Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemoglobin
Uploaded by
Cutepolaris GurlzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemoglobin
Uploaded by
Cutepolaris GurlzCopyright:
Available Formats
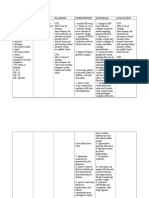
Nursing Care Plan
Return to Care Plan Listing <a href="pt_google_search.htm"> Search Page</a>
Medical Diagnoses: Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiac, renal, cerebral). Decreased hemoglobin concentration in blood, exchange problems, impaired transport of oxygen and interruption of blood flow secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage
Assessment Nursing DX/Clinical Problem Problem Client Goals/Desired Outcomes/Objectives Long Term: Client will verbalize knowledge of their treatment regimen, including appropriate exercise and medications, their actions and possible side effects by [date] at 16:00. Nursing Interventions/Actions/Orders and Rationale
Subjective: Daughter reported patient exhibited mood swings and periods of confusion. Client expressed she didnt want to move anymore than she has to. Hx of DM II, CAD Objective: Temp: 101.0 Basilar rales bilaterally Elevated BP (145/86) Elevated HR (110) Client is in atrial fibrillation w/ rapid ventricular response EKG findings of inferior infarction and left axis deviation Decreased grips/weakness on left side
Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiac, renal, cerebral)
-Assess current level of knowledge r/t treatment regimen, exercise and medications. -Aggressively counsel the patient to stop smoking and refer to the physician for medications to support nicotine withdrawal and a smoking withdrawal program. There is a 45% smaller hyperemic vascular responsive in smokers than non-smokers (Noble, Voegeli, McClough, 2003). -Teach client the treatment regimen, exercise goals and plan, and medication regimen along with actions and side effects. All interventions to be evaluated [date], 16:00. -Monitor for s/s of heart failure and decreased cardiac output; listen to heart sounds, lung sounds; note symptoms. -If symptoms of renal failure, cardiac failure or another CVA occur, notify the physician immediately. -Monitor peripheral pulses. If there is a new onset of loss of pulses with bluish, purple or
R/T Decreased hemoglobin concentration in blood, exchange problems, impaired transport of oxygen and interruption of blood flow secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage
Short Term: Client will demonstrate adequate tissue perfusion AEB blood pressure, pulse rate and rhythm within normal parameters for client; strong peripheral pulses, and ability to tolerate activity without
Decreased urine output (0 ml/10 hours) Elevated potassium level of 5.3 Elevated BUN (41) Elevated Creatinine (1.73) Post-CVA
AEB: Altered mental status, behavior changes, changes in papillary reactions, difficulty in swallowing, left side extremity weakness, right side hemiparesis, altered BP outside of acceptable parameters, oliguria (0 ml/10 hr), elevated BUN (41), elevated creatinine (1.73), dysrhythmias, altered respiratory rate (24).
dyspnea, syncope or chest pain, and increased urine output by [date] at 16:00.
black areas and extreme pain, notify the physician immediately. -Monitor neuro status frequently -Administer oxygen via nasal cannula to increase O2 to at least 92% as ordered
Return to Table of Contents <a href="pt_google_search.htm"> Search Page</a>
You might also like
- Portal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPortal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term ObjectiveDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNDocument42 pagesHeart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument14 pagesCongestive Heart Failurelolo0880No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertensionanon_9189425950% (2)
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- HYPERTENSIONDocument5 pagesHYPERTENSIONRajesh RamanNo ratings yet
- Course Task Week 7 NCMB 312Document6 pagesCourse Task Week 7 NCMB 312Angie BaylonNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDocument6 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Exercise: Cristi Day RN, MSN, FNP-C Texas A&M University - Corpus ChristiDocument19 pagesCare Plan Exercise: Cristi Day RN, MSN, FNP-C Texas A&M University - Corpus ChristiPhyu Lin0% (1)
- Management of Hypertensive EmergencyDocument17 pagesManagement of Hypertensive EmergencyGiovanna AlguNo ratings yet
- Decreased Urine OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Urine OutputSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- Pemicu 1 KGD: Muhammad Fahmi Rosyadi 405140220Document137 pagesPemicu 1 KGD: Muhammad Fahmi Rosyadi 405140220fahmi rosyadiNo ratings yet
- Sim Questions CHFDocument5 pagesSim Questions CHF5Dragoon5No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NadlawanflorianneNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPRobby James Rabe100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure ReportDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure ReportSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (1)
- Blood Circulation System 10 PDFDocument29 pagesBlood Circulation System 10 PDFSardar jiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure New SlidesDocument41 pagesHeart Failure New SlidesjawadNo ratings yet
- Heart To HeartDocument110 pagesHeart To HeartmahyorwaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument38 pagesCardiovascular Disordersmark100% (4)
- Braunwald Lecture Series #2Document33 pagesBraunwald Lecture Series #2usfcards100% (2)
- Hypertension AlgorithmDocument3 pagesHypertension AlgorithmCharlene Robelle LocaylocayNo ratings yet
- Integrated Therapeutics IiiDocument160 pagesIntegrated Therapeutics IiiSalahadinNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP and DSDocument6 pagesNCP and DSfranzcatchie100% (1)
- Hypertension Management 2009Document6 pagesHypertension Management 2009Samnai RifaiNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- Hypertension NCPDocument4 pagesHypertension NCPChristian Karl B. Llanes0% (2)
- Uncontrolled Blood PressureDocument6 pagesUncontrolled Blood PressureFika SilviaNo ratings yet
- HIPERTENSI Untuk MahasiswaDocument34 pagesHIPERTENSI Untuk MahasiswaSarah HaerumanNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis CHFDocument4 pagesMedical Diagnosis CHFKenneth Smith IINo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonathan LiscanoNo ratings yet
- Anti HypretensivesDocument18 pagesAnti HypretensivesLeena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Anti HypretensivesDocument18 pagesAnti HypretensivesLeena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3Document42 pagesPharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3sho bartNo ratings yet
- Plan of Care 1Document9 pagesPlan of Care 1api-629160093No ratings yet
- Altered Cerebral PerfusionDocument3 pagesAltered Cerebral PerfusionRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- CHF Preparation QuestionsDocument6 pagesCHF Preparation Questionsgenium0689% (9)
- CHFDocument35 pagesCHFMarione GimenezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SurgeryDocument19 pagesCardiac SurgerySimon JosanNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- Shock in The Pediatric Patient: or Oxygen Don't Go Where The Blood Won't Flow!Document63 pagesShock in The Pediatric Patient: or Oxygen Don't Go Where The Blood Won't Flow!Nishanth BabuNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in CVSDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument12 pagesHypovolemic ShockHassanal DimaporoNo ratings yet
- CHF Concept MapDocument4 pagesCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsDocument125 pagesDrugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- HTN - Emerg EDDocument37 pagesHTN - Emerg EDAyesh EKNo ratings yet
- HTNDocument54 pagesHTNapi-232466940No ratings yet
- NCP 2Document5 pagesNCP 2Donna Co IgNo ratings yet
- 11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument85 pages11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJaps De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in HF IIDocument40 pagesDrugs Used in HF IIJamal LudinNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet