Professional Documents
Culture Documents
53-Article Text-113-1-10-20161018
Uploaded by
RadCalc IOL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pages53-Article Text-113-1-10-20161018
Uploaded by
RadCalc IOLCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
2016 CMBEC39 Conference
Calgary AB
May 24–27, 2016
AIM CT ACCREDITATION PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT FOR
CT X-RAY SYSTEMS
Douglas McTaggart, C.E.T., Medical Engineering Department
University Health Network,Toronto, ON
ADVANCEMENTS IN IMAGING (AIM) CT provide comprehensive image quality
ACCREDITATION PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT evaluation, dose monitoring and structured
CT reporting.
Abstract
Introduction
The University Health Network (UHN)
maintains 22 CT X-ray systems at five A comprehensive Accreditation program on
hospital locations. The problem that was computed tomography (CT) systems [1]
addressed was how to develop and should include:
implement a CT Accreditation Program at
the University Health Network. - Daily testing of Hounsfield units
- Regular Air and Water Calibration of
This program was developed to satisfy the the CT systems
needs for a standardized annual testing of - Annual Image Quality Measurement
CT dose and image quality parameters [1].
Appropriate image quality test phantoms The University Health Network has
were selected and evaluated [3]. This topic developed a program, which we call “AIM”
deals with the problem of how to develop to perform and track all components of a CT
and implement a CT Accreditation Program QA program.
for the CT systems at the University Health
Network. The project will deal with the Methods
selection of image quality and dose
phantoms, establishing baseline data
Development of the AIM interface
derived from the phantoms and storing the
data for future reference. Another challenge
We worked with our hospital’s technology
of the project was to develop a quality
department to setup a dedicated server
assurance program that will satisfy the
which manages a daily CT QA SQL database.
corporate vision of the University Health
Portals on this interface connect to clinical
Network. This vision is concerned with
and engineering Sharepoint sites. It also
achieving global impact. The work done in
features educational presentations, an
this report will be relevant to Canadian
electronic CT Service logbook and AIM
standards and incorporate global standards
Accreditation Program (AAP) document
as well.
storage and review.
A comprehensive CT Accreditation Program
was then developed and implemented. The
program was used to report on CT image
quality and dose parameters. It is
recommended that the AIM CT Accreditation
Program be used at other hospitals to
Daily CT Density QA Database APP index calculations. It has features
to measure the following parameters for
image quality analysis; Hounsfield units
(densities), slice thickness, high
contract, and low contrast. Head and
Body Annulus (CTP299/579) can be
added to the phantom to simulate the
attenuation of a 20 cm Head and 35 cm
Body. Figure 2 gives examples of the
images created by the Catphan 600.
Image Quality Reports
Reports have been developed for image
quality and dose results that can easily
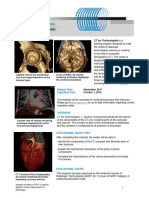
Figure 1: Screenshot of QA database be interpreted. Satisfactory results are
highlighted in “green” and poor results in
A Toshiba TOS phantom [3] is used each “red”. Figure 3 is a sample of the AAP
morning to measure the Hounsfield unit Image Quality report and. The imaging
and Standard Deviation values of six ranges are setup using acceptable levels
areas of interest. This data is then of deviation as required for optimal
entered using the AIM application and image quality.
stored on the AIM server database [1].
Please see “Figure 1: Screenshot of QA
Database” for an example of this.
Annual Image Quality Measurements
Image Quality Phantom
Figure 2: Catphan 600 Phantom images
We chose the Catphan 600 phantom [3]
Figure 3: AAP Image Quality details
as our image quality reference because it
is a current industry standard for
measuring all the necessary imaging
parameters. The high contrast module
(21 line pairs) and the low contrast
module (sub-slice and supra-slice
objects) offer a wide range of testing for
AAP Index
The AAP Index (1) was developed to
provide an overall summary of the
Image Quality measurements. The goal
of the index was to evaluate and more
accurately compare image quality on
different CT systems by providing a
complete single source evaluation that is
clinically relevant. This relevance makes
the AAP index unique to other forms of
contrast evaluation.
𝐵𝑜𝑑𝑦 𝐼𝑄+𝐻𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝐼𝑄)
𝐴𝐴𝑃 𝐼𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑥 = ( (𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐼𝑄 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒)
) 𝐷𝑅𝐿 (1)
The AAP index is calculated using high
and low contrast results from the Head
and Body image quality measurements.
Figure 4: AAP dose report
This value is then rated using UHN
Diagnostic Reference Levels (DRLs) with
Clinical Evaluation
CTDI (vol) recorded values.
The Radiation Protection Office (RPO)
Annual Dose Measurement
provides an audit of our QA process and
AAP reports. RPO review is necessary to
CT dose index (CTDI) is a standardized
maintain a complete CT Accreditation
measurement of radiation dose output of
Program. The RPO can also conduct a
a CT scanner which allows the user to
clinical image review of standard
compare radiation output of different CT
protocols and Diagnostic Reference
scanners. AAPM Summit reporting on CT
Levels.
dose indicates the use of standardized
dose phantoms to measure average head
Conclusion
and body dose values [4].
The AIM CT Accreditation program has
CTDI dose values are measured using
been operating for 8 years. We are
routine Head and Body Clinical CT
continually improving it with clinical
protocols with the CTP 553/554 16cm
involvement and engineering
Head dose phantom and 32cm Body
enhancements. The clinical feedback has
dose phantom. A RADCAL 9096 dose
been very positive and the program is
meter with a CT pencil probe is used to
now considered a necessary tool to
measure average dose values in the
provide enhanced patient care.
Head and Body phantoms. CTDI dose
values are calculated and compared to
console values. Figure 4 is a sample of
the AAP Dose Report.
AAP Future Development
AAP development includes setting new
standards in AAP reporting, Clinical
protocols and CT Diagnostic Reference
Levels. The goal is to establish a network
of partnership hospitals across Canada to
share CT image quality and dose working
based on a common standard. We have
begun work with an image quality
program software development team at
UHN (“AQUA” of Acumyn) at UHN to
further enhance database and dose
measuring capabilities. This will enable
our team to track image quality trends
more closely and assist with scheduling
annual testing.
Hospitals can work together to form a
stronger knowledge base and share new
ideas.
REFERENCES
[1] American College of Radiology, CT Accreditation
Program Requirements, pp. 1-16, Revised 10-4-11
[2] Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation, Installation Manual
2C201-175EN, vol. TSX-101A, pp. 208-209, 2005.
[3] The Phantom Laboratory, Catphan 500 and 600
Manual, pp. 3-36, 2013.
[4] Michael McNitt-Gray, PhD, David Geffen School of
Medicine at UCLA, pp. 2-55, AAPM 2011 Summit on CT
Dose.
You might also like
- 10 1259@dmfr 20190229Document17 pages10 1259@dmfr 20190229Yady S. Londoño L.No ratings yet
- qt5550b9jz NosplashDocument6 pagesqt5550b9jz NosplashPartha ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- COMP Report: CPQR Technical Quality Control Guidelines For CT SimulatorsDocument6 pagesCOMP Report: CPQR Technical Quality Control Guidelines For CT SimulatorsEskadmas BelayNo ratings yet
- Arts Paper UpdatedDocument8 pagesArts Paper UpdatedChristopher Scott RoseNo ratings yet
- CT Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality GuideDocument47 pagesCT Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality GuideAndreasNo ratings yet
- معايرة جهاز ct PDFDocument16 pagesمعايرة جهاز ct PDFmouazNo ratings yet
- Ei Values CarestreamDocument2 pagesEi Values Carestreamapi-276884981100% (1)
- A Software Tool For Quality Assurance of Computed / Digital Radiography (CR/DR) SystemsDocument11 pagesA Software Tool For Quality Assurance of Computed / Digital Radiography (CR/DR) SystemsYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- CTsimDocument40 pagesCTsimServicios Radfis C.a.No ratings yet
- Radiotherapy and OncologyDocument7 pagesRadiotherapy and Oncologyface bookNo ratings yet
- Physics and Imaging in Radiation OncologyDocument6 pagesPhysics and Imaging in Radiation Oncologydarr artNo ratings yet
- A Routine Quality Assurance Test For CT Automatic Exposure Control SystemsDocument16 pagesA Routine Quality Assurance Test For CT Automatic Exposure Control SystemsrenatafisicamNo ratings yet
- MRI Quality Assurance Using The ACR Phantom in A Multi Unit Imaging CenterDocument8 pagesMRI Quality Assurance Using The ACR Phantom in A Multi Unit Imaging CenterJulio MartiniNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Cone-Beam CT Imaging in Radiotherapy Parallel Computation and Comprehensive Evaluation On The TrueBeam SystemDocument8 pagesQuantitative Cone-Beam CT Imaging in Radiotherapy Parallel Computation and Comprehensive Evaluation On The TrueBeam SystemKe LuNo ratings yet
- CT For Techs System ComponentsDocument32 pagesCT For Techs System ComponentsB YNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics - 2021 - Praagh - Fully Automated Quantification Method FQM of Coronary Calcium in An AnthropomorphicDocument12 pagesMedical Physics - 2021 - Praagh - Fully Automated Quantification Method FQM of Coronary Calcium in An AnthropomorphicAmril MukminNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance For Image-Guided Radiation Therapy Utilizing CT-basedDocument18 pagesQuality Assurance For Image-Guided Radiation Therapy Utilizing CT-based2016508吳翊晨No ratings yet
- DH AI Rad Companion Chest CT Whitepaper 2Document18 pagesDH AI Rad Companion Chest CT Whitepaper 2titelcosminelNo ratings yet
- Overview of Artificial Intelligence-Based ApplicatDocument12 pagesOverview of Artificial Intelligence-Based ApplicatMilo VanvanNo ratings yet
- 1361 6498/aa8f61Document28 pages1361 6498/aa8f61mehedihasantito2510No ratings yet
- Image Quality Standards For Digital Imaging and Interventional RadiologyDocument8 pagesImage Quality Standards For Digital Imaging and Interventional RadiologyAnonymous 2gLSPeNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTDocument27 pagesPractical Exercise: Effective Dose Estimate in CTHarley Alejo MNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer Detection From CT Image UsinDocument11 pagesLung Cancer Detection From CT Image UsinJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- ISO-GUM and Supplements Are Utilized For QA of BCA Data: Yasuo IwakiDocument31 pagesISO-GUM and Supplements Are Utilized For QA of BCA Data: Yasuo IwakiKemo TufoNo ratings yet
- Aapm TG 179Document18 pagesAapm TG 179Ahmet Kürşat ÖzkanNo ratings yet
- Aapm TG 142 PDFDocument47 pagesAapm TG 142 PDFAde RianaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Lung Cancer in CT Images Using Image ProcessingDocument4 pagesDetection of Lung Cancer in CT Images Using Image ProcessingDharpure Mr. Harshal Namdeorao --No ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Computed and Digital Radiography SystemsDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance of Computed and Digital Radiography SystemsYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Chaudhary2012 PDFDocument5 pagesChaudhary2012 PDFSnehaNo ratings yet
- Recommendations For A Digital Mammography Quality Assurance Program v3.0Document47 pagesRecommendations For A Digital Mammography Quality Assurance Program v3.0Anonymous 2gLSPeNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Assessment of Computed Radiography Quality Control ParametersDocument19 pagesQuantitative Assessment of Computed Radiography Quality Control ParametersrezaczNo ratings yet
- Application of QC DR Software For AcceptDocument11 pagesApplication of QC DR Software For AcceptRiyanto Dhiya FikriNo ratings yet
- New 2014 Joint Commission Accreditation Standards For Diagnostic Imaging Services - Ambulatory Care CentersDocument6 pagesNew 2014 Joint Commission Accreditation Standards For Diagnostic Imaging Services - Ambulatory Care CentersaegysabetterwayNo ratings yet
- Computed TomographyDocument4 pagesComputed TomographyemilyNo ratings yet
- IQAWCEDocument8 pagesIQAWCEAbdulahi AbebeNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation System For Pacs: Dinu Dragan, Dragan IveticDocument9 pagesA Comprehensive Quality Evaluation System For Pacs: Dinu Dragan, Dragan IveticUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Kim 2010Document13 pagesKim 2010face bookNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer Detection by Using Image Processing Approach: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesLung Cancer Detection by Using Image Processing Approach: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and EngineeringROHITH KATTANo ratings yet
- 2014 Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels in Computed Tomography For Select Procedures in Pudhuchery, IndiaDocument14 pages2014 Establishment of Diagnostic Reference Levels in Computed Tomography For Select Procedures in Pudhuchery, Indiap110054No ratings yet
- Ecr2015 C-2035Document23 pagesEcr2015 C-2035eka juliantaraNo ratings yet
- H2 PDFDocument110 pagesH2 PDFCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Dictionary Learning Based Low Dose Helical CT Reconstruction With Longitudinal TV ConstraintDocument1 page2017 - Dictionary Learning Based Low Dose Helical CT Reconstruction With Longitudinal TV ConstraintL AndyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine Instrumentation QC GUIDELINES Maria Lyra Et Al 2007Document69 pagesNuclear Medicine Instrumentation QC GUIDELINES Maria Lyra Et Al 2007knno87No ratings yet
- Surveying Dose Levels For Computed Radiography in The UKDocument18 pagesSurveying Dose Levels For Computed Radiography in The UKMatheus AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Imaging Informatics To Prevent Harm: John F Kalafut PHDDocument53 pagesImaging Informatics To Prevent Harm: John F Kalafut PHDJohn KalafutNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Test and Clinical Commissioning of CT SDocument8 pagesAcceptance Test and Clinical Commissioning of CT SEskadmas BelayNo ratings yet
- Ge Healthcare Discovery Pet CT 710 CT Scan MachineDocument3 pagesGe Healthcare Discovery Pet CT 710 CT Scan MachineMadan KumarNo ratings yet
- J Applied Clin Med Phys - 2020 - Mehrens - Survey Results of 3D CRT and IMRT Quality Assurance PracticeDocument7 pagesJ Applied Clin Med Phys - 2020 - Mehrens - Survey Results of 3D CRT and IMRT Quality Assurance Practicephutycharm15No ratings yet
- Iterative Reconstruction 1-s2.0-S0720048X18303747-mainDocument8 pagesIterative Reconstruction 1-s2.0-S0720048X18303747-mainMurilo AssunçãoNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer Detection Using Digital Image Processing On CT Scan ImagesDocument7 pagesLung Cancer Detection Using Digital Image Processing On CT Scan ImagesShaka TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation CR SystemsDocument11 pagesPerformance Evaluation CR SystemsWahyu WidhiantoNo ratings yet
- Rev3.20 Guidelines For The Use of Radiomics in NRG Oncology Clinical Trials Involving Brain TumorsDocument3 pagesRev3.20 Guidelines For The Use of Radiomics in NRG Oncology Clinical Trials Involving Brain TumorsarifpharmjuNo ratings yet
- Implementation of a Remote and Automated Quality Control Programme for Radiography and Mammography EquipmentFrom EverandImplementation of a Remote and Automated Quality Control Programme for Radiography and Mammography EquipmentNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar by Pavan KumarDocument18 pagesTechnical Seminar by Pavan KumarPavan KolisettyNo ratings yet
- Radiation Dose Modulation Techniques MDCTDocument10 pagesRadiation Dose Modulation Techniques MDCTFelipe Gustavo Tercero Vega AbantoNo ratings yet
- Affordable and Mountable Dosimeter For X-Ray 2Document32 pagesAffordable and Mountable Dosimeter For X-Ray 2Rad Biomedical Engineering PLCNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Diagnostic X-Ray DepartmentDocument33 pagesQuality Control in Diagnostic X-Ray Departmentemmaudofia20033171100% (15)
- ACR Quality Control - MRI - Breast MRI (Revised 10-21-2020) - Accreditation SupportDocument5 pagesACR Quality Control - MRI - Breast MRI (Revised 10-21-2020) - Accreditation SupportJulio MartiniNo ratings yet
- A NIM PETCT Phantom For Evaluating The PET Image Quality of Micro Lesions and The Performance Parameters of CTDocument13 pagesA NIM PETCT Phantom For Evaluating The PET Image Quality of Micro Lesions and The Performance Parameters of CTp110054No ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Recording, Reconstruction and AssessmentFrom EverandMagnetic Resonance Imaging: Recording, Reconstruction and AssessmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Xing 1999Document17 pagesXing 1999RadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- Zhu Et Al-2009-Medical PhysicsDocument32 pagesZhu Et Al-2009-Medical PhysicsRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- AAPM Medical Physics Practice Guideline 2.a - Commissioning and Quality Assurance of X Ray Based Image Guided Radiotherapy SystemsDocument11 pagesAAPM Medical Physics Practice Guideline 2.a - Commissioning and Quality Assurance of X Ray Based Image Guided Radiotherapy SystemsRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- 08followill TG 51ClinicalIssuesDocument33 pages08followill TG 51ClinicalIssuesRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1507136716300864 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1507136716300864 MainRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- IMRT Implementation and Patient Specific Dose Verification With Film and Ion Chamber Array DetectorsDocument16 pagesIMRT Implementation and Patient Specific Dose Verification With Film and Ion Chamber Array DetectorsRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- Multi-Parametric Improvements in The CCD Camera-Based EPID For Portal DosimetryDocument13 pagesMulti-Parametric Improvements in The CCD Camera-Based EPID For Portal DosimetryRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- Mellenberg 1990Document5 pagesMellenberg 1990RadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- NBS 79Document48 pagesNBS 79RadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Dosimetry - MOSkin Dosimetric Characteristics in A 6MV X-RaDocument108 pagesMOSFET Dosimetry - MOSkin Dosimetric Characteristics in A 6MV X-RaRadCalc IOLNo ratings yet
- "Organized Crime" and "Organized Crime": Indeterminate Problems of Definition. Hagan Frank E.Document12 pages"Organized Crime" and "Organized Crime": Indeterminate Problems of Definition. Hagan Frank E.Gaston AvilaNo ratings yet
- Passage To Abstract Mathematics 1st Edition Watkins Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesPassage To Abstract Mathematics 1st Edition Watkins Solutions ManualMichaelWilliamscnot100% (50)
- Designed For Severe ServiceDocument28 pagesDesigned For Severe ServiceAnthonyNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Intelligence As A Predictor of Outcome in Short-And Long-Term PsychotherapyDocument9 pages2014 - Intelligence As A Predictor of Outcome in Short-And Long-Term PsychotherapyZayne CarrickNo ratings yet
- Rsi r2 Super Rsi FaqDocument14 pagesRsi r2 Super Rsi FaqChandrasekar Chandramohan100% (1)
- The Essence of Technology Is by No Means Anything TechnologicalDocument22 pagesThe Essence of Technology Is by No Means Anything TechnologicalJerstine Airah SumadsadNo ratings yet
- MLX90614Document44 pagesMLX90614ehsan1985No ratings yet
- TIA Guidelines SingaporeDocument24 pagesTIA Guidelines SingaporeTahmidSaanidNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Civil Engineers PiceDocument3 pagesCode of Ethics For Civil Engineers PiceEdwin Ramos Policarpio100% (3)
- Homework 9Document1 pageHomework 9Nat Dabuét0% (1)
- Core CompetenciesDocument3 pagesCore Competenciesapi-521620733No ratings yet
- TTDM - JithinDocument24 pagesTTDM - JithinAditya jainNo ratings yet
- Uniform Motion WorksheetDocument8 pagesUniform Motion Worksheetnikhil patro100% (1)
- Strategic Management SlidesDocument150 pagesStrategic Management SlidesIqra BilalNo ratings yet
- Aashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDocument1 pageAashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDem DemNo ratings yet
- Anker Soundcore Mini, Super-Portable Bluetooth SpeakerDocument4 pagesAnker Soundcore Mini, Super-Portable Bluetooth SpeakerM.SaadNo ratings yet
- Approvals Management Responsibilities and Setups in AME.B PDFDocument20 pagesApprovals Management Responsibilities and Setups in AME.B PDFAli LoganNo ratings yet
- Tomb of Archimedes (Sources)Document3 pagesTomb of Archimedes (Sources)Petro VourisNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Compressive Strength of Research PaperDocument9 pagesPrediction of Compressive Strength of Research PaperTaufik SheikhNo ratings yet
- 06 SAP PM Level 1 Role Matrix Template SampleDocument5 pages06 SAP PM Level 1 Role Matrix Template SampleRiteshSinhmar100% (1)
- BPS C1: Compact All-Rounder in Banknote ProcessingDocument2 pagesBPS C1: Compact All-Rounder in Banknote ProcessingMalik of ChakwalNo ratings yet
- ISO Position ToleranceDocument15 pagesISO Position ToleranceНиколай КалугинNo ratings yet
- Transportation of CementDocument13 pagesTransportation of CementKaustubh Joshi100% (1)
- Configuration Guide - Interface Management (V300R007C00 - 02)Document117 pagesConfiguration Guide - Interface Management (V300R007C00 - 02)Dikdik PribadiNo ratings yet
- Saflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetDocument5 pagesSaflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetrasheedgotzNo ratings yet
- JUnit 5 User GuideDocument90 pagesJUnit 5 User GuideaawaakNo ratings yet
- Jinivefsiti: Sultan LorisDocument13 pagesJinivefsiti: Sultan LorisSITI HAJAR BINTI MOHD LATEPINo ratings yet
- Cap1 - Engineering in TimeDocument12 pagesCap1 - Engineering in TimeHair Lopez100% (1)
- Executive Summary: 2013 Edelman Trust BarometerDocument12 pagesExecutive Summary: 2013 Edelman Trust BarometerEdelman100% (4)
- SAMPLE MCQuestions ByTopicsDocument45 pagesSAMPLE MCQuestions ByTopicsVeeru ManikantaNo ratings yet