Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 11
CH 11
Uploaded by
Avadh Malaviya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views19 pagesOriginal Title
ch 11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views19 pagesCH 11
CH 11
Uploaded by
Avadh MalaviyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
introduction 7
nywhich -OH group IS
organic compounds i
> These are hydroxy! derivatives: of alkanes and mono alkyl dt
Their general formula is CaHtwiOH OF GaHl2n420.
> The hybridization state of Cis sp"
> Geometry is tetrahedral.
> Alcohol shows chain position and functional group is
“itm is present, they shows optical isomerism: AS
> These are the
carbon.
‘omerism If chiral carbon
ose
jased on nO of -OH group.
GoH:OH
Classification of ‘Alcohol-
1. Alcohols and phenols may be classified as ~ B
Monohydric alcohol- Contains one -O group only .Eg-
Dinydricalcohol- Contains two -OH group FgBlycol
‘Trihydric alcohol- Contains three -OH group Eg- glycerol
polyhydric alcohol- Contains more than three -OH group Eg: sorbitol
2. n the basis of the nature of the carbon to which -OH atom is attached,
hydroxl derivatives are classified as 1°, 2% 3° allylic, benzyl; vinylic and
aryl derivatives.
For example:
“On the basis ofthe nature of the carbon to which -OH atom is attached-
Compounds containing sp?C-X bond-
2» and 3° alcohol: hydroxyl atom is bonded to primary, secondary or
tertiary carbon atom of an alkyl group.
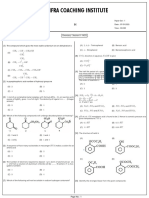
te OH oH
1+ ae Dae ee
a bk be
mama *Gisoma > “ages!”
> Allylic alcohol: -OH atom is bonded t:
'o an sp?-hybri
to carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) ie. oat ye acai oy
PRIYANKA SINGHAL 8160743860 c
sono x
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 11th, 12th (E) Question AnswerDocument8 pages11th, 12th (E) Question AnswerAvadh MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Journey To Antarctica MCQDocument8 pages3 Journey To Antarctica MCQAvadh MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 PhysicsDocument6 pagesExp 3 PhysicsAvadh MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- Infra Coaching Institute: CH CH CH Oh - CH CH - CH C Oh - CH CH CH CH Oh CH - CH CH CH CH CroDocument15 pagesInfra Coaching Institute: CH CH CH Oh - CH CH - CH C Oh - CH CH CH CH Oh CH - CH CH CH CH CroAvadh MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- Poem 1,2,3Document9 pagesPoem 1,2,3Avadh MalaviyaNo ratings yet