Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rigid 3
Uploaded by
Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
Rigid-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageRigid 3
Uploaded by
Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
j
θy
y k My
i θx
x l MX
z w, Fz
Figure (2): Coordinate system, forces and corresponding displacements in the rectangular
plate element
5. Effect of the Raft Foundation Rigidity
For the typical and symmetric raft foundation shown in figure (3), a parametric study
is carried out in order to investigate the effect of the flexural rigidity (thickness) on the
analysis. The following values are used:
L= 6.0 m, d=0.5 m, column dimensions: 0.4 m x 0.4 m, column load = 1.0 MN, modulus
of elasticity for the raft material = 21 GPa, modulus of subgrade reaction for the
supporting soil (k) = 80 MN/m3 and the thickness (t) is variable.
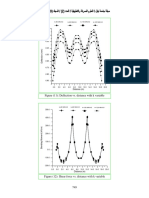
In figures (4), (5), (6) and (7), the adopted thicknesses were 0.4 m, 0.6 m, 0.8 m and
1.0 m respectively. In each case, the reaction of the soil is drawn against the distance
along the raft for both an interior column strip and a central middle strip of the raft, and
the finite element pressure is compared to the uniform pressure, which is calculated by
the conventional rigid method (i.e.: total load / total area).
Figure (8) represents the deflected shape of a section under an interior columns line
with various values of the raft thickness (t), while figures (9) and (10) show the bending
moments and shear forces respectively, drawn for an interior column strip.
743
You might also like
- Stability and Vibration of Initially Stressed Plates Composed of Spatially Distributed Fiber CompositesDocument19 pagesStability and Vibration of Initially Stressed Plates Composed of Spatially Distributed Fiber CompositesFranco VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Cross-Ply Laminated Beams With General Boundary Conditions by Ritz MethodDocument16 pagesVibration Analysis of Cross-Ply Laminated Beams With General Boundary Conditions by Ritz MethodHakim KaciNo ratings yet
- Manuscript 3Document25 pagesManuscript 3Julian OssaNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab by FemDocument8 pagesFlat Slab by Femanuj kumarNo ratings yet
- Nme 1620361106Document25 pagesNme 1620361106Miguel SerraNo ratings yet
- MCHE485 Final Spring2018Document7 pagesMCHE485 Final Spring2018Mahdi KarimiNo ratings yet
- Exercises3120 PDFDocument82 pagesExercises3120 PDFJames MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Bertagnoli Carbone Giordano Mancini 1Document8 pagesBertagnoli Carbone Giordano Mancini 1deba_jyoti_dasNo ratings yet
- Stress Concentration Factor Measurement of Tensile Plate With Circular and Elliptical Hole by Digital Hybrid Photoelastic ExperimentDocument4 pagesStress Concentration Factor Measurement of Tensile Plate With Circular and Elliptical Hole by Digital Hybrid Photoelastic ExperimentYasser BahaaNo ratings yet
- Composite Cantilever PlatesDocument7 pagesComposite Cantilever PlatesDharmeswar SahNo ratings yet
- 1988 Finite Element Analysis of Stability of Thin-Walled Beams of Open SectionDocument15 pages1988 Finite Element Analysis of Stability of Thin-Walled Beams of Open SectionHussein M. H. Al-KhafajiNo ratings yet
- On The Theory of Transverse Bending of Elastic PlatestDocument10 pagesOn The Theory of Transverse Bending of Elastic PlatestArthur LeandroNo ratings yet
- Fu 1998Document19 pagesFu 1998nevinkoshyNo ratings yet
- Bending Response of FGM Plate Under Sinusoidal Line Load.Document9 pagesBending Response of FGM Plate Under Sinusoidal Line Load.International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Brannon - Large Deformation KinematicsDocument66 pagesBrannon - Large Deformation KinematicsPatrick SummersNo ratings yet
- XTRACT: A Tool For Axial Force - Ultimate Curvature InteractionsDocument9 pagesXTRACT: A Tool For Axial Force - Ultimate Curvature InteractionscvlengNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Behavior of Laminated Glass Plates, Challenging Glass 7Document10 pagesDynamic Behavior of Laminated Glass Plates, Challenging Glass 7Felipe SimõesNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Computational Analysis oDocument10 pagesTheoretical and Computational Analysis oAmal SmimineNo ratings yet
- Albuquerque 2002Document4 pagesAlbuquerque 2002Boris Atenas NuñezNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Stability Analysis of Composite Plates Including Delaminations Using A Higher Order Theory and Transformation Matrix ApproachDocument17 pagesDynamic Stability Analysis of Composite Plates Including Delaminations Using A Higher Order Theory and Transformation Matrix ApproachRakshith H SNo ratings yet
- Ceoff Friction LabDocument3 pagesCeoff Friction LabAman YadavNo ratings yet
- Geometric Aspects of The Lame Equation and Plate TDocument9 pagesGeometric Aspects of The Lame Equation and Plate TSanu SharmaNo ratings yet
- V.OPROIU, N.PAPAGHIUC - SOME NEW Geometric Structures of Natural Lift Type On The Tangent BundleDocument14 pagesV.OPROIU, N.PAPAGHIUC - SOME NEW Geometric Structures of Natural Lift Type On The Tangent BundleVasile OproiuNo ratings yet
- A Constitutive Model For Jointed Rock Mass PDFDocument7 pagesA Constitutive Model For Jointed Rock Mass PDFSergio CastroNo ratings yet
- Finite Strip MethodDocument23 pagesFinite Strip MethodNirav SoniNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Professional HandbookDocument13 pagesRisk Management Professional HandbookYorman LPNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structures Cvle 6111Document9 pagesAdvanced Structures Cvle 6111NKWENTI FLAVIOUS TANUENo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells - Chapter - Encyclopedia of Aerospace Engineering - 2010 PDFDocument10 pagesPlates and Shells - Chapter - Encyclopedia of Aerospace Engineering - 2010 PDFOSCARDELTANo ratings yet
- 146 - Sandwich Plate - FULL - FINALDocument6 pages146 - Sandwich Plate - FULL - FINALSubhankar PramanikNo ratings yet
- Oscillation and Stability in A Mass Spring System: June 2018Document7 pagesOscillation and Stability in A Mass Spring System: June 2018Diana ApetreiNo ratings yet
- A Constitutive Model For Jointed Rock MassDocument7 pagesA Constitutive Model For Jointed Rock MassHồ Xuân NamNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Impact Response of Doubly Curved Composite ShellsDocument6 pagesNonlinear Impact Response of Doubly Curved Composite ShellsVenkata Swamy Naidu NeigapulaNo ratings yet
- 524766.beam Structural Modelling in HydroelasticityDocument30 pages524766.beam Structural Modelling in Hydroelasticityمجتبی فرامرزیNo ratings yet
- 1 Modeling Crack Singularities in FEM/X-FEMDocument11 pages1 Modeling Crack Singularities in FEM/X-FEMmilad66tehNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials and StructuresDocument25 pagesMechanics of Materials and StructuresSubodh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction: 1.1 Contents of Theory of ElasticityDocument9 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: 1.1 Contents of Theory of ElasticitySreekumar RajendrababuNo ratings yet
- A Simple Method For Determining Large Deflections (M Sitar)Document14 pagesA Simple Method For Determining Large Deflections (M Sitar)Jason UchennnaNo ratings yet
- Research Letter: An Analytical Description of The Frictional Behaviour of A Titanium AlloyDocument4 pagesResearch Letter: An Analytical Description of The Frictional Behaviour of A Titanium Alloykannanmech87No ratings yet
- Deformation PDFDocument66 pagesDeformation PDFRicardo ColosimoNo ratings yet
- Shell Elements ABAQUSDocument45 pagesShell Elements ABAQUSSsr Saane71% (7)
- Fatigue Life Prediction of Notched Composite Components: and A. PlumtreeDocument15 pagesFatigue Life Prediction of Notched Composite Components: and A. PlumtreeJian XuNo ratings yet
- V.OPROIU - Hyper-Kahler Structures On The Tangent Bundle of A Kahler MainfoldDocument16 pagesV.OPROIU - Hyper-Kahler Structures On The Tangent Bundle of A Kahler MainfoldVasile OproiuNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machine-5Document2 pagesDynamics of Machine-5ABIR ROYNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Gauge FieldsDocument24 pagesGeometry of Gauge FieldsZaratustra NietzcheNo ratings yet
- BEM1Document4 pagesBEM1Andrijana KuharNo ratings yet
- Design of Domes For Polymeric Composite Pressure Vessels-Hojjati1995Document9 pagesDesign of Domes For Polymeric Composite Pressure Vessels-Hojjati1995Hiến Đinh VănNo ratings yet
- Metals 10 00491 v2Document16 pagesMetals 10 00491 v2Nishar Alam Khan 19MCD0042No ratings yet
- Chen-Li2013 Article Size-dependentFreeVibrationAnaDocument15 pagesChen-Li2013 Article Size-dependentFreeVibrationAnaSilas Sverre ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Torsion PDFDocument20 pagesTorsion PDFBryan VillalobosNo ratings yet
- TFT Construction of RCFT Correlators V: Proof of Modular Invariance and FactorisationDocument91 pagesTFT Construction of RCFT Correlators V: Proof of Modular Invariance and Factorisationjsdmf223No ratings yet
- CJK-OSM 6 (Kyoto) Full-PaperDocument8 pagesCJK-OSM 6 (Kyoto) Full-PaperMasaaki MikiNo ratings yet
- A New Layerwise Trigonometric Shear Deformation Theory For Two-Layered Cross-Ply BeamsDocument13 pagesA New Layerwise Trigonometric Shear Deformation Theory For Two-Layered Cross-Ply BeamsHichem SofNo ratings yet
- Partial: Texture AnalysisDocument17 pagesPartial: Texture AnalysisMohamed YousufNo ratings yet
- Discrete Crack Modeling in Concrete StructuresDocument16 pagesDiscrete Crack Modeling in Concrete StructuresjahidNo ratings yet
- amm 638-640 1716Document5 pagesamm 638-640 1716Raymond FuentesNo ratings yet
- Infilled Frames: Influence of Vertical Load On The Equivalent Diagonal Strut ModelDocument8 pagesInfilled Frames: Influence of Vertical Load On The Equivalent Diagonal Strut ModelΦελήνε ΓιαννοπάπουNo ratings yet
- Response of Sliding Structures To Harmonic Support MotionDocument12 pagesResponse of Sliding Structures To Harmonic Support MotionAbdul Monish SheikhNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Study Material PDFDocument35 pagesSolid Mechanics Study Material PDFirinat101No ratings yet
- 14Document1 page14Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Concluding RemarksDocument1 pageConcluding RemarksArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 13Document1 page13Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 16Document1 page16Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 3Document1 pageExhibit 3Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 4Document1 pageExhibit 4Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Barto Thesis 2020Document34 pagesBarto Thesis 2020Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 5Document1 pageExhibit 5Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 2Document1 pageExhibit 2Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 1Document1 pageExhibit 1Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 4Document1 pageRigid 4Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 2Document1 pageRigid 2Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 1Document1 pageRigid 1Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Dark Side of Thermal ProjectsDocument117 pagesDark Side of Thermal ProjectsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- SRAS ChemicalDocument22 pagesSRAS ChemicalArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Eq - Madhya PradeshDocument1 pageEq - Madhya PradeshArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Iscience: Systematic Characterization of Wing Mechanosensors That Monitor Airflow and Wing DeformationsDocument23 pagesIscience: Systematic Characterization of Wing Mechanosensors That Monitor Airflow and Wing DeformationsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response of Concrete Frame Structure Under A Blasting Demolition EnvironmentDocument15 pagesDynamic Response of Concrete Frame Structure Under A Blasting Demolition EnvironmentArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- APL - Cantilever SupportDocument11 pagesAPL - Cantilever SupportArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Temperature Effects On Concrete Structure Cracks by ANSYS: Li Yan, Nie Hui, Wang TonghuiDocument4 pagesTemperature Effects On Concrete Structure Cracks by ANSYS: Li Yan, Nie Hui, Wang TonghuiArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Seismic Response Analysis Of Reinforced Concrete Chimneys Nonlinear Seismic Response Analysis Of Reinforced Concrete Chimneys 金 秀 禧 ,塩 原 等Document7 pagesNonlinear Seismic Response Analysis Of Reinforced Concrete Chimneys Nonlinear Seismic Response Analysis Of Reinforced Concrete Chimneys 金 秀 禧 ,塩 原 等Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Publications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleDocument63 pagesPublications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Technical Note No. 6Document4 pagesFly Ash Technical Note No. 6Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Predict Local Site Effects Related To Blast-Induced Ground VibrationsDocument8 pagesA New Approach To Predict Local Site Effects Related To Blast-Induced Ground VibrationsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Tal 617Document21 pagesTal 617Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Earthquake Response Analysis of Tall Reinforced Concrete Chimneys Considering EccentricityDocument21 pagesResearch Article: Earthquake Response Analysis of Tall Reinforced Concrete Chimneys Considering EccentricityArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Cracking Risk of Concrete at Early Age Based On Thermal Stress AnalysisDocument16 pagesEstimation of Cracking Risk of Concrete at Early Age Based On Thermal Stress AnalysisArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet