Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assigment 02docx
Uploaded by
Andy Claud MassaliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assigment 02docx
Uploaded by
Andy Claud MassaliCopyright:
Available Formats
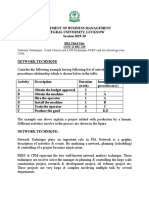
SCHEDULING PRINCPLES
There are a number of different forms of schedules that may be used, including
i. Written schedules
ii. Bar graphs schedules (Gantt charts)
iii. Network schedules.
BAR GRAPH METHOD OR GANTT CHART
The bar graph or bar chart schedule is a graphical schedule relating progress of items of work to
a time schedule.
The bar schedule traces its origin to a chart developed by Henry L. Gantt, a pioneer in the
application of scientific management methods to industrial production. These charts, referred to
as Gantt Charts, took several different forms, depending on their application. Because of their
origin, all forms of graph schedules are sometimes called Gantt Charts. In spite of the advent of
network planning methods, the bar graph schedule is still the most widely used schedule form
found in construction work.
A simple bar graph schedule is a graph where the major work items, or activities, making up the
project are listed on the left the schedule with a time scale across the top. The time scale can be
given in hours, days, weeks, months or years depending on project size and planner’s
preferences. It should be noted that two horizontal blocks are provided opposite each activity.
The upper block (SCH) represents scheduled progress and the lower block (ACT) is used to
record actual progress as work proceeds. For each block, a bar extends from starting to end
times. The number above each bar indicates the percentage of activity completion at each major
time division. Such a system simplifies calculations of scheduled cumulative progress and its
comparison with actual progress. To aid in the evaluation of progress, it is suggested that the
actual progress of each activity be inserted at the end of each major time period.
Figure 1: Gantt chart
THE NETWORK DIAGRAM
As indicated, network graphically portrays major project activities and their relationships. There
are basically two methods of drawing such networks:
i. The ACTIVITY-ON-ARROW DIAGRAM
ii. The ACTIVITY-ON-NODE DIAGRAM.
Special forms of activity-on-node diagram, such as PRECEDENCE DIAGRAMS, also do exist.
While activity-on-node diagrams have certain advantages, activity-on-arrow diagrams will be
utilized to illustrate network construction and time calculations.
Figure 2: Network diagram
CRIRICAL PATH METHOD
A related weakness of the bar graph schedule is its failure to identify those activities which
actually control the project duration. These duration-controlling activities are referred to as
CRITICAL ACTIVITIES. As a result of its failure to identify activity relationships and critical
activities, the bar graph schedule also fails to show the effect of delay or change in one activity
on the entire project. Recognizing these weaknesses in bar graph schedules, planners have for a
number of years attempted to devise improved planning and scheduling methods
PERT DIAGRAM
A PERT chart, sometimes called a PERT diagram, is a project management tool used to
schedule, organize and coordinate tasks within a project. It provides a graphical representation of
a project's timeline that enables project managers to break down each individual task in the
project for analysis.
The PERT chart template uses nodes drawn as rectangles or circles to represent events and
milestones throughout the project. The nodes are connected by vectors drawn as lines which
represent the various tasks that need to be completed. PERT charts provide project managers
with an estimation of the minimum amount of time needed to complete a project. Managers can
also analyze the work breakdown and task connections, as well as assess the risk associated with
the project. The breakdown structure makes it easy to organize a complex project with a variety
of moving parts by visualizing the dependencies between each step of the process.
Figure 3: PERT DIAGRAM
CONTRACT
Contract is an agreement between two or more people which is enforceable in a courts of law.
The following are ways of making contract;-
i. Orally
ii. Express written
iii. Implication
iv. Ratification
v. Deed
Any building or structure starts with
i. Needs establishment/ opportunity/ idea
ii. Feasibility study
iii. Design phase or stage it involves architects, engineers and planners.
iv. Tendering process or contract pro current process.
v. Tender evaluation and tender award.
vi. Construction stage / stage ( for big projects they are divided into lots to minimize or
educe completion time)
vii. Commissioning stage.
viii. Defect liability stage.
ix. Final account report and project closure
You might also like
- Linear Survey ReportDocument15 pagesLinear Survey ReportSyahmi Fadzi100% (1)
- Agriculture Project ManagementDocument45 pagesAgriculture Project Managementkhitishs67% (3)
- HS05311Notes 6Document42 pagesHS05311Notes 6ram prasadNo ratings yet
- Task Involved in Project Planning AreDocument22 pagesTask Involved in Project Planning AreLijish Balan100% (1)
- Interpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingDocument13 pagesInterpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingAyush SalveNo ratings yet
- Lectures_13,14 & 16 March 2024Document34 pagesLectures_13,14 & 16 March 2024RiyaNo ratings yet
- Terms ExplanationDocument8 pagesTerms ExplanationMy BusinessNo ratings yet
- Construction Scheduling TechniquesDocument35 pagesConstruction Scheduling TechniquesFazlin ZaibNo ratings yet
- Group 6 & 7 - Planning and SchedulingDocument122 pagesGroup 6 & 7 - Planning and SchedulingPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- CEC Notes LO5-6. Done by RyanDocument16 pagesCEC Notes LO5-6. Done by RyanFrancis ZhuwaoNo ratings yet
- CPM, Pert, Bar ChartsDocument32 pagesCPM, Pert, Bar ChartsAr Manish SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Network Schedule (Final)Document16 pagesNetwork Schedule (Final)Mariel Paz MartinoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gantt ChartDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Gantt ChartsayedNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design: 03 Managing The Information Systems ProjectDocument40 pagesSystems Analysis and Design: 03 Managing The Information Systems ProjectJ A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- 4.4.3 Project Management 27Document30 pages4.4.3 Project Management 27boohooNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and Management CM 632Document22 pagesProject Planning and Management CM 632makenyworldNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 110Document5 pages02 Handout 110Eliza ColomaNo ratings yet
- Network Techniques For Project Management: StructureDocument15 pagesNetwork Techniques For Project Management: StructureManita DhandaNo ratings yet
- BM319 Unit2 Part ADocument7 pagesBM319 Unit2 Part Aitsgsb13No ratings yet
- Bar Chart & Kurva-SDocument25 pagesBar Chart & Kurva-SAnisah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3 - Pert and CPM and Bar ChartDocument6 pagesAssignment - 3 - Pert and CPM and Bar ChartGauri WaikarNo ratings yet
- Gantt Chart: "Gantt" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument9 pagesGantt Chart: "Gantt" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeAnkita Tiwary100% (2)
- Edited ContentDocument21 pagesEdited ContentUday SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Scheduling The WorkDocument18 pagesScheduling The WorkMaclins ColloNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Sceduling - FinalDocument76 pagesChapter-4 Sceduling - FinalmelakadugnaNo ratings yet
- Application of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project ManagementDocument14 pagesApplication of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project Managementgcc_5083708No ratings yet
- Presented By-Mr. Yogesh A. DengaleDocument33 pagesPresented By-Mr. Yogesh A. Dengalesandeepv08No ratings yet
- Lec#03Document23 pagesLec#03Muhammad MoizNo ratings yet
- CPM and PERT Unit 2Document5 pagesCPM and PERT Unit 2SavantNo ratings yet
- Gantt ChartsDocument18 pagesGantt ChartsKinjal VasavaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools: What These Tools Are Used For?Document14 pagesProject Management Tools: What These Tools Are Used For?9986212378No ratings yet
- Network TichniquesDocument15 pagesNetwork Tichniquesadan awaleNo ratings yet
- IT Project Time Management GuideDocument51 pagesIT Project Time Management GuidevaibhavikanthariaNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Construction Management and Research GOADocument13 pagesNational Institute of Construction Management and Research GOASeyed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- BM-319 Network TechniqueDocument6 pagesBM-319 Network TechniqueMohd AqdasNo ratings yet
- Gantt Chart HistoryDocument9 pagesGantt Chart HistoryJonathan AmpisNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructuresDocument45 pagesWork Breakdown Structuresaswathi1No ratings yet
- Gantt ChartDocument2 pagesGantt ChartReshma Georgi100% (1)
- CPM/PERT Project Management ToolsDocument15 pagesCPM/PERT Project Management ToolsChristine Mae Pangilinan RamosNo ratings yet
- Project SchedulingDocument22 pagesProject SchedulingRAHUL16398100% (1)
- Create Gantt Charts (GDocument9 pagesCreate Gantt Charts (GvishwassaimsNo ratings yet
- Project Time ManagementDocument56 pagesProject Time ManagementusmansafdarNo ratings yet
- Gantt Charts: A Visual Project Management ToolDocument20 pagesGantt Charts: A Visual Project Management Toolreddy krishnaNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 2: Activity & Activity Network ActivityDocument4 pagesExperiment - 2: Activity & Activity Network ActivityVijay BhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment OR Vishal ShakyaDocument13 pagesAssignment OR Vishal Shakyashyamsingh4930No ratings yet
- Time Series AnalysisDocument6 pagesTime Series AnalysisminalNo ratings yet
- San Agustin, Michael Angelo - SchedulingDocument19 pagesSan Agustin, Michael Angelo - SchedulingAnghelikaaaNo ratings yet
- Mba or Unit-V NotesDocument18 pagesMba or Unit-V NotesAmruta PeriNo ratings yet
- project tools and techsDocument20 pagesproject tools and techsjackson1.businessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document33 pagesChapter 6Hassan Abib BasalNo ratings yet
- Network ModelDocument69 pagesNetwork ModelAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structures de PMI PDFDocument45 pagesWork Breakdown Structures de PMI PDFGladys Sánchez100% (1)
- Gantt ChartDocument5 pagesGantt ChartchacharancharanNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Project Management (UCCD2043)Document38 pagesInformation Technology Project Management (UCCD2043)vickramravi16No ratings yet
- Project Schedule and Network AnalysisDocument11 pagesProject Schedule and Network AnalysisParul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Visual Project Management Tools ComparedDocument5 pagesVisual Project Management Tools ComparedJonjeffrey AgustinNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management Unit-4 - 3 PDFDocument3 pagesSoftware Project Management Unit-4 - 3 PDFgambler yeagerNo ratings yet
- Object:-: Experiment No:-8Document10 pagesObject:-: Experiment No:-8Dhruv Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument32 pagesProject Management Tools and TechniquesReena Sanehi100% (2)
- Introduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookFrom EverandIntroduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookNo ratings yet
- How to Visualize a Project: Complete Guide to Project Management and PlanningFrom EverandHow to Visualize a Project: Complete Guide to Project Management and PlanningNo ratings yet
- Data CollectDocument2 pagesData CollectAndy Claud MassaliNo ratings yet
- Design 2Document5 pagesDesign 2Andy Claud MassaliNo ratings yet
- A. ReferencesDocument5 pagesA. ReferencesAndy Claud MassaliNo ratings yet
- Law AssignmentDocument1 pageLaw AssignmentAndy Claud MassaliNo ratings yet
- CAM - Training (CNC Simulator)Document110 pagesCAM - Training (CNC Simulator)farid_a_dzNo ratings yet
- 16 17 CILLI RobertoDocument81 pages16 17 CILLI RobertosandroNo ratings yet
- 2019-2020 IMAS - 2nd Round - MP - Solution - EngDocument10 pages2019-2020 IMAS - 2nd Round - MP - Solution - EngLes YaoNo ratings yet
- Kmpme 2 PDocument889 pagesKmpme 2 PIlie CiorneiNo ratings yet
- Liquidity, Asset Utilization, Debt Ratio and Firm Performance: Evidence From EgyptDocument32 pagesLiquidity, Asset Utilization, Debt Ratio and Firm Performance: Evidence From EgyptMsa-Management Sciences JournalNo ratings yet
- Lucene Rank Engine DataDocument13 pagesLucene Rank Engine DataGayane PetrosyanNo ratings yet
- Application of The Ruling Span Concept For Overhead Lines in Mountainous Terrain.Document6 pagesApplication of The Ruling Span Concept For Overhead Lines in Mountainous Terrain.diux96No ratings yet
- Kondrashov 1995 Contamination of The Genome by Very Slightly Deleterious Mutations Why Have We Not Died 100 Times OverDocument1 pageKondrashov 1995 Contamination of The Genome by Very Slightly Deleterious Mutations Why Have We Not Died 100 Times OverConner DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7Marilou RagpalaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Digital Electronics: G.H. Patel College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument31 pagesSubject: Digital Electronics: G.H. Patel College of Engineering and TechnologyMd Riyajon ShuvroNo ratings yet
- CG 2019 SolutionDocument19 pagesCG 2019 SolutionSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Floor Beam DesignDocument35 pagesProject Floor Beam DesignRoxanneDequinaNo ratings yet
- Molegro Virtual Docker PDFDocument270 pagesMolegro Virtual Docker PDFjorge nogalesNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering - Final PDFDocument248 pagesMechanical Engineering - Final PDFRubal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Review 1: Research Achievements Report NoDocument57 pagesReview 1: Research Achievements Report NoMourad BenabderrahmaneNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Module-3 Different Types of Vector Data and Concept of Topology PDFDocument17 pagesWeek-1 Module-3 Different Types of Vector Data and Concept of Topology PDFNagendra DuhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Preliminaries: K J 1 2 K JDocument8 pages1 Preliminaries: K J 1 2 K JSiraj Ud-DoullaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Theorems NOTESDocument2 pagesParallel Lines Theorems NOTESAmy SchillNo ratings yet
- Formulae of Mathematics PDFDocument301 pagesFormulae of Mathematics PDFJwalant100% (1)
- Reading & Writing Numbers GuideDocument34 pagesReading & Writing Numbers Guideintanssl100% (1)
- Water MarkingDocument24 pagesWater Markinghamed razaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE-I Dec Assessment Syllabus 2023-24Document5 pagesIGCSE-I Dec Assessment Syllabus 2023-24Khadijah AbbasiNo ratings yet
- AI - Question BankDocument6 pagesAI - Question BankSARATH KUMAAR J SEC 2020No ratings yet
- IT-UG Curriculum and SyllabusDocument257 pagesIT-UG Curriculum and SyllabusKak SakaNo ratings yet
- 2021MATHADVHO9.2 Learning ModuleDocument120 pages2021MATHADVHO9.2 Learning ModuleChang CarelNo ratings yet
- EM72 - 2007 Vibrations Article-Rene ArchambaultDocument4 pagesEM72 - 2007 Vibrations Article-Rene ArchambaultChad HuntNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument2 pagesApplied Thermodynamics and Heat TransferJOLYNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 MITx+CTL - SC0x+1T2021+type@asset+block@SC0x W7L2 ManagingUncertainty2 FINAL CLEAN UpdDocument27 pagesAsset-V1 MITx+CTL - SC0x+1T2021+type@asset+block@SC0x W7L2 ManagingUncertainty2 FINAL CLEAN UpdNguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- JAVA Lab PracticesDocument7 pagesJAVA Lab PracticesSubhajit GhoshNo ratings yet