + dit
↳ connected
. -
+
-
s
Boxes boxes)Lifts (if in equilibrium)
by t I on anticlockwise = clockwise
I
Ps B
"
- - -
a-
-
A kg
-
l : m
¥ 19*44 t
Find of A
a
the speed and direction motion at Lift :L kg
Mkg using
B:
, a , ;
spied Pythagoras
a
Horizontal
} for speed "
l .
A
A B ¥3
tan " for
:[
Vertical speed direction :
, gunships ,
poor mousing
q \
Method :
A l B
Modelling Assumptions t
mlvgly il Resolve upldownt Y W
-
i
,
mg ,
smooth tension on either side of the
pulley :
pulley is equal - - - - - -
,
- - - -
-
light string :
tension is equal throughout the sting . Lift :
i Whole
system :
4 Resolve leftlnght X =P
inextensible string both I 1 it
:
particles have same acceleration
particle ignore :
air resistance , ignore rotational effects
I
*
3) Moments about A
rod so it doesn't bend it has thickness ! most xw Lasing xp
rigid , By
: =
no
, y y
.
+ obvious ones like smooth rough etc .
Lg Ny Bpuosnhifdar (Mt Mt 49
, ,
You might also like
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanEraj NoumanNo ratings yet
- ANFODocument2 pagesANFOYef PumacayoNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesComputer Architecture Cheat SheetxdslNo ratings yet
- Structural DynamicsDocument213 pagesStructural DynamicsJaime Alberto Flores PeñaNo ratings yet
- Servo Solenoid ValvesDocument204 pagesServo Solenoid Valveschandushar1604100% (1)
- Tema 6Document2 pagesTema 6Marua AbselamNo ratings yet
- The Heat EquationDocument13 pagesThe Heat EquationRahulNo ratings yet
- 17a TodayDocument1 page17a TodayAVD CONSTRUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- NC Coastal EvacDocument1 pageNC Coastal EvacStephanie Dube DwilsonNo ratings yet
- Perspective: This SiteDocument1 pagePerspective: This SiteAurelio SumeguinNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet OM Finals PDFDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet OM Finals PDFEylul KarahanNo ratings yet
- PB EnglishDocument1 pagePB EnglishSharan SethiNo ratings yet
- Vicinity Map ExampleDocument1 pageVicinity Map ExampleJenesis de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- WakeUnion Site Study Three 11-02-22 MillerArchitecture 1-60Document1 pageWakeUnion Site Study Three 11-02-22 MillerArchitecture 1-60Nancie BrennanNo ratings yet
- Site Layout FO KIK-CCTV-ARIF - New Rev1Document1 pageSite Layout FO KIK-CCTV-ARIF - New Rev1Adi PriyapurnatamaNo ratings yet
- NC Hurricane Route MapDocument1 pageNC Hurricane Route MapAnonymous X3NoCINo ratings yet
- Existing MATA NetworkDocument1 pageExisting MATA Networkmcorbet6231No ratings yet
- Creativeevolutio 00 BerguoftDocument450 pagesCreativeevolutio 00 BerguoftGabriel ProañoNo ratings yet
- Rise of The SeparatistsDocument148 pagesRise of The Separatiststhrawn74No ratings yet
- College ListDocument8 pagesCollege ListAbhrajit KarNo ratings yet
- MP DataDocument484 pagesMP DataNavdurga RetailNo ratings yet
- Steeldeck 3F PDFDocument1 pageSteeldeck 3F PDFlouie n. gustoNo ratings yet
- Steeldeck 3F PDFDocument1 pageSteeldeck 3F PDFlouie n. gustoNo ratings yet
- Modul Praktikum Perancangan Tata Letak FasilitasDocument74 pagesModul Praktikum Perancangan Tata Letak FasilitasHafidz Asy'ari AkbarNo ratings yet
- Vermont School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2014 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Document8 pagesVermont School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2014 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Lori MendezNo ratings yet
- Bme 3.2.7 PDFDocument41 pagesBme 3.2.7 PDFRosina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Project 257 DBPDocument10 pagesProject 257 DBPĐỨC LÊ QUANGNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionDocument1 pageIGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionskyeNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Understanding Learning and Learners Custom Edition 2e PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Understanding Learning and Learners Custom Edition 2e PDFferne.bass217100% (32)
- New Mexico School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Document4 pagesNew Mexico School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Gerson Tampolino AcostaNo ratings yet
- Mazowe DevelopmentDocument1 pageMazowe DevelopmentRodney ZephaniaNo ratings yet
- (H5) Setup Venture Training Matrix 1Document1 page(H5) Setup Venture Training Matrix 1basdNo ratings yet
- According To ThermodynamicDocument4 pagesAccording To Thermodynamicali madjidNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanHamza J. KhanNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanmehrunisaNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanSana Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanRehan ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanParas AliNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanArfan SialNo ratings yet
- Political Map Pakistan PDFDocument1 pagePolitical Map Pakistan PDFAtif NaeemNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanpartookNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanZaheer BaltistaniNo ratings yet
- Political Map Pakistan-1 PDFDocument1 pagePolitical Map Pakistan-1 PDFOmerNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanAhver BaigNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanUzair AhmadNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanmehrunisaNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Map PDFDocument1 pagePakistan Map PDFMaiymona ShahNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanAbdullah NaeemNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map Pakistannaveed meherNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanNazakat HussianNo ratings yet
- Political Map of PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map of PakistanFarooq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanImranNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanAhmet ÖzdenNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map Pakistansydasif78No ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanGhulam Mustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Political Map PakistanDocument1 pagePolitical Map PakistanadnanjamilNo ratings yet
- Vicinity Map - Kalamboan - 3Document1 pageVicinity Map - Kalamboan - 3reyquidong04No ratings yet
- Mars A1011Document2 pagesMars A1011Marsi BaniNo ratings yet
- BP805 BP805 BP806 BP806: Bav70 (Sot-23) Bav70 (Sot-23)Document3 pagesBP805 BP805 BP806 BP806: Bav70 (Sot-23) Bav70 (Sot-23)Adilson ManoelNo ratings yet
- India + Local Area Frequency Chart MK 20Document1 pageIndia + Local Area Frequency Chart MK 20hahsjkNo ratings yet
- A Room-by-Room Guide For Ergonomic Lighting LevelsDocument4 pagesA Room-by-Room Guide For Ergonomic Lighting LevelsshamsNo ratings yet
- RINOL Surgical Medical Industrial Flooring Application and CatalogueDocument6 pagesRINOL Surgical Medical Industrial Flooring Application and CataloguedesignfNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Girder A20 b5Document16 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Girder A20 b5IkhsanRizaldiNo ratings yet
- Autoeng Advising Document Fall 2013 Entry or EarlierDocument11 pagesAutoeng Advising Document Fall 2013 Entry or Earlieranonimus19No ratings yet
- What Is Multivariable Calculus (MVC) ?Document6 pagesWhat Is Multivariable Calculus (MVC) ?Muhammad ArshadNo ratings yet
- Astro Solar Information-EDocument1 pageAstro Solar Information-EMutoha ArkanuddinNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument6 pagesProjectile MotionArseniojakejr FloresNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: JEE (Advanced) - 2019Document40 pagesAnswers & Solutions: JEE (Advanced) - 2019Amogh VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document125 pagesChapter 1王富安No ratings yet
- Drawing Numbering System: Client: ProjectDocument23 pagesDrawing Numbering System: Client: ProjectPrasanna kumar subudhiNo ratings yet
- TYPD ExercisesDocument10 pagesTYPD ExercisesConstance Lynn'da GNo ratings yet
- The Knelson Concentrator: Application and Operation at RoseberyDocument9 pagesThe Knelson Concentrator: Application and Operation at RoseberyVivek RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Elementary Linear Algebra: Howard Anton Chris RorresDocument78 pagesElementary Linear Algebra: Howard Anton Chris Rorresdeandra isabelleNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 TransformationDocument26 pagesTopic 8 Transformationayie4256017No ratings yet
- Basic Data Viper40 15066 enDocument10 pagesBasic Data Viper40 15066 enArmando RiveraNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Electronics NanobioelectronicsDocument13 pagesEmerging Trends in Electronics Nanobioelectronicsapi-26871643100% (2)
- SOM 2-2 (Students Note)Document15 pagesSOM 2-2 (Students Note)HasmitthaNo ratings yet
- Kcet Chemistry 2015Document11 pagesKcet Chemistry 2015BURHAN0% (1)
- FEBio Theory Manual 1.0Document43 pagesFEBio Theory Manual 1.0palmajoaquin99No ratings yet
- Homework 07 ProblemsDocument6 pagesHomework 07 ProblemsBrianna ChapaNo ratings yet
- Separation of Drugs by Packed-Column Supercritical Fluid ChromatographyDocument18 pagesSeparation of Drugs by Packed-Column Supercritical Fluid ChromatographySameh QanadiloNo ratings yet
- Tackifierdispersions 100106010935 Phpapp01 PDFDocument37 pagesTackifierdispersions 100106010935 Phpapp01 PDFCarina CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Mmse Journal Vol11Document319 pagesMmse Journal Vol11Mmse JournalNo ratings yet
- KrishnaDocument9 pagesKrishnaKrishna KashyapNo ratings yet
- Derrick Scott Van Heerden - Mathemagical Music Scales, 2013Document54 pagesDerrick Scott Van Heerden - Mathemagical Music Scales, 2013Tiago Ramos100% (1)
- RTD of CSTR Observation and CalculatoinsDocument27 pagesRTD of CSTR Observation and CalculatoinsLucifer MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Cancela - Analise de TensãoDocument35 pagesCancela - Analise de TensãoMarco JustinoNo ratings yet