Professional Documents
Culture Documents
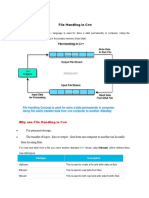
File Handling 1
Uploaded by
harshil yadav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesFile Handling 1
Uploaded by
harshil yadavCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
•Detecting End-of-File
•File opening modes
•File pointers and their manipulations
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
Detecting End-of-File
An ifstream object returns a value zero on reaching the
end-of-file condition.
For example-
ifstream fin;
while(fin)
{ ----------- }
The while loop terminates on end-of-file condition.
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
Detecting End-of-File
Another approach by using eof() member function of
ios class.
It returns a non-zero value on reaching end-of-file
condition otherwise returns zero.
For example-
if(fin.eof()!=0)
{ exit(1);}
The above statement terminate the program on
reaching end-of-file condition.
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File opening modes
The open() function can take two arguments.
Syntax-
stream-object.open(“filename”, mode);
The mode specifies the purpose for which the file is
opened.
The default file mode for ifstream functions is-
ios::in // open file for reading only
The default file mode for ofstream functions is-
ios::out // open file for writing only
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File opening modes
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File opening modes
ios::app add data to end of the file only, while ios::ate
add data or modify the existing data anywhere in the
file.
The mode can be combine two or more parameters
using the bitwise OR operator(|) as shown below-
fout.open(“data”, ios::app | ios::nocreate)
This opens the file in append mode but fails to open
the file if it does not exist.
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
Each file has two associated pointers known as file
pointers.
1. Input pointer(get pointer) is used for reading
from the file.
2. Output pointer(put pointer) is used for writing
to the file.
In read-only mode, the input pointer is
automatically set at the beginning of the file.
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
In write-only mode, the existing contents
are deleted and the output pointer is set at
the beginning of the file.
Functions for manipulations of file pointers
seekg() Moves get pointer to a specified
location
seekp() Moves put pointer to a specified
location
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
tellg() Gives the current position of the get
pointer
tellp() Gives the current position of the put
pointer
Example-
infile.seekg(10);
Moves the get pointer to the byte number 10.
Note that the bytes in a file are numbered from
zero.
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
Example-
ofstream fout;
fout.open(“hello”, ios::app);
int p = fout.tellp();
The output pointer moved to the end of the file
and the value of p gives number of bytes in the file.
seek() functions can also take two arguments-
seekg(offset, reposition);
seekp(offset, reposition);
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
offset represents the number of bytes the
file pointer is to be moved from the location
specified by the parameter reposition.
The reposition takes one of following three
constants-
ios::beg Start of the file
ios::cur Current position of the pointer
ios::end End of the file
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
File pointers and their
manipulations
Pointer offset calls and their actions where fin is an
ifstream object.
Seek Call Action
fin.seekg(0, ios::beg) Go to start
fin.seekg(0, ios::cur) Stay at the current position
fin.seekg(0, ios::end) Go to the end of file
fin.seekg(m, ios::beg) Move to (m+1)th byte in the file
fin.seekg(m, ios::cur) Go forward by m bytes from the current
position
fin.seekg(-m, ios::cur) Go backward by m bytes from the
current position
fin.seekg(-m, ios::end) Go backward by m bytes from the end
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
Thank You
Prepared by: Anil Kumar Tailor, Assistant Professor
Engineering College Ajmer
You might also like
- Unit 3 and 4Document26 pagesUnit 3 and 4Kudipudi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- File Handling in C++Document11 pagesFile Handling in C++Prakash JayaramanNo ratings yet
- File Handling in CDocument7 pagesFile Handling in CvinyagamoorthyNo ratings yet
- File Pointers2938Document12 pagesFile Pointers2938Sureshkumar CNo ratings yet
- File Handling in C++: By: Haya Majid Qureshi BS (CS) - IIDocument28 pagesFile Handling in C++: By: Haya Majid Qureshi BS (CS) - IIfairy178No ratings yet
- File Handling in C++: Datatype DescriptionDocument5 pagesFile Handling in C++: Datatype Descriptionshrujal ghuleNo ratings yet
- 133 16sccca2-16sccit3 2020052910043386Document37 pages133 16sccca2-16sccit3 2020052910043386sablerohit718No ratings yet
- Working With Files: A Presentation OnDocument27 pagesWorking With Files: A Presentation OnÊvîl ÂttïtùðeNo ratings yet
- FilesDocument31 pagesFilesVinay GuptaNo ratings yet
- File HandlingDocument35 pagesFile Handlingginol76330No ratings yet
- File Handling in C++Document17 pagesFile Handling in C++Sunil SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 L11Document85 pagesUnit 4 L11bibajev147No ratings yet
- Unit-4 PPTsDocument20 pagesUnit-4 PPTsfearless61022No ratings yet
- E Balagurusamy: File I/O With StreamsDocument8 pagesE Balagurusamy: File I/O With StreamsPrafulla GawadeNo ratings yet
- C-7 File HandlingDocument9 pagesC-7 File HandlingJaideepKhuranaNo ratings yet
- File Handling NotesDocument4 pagesFile Handling NotesP.PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- File Handling PDFDocument15 pagesFile Handling PDFdevil kanuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.2 Reading and Writing To Files Random Access To FilesDocument41 pagesLecture 3.3.2 Reading and Writing To Files Random Access To FilesTEJESNo ratings yet
- Session16 DraftDocument8 pagesSession16 Draftapi-3845857No ratings yet
- File Handling Part 1Document51 pagesFile Handling Part 1Karan KaranNo ratings yet
- Data File HandlingDocument21 pagesData File HandlingManiNo ratings yet
- Data File Handling in C++Document10 pagesData File Handling in C++Sarthak RoyNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Techno School: Computer ScienceDocument37 pagesSri Chaitanya Techno School: Computer ScienceAfreed AhamedNo ratings yet
- 337 16sccca2-16sccit3 2020052512075565Document32 pages337 16sccca2-16sccit3 2020052512075565Ravi Kiran GoswamiNo ratings yet
- File Processing: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument66 pagesFile Processing: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedYSheng ChanNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming: File Handling in C++Document58 pagesObject Oriented Programming: File Handling in C++Salman Javed BajwaNo ratings yet
- File Handling in JavaDocument17 pagesFile Handling in JavaAman YadavNo ratings yet
- PSPP Part-B Unit5Document14 pagesPSPP Part-B Unit5AkilanNo ratings yet
- Updating in A Binary FileDocument8 pagesUpdating in A Binary FileSwayam ShrikondwarNo ratings yet
- Programming in C++ CST-152Document30 pagesProgramming in C++ CST-152Khushi bhandariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Advanced File Operations123Document18 pagesChapter 12 Advanced File Operations123AntonyNo ratings yet
- File ManagmentDocument37 pagesFile ManagmentBacha TarikuNo ratings yet
- Classes For File Stream Operation: Stream-Object - Open ("Filename", Mode)Document9 pagesClasses For File Stream Operation: Stream-Object - Open ("Filename", Mode)munoNo ratings yet
- Oop Chapter 05Document15 pagesOop Chapter 05Vaibhav DhandeNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals in C++: Practical#14)Document24 pagesProgramming Fundamentals in C++: Practical#14)Pawang Rai LohanaNo ratings yet
- File HandlingDocument14 pagesFile Handlingmanishbhardwaj8131No ratings yet
- R20-N-Python Unit 4 - ChanduDocument56 pagesR20-N-Python Unit 4 - ChanduMahesh SahuNo ratings yet
- C++010 (Working With Files) ADocument13 pagesC++010 (Working With Files) ADeepak Kumar PrajapatNo ratings yet
- C++ Prog and ApplDocument5 pagesC++ Prog and ApplClairType ServicesNo ratings yet
- Cse 202 LpuDocument26 pagesCse 202 LpuDhruva is liveNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals in C++: Practical#14)Document27 pagesProgramming Fundamentals in C++: Practical#14)Tooba AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Data File Handling - NRDocument30 pagesData File Handling - NRkeyul007No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11: Working With Files: File Field1 Field2Document8 pagesCHAPTER 11: Working With Files: File Field1 Field2darshanNo ratings yet
- Files and Streams in C++Document6 pagesFiles and Streams in C++RaniNo ratings yet
- Binary Files 3Document12 pagesBinary Files 3graandhikaa sriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3 - File ManagementDocument16 pagesChapter 2 and 3 - File ManagementNohaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Using C++ CST-157 Unit-Iii Files Chapter-9Document29 pagesObject Oriented Programming Using C++ CST-157 Unit-Iii Files Chapter-9SheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - DATA FILE HANDLING IN CPP, Chapter Notes, Class 12, Computer Science Class 12 Notes - EduRevDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - DATA FILE HANDLING IN CPP, Chapter Notes, Class 12, Computer Science Class 12 Notes - EduRevtresa_mNo ratings yet
- File ManagementDocument16 pagesFile ManagementEnqu kNo ratings yet
- Get and Put Stream PointersDocument4 pagesGet and Put Stream PointersgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- File Stream Classes:-: Steps of File OperationsDocument28 pagesFile Stream Classes:-: Steps of File OperationscnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing FilesDocument30 pagesReading and Writing FilesGanesh NelluriNo ratings yet
- File and Streams in C++Document8 pagesFile and Streams in C++Gemex4fshNo ratings yet
- M5 FilehandlingDocument32 pagesM5 FilehandlingMalavika VipinNo ratings yet
- Input/Output With Files: Open A FileDocument3 pagesInput/Output With Files: Open A FileVijay PrasathNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Fundamental File Processing Unit IV Fundamental File Processing OperationsDocument39 pagesUnit IV Fundamental File Processing Unit IV Fundamental File Processing Operationsduvvuru familyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight-FileDocument47 pagesChapter Eight-FileTigist TilahunNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals Lab 10 (File Handling) New BatchDocument9 pagesProgramming Fundamentals Lab 10 (File Handling) New BatchAhmad AbduhuNo ratings yet
- Mastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionFrom EverandMastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Inheritance III SlidesDocument18 pagesInheritance III Slidesharshil yadavNo ratings yet
- Stream Classes SlidesDocument20 pagesStream Classes Slidesharshil yadavNo ratings yet
- TemplateDocument14 pagesTemplateharshil yadavNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling 1Document15 pagesException Handling 1harshil yadavNo ratings yet
- Bcd-Adder 1Document21 pagesBcd-Adder 1PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.Inggris 2Document37 pagesTugas B.Inggris 2bxcoolNo ratings yet
- Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Edge Network ServicesDocument9 pagesImplementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Edge Network Servicesnwytg48No ratings yet
- Steam Community - Guide - How To Downgrade Game VersionDocument8 pagesSteam Community - Guide - How To Downgrade Game VersionZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Pexpect TutorialDocument143 pagesPexpect TutorialAnkit SethiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Windows 10Document19 pagesPresentation On Windows 10SAmim Sheikh0% (1)
- Keyboard InterruptDocument22 pagesKeyboard InterruptTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Apache KafkaDocument37 pagesApache KafkaPhani Karthik MaradaniNo ratings yet
- JuliaDocv0 3 5Document537 pagesJuliaDocv0 3 5gastromonoNo ratings yet
- 3DECDocument178 pages3DECDaniele Baraldi100% (1)
- Blue Prism - Solution Design Overview PDFDocument27 pagesBlue Prism - Solution Design Overview PDFbnanduriNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Bhs InggrisDocument13 pagesPresentasi Bhs InggrisSukron JazilaNo ratings yet
- Compal La-9902p r1.0 Schematics PDFDocument53 pagesCompal La-9902p r1.0 Schematics PDFhiteshNo ratings yet
- CamutilsDocument12 pagesCamutilsMuhammad AsadNo ratings yet
- Final Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesFinal Seminar ReportIsmail Rohit RebalNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL Developer VMDocument3 pagesOracle SQL Developer VMKhoa DiepNo ratings yet
- GNUSim8085 Assembly Language GuideDocument3 pagesGNUSim8085 Assembly Language GuideKomalNo ratings yet
- System Software SeminarDocument11 pagesSystem Software SeminarAVETA JOYNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For J2SEDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank For J2SEAlpa Dalal SandesaraNo ratings yet
- Application Note Usrp and HDSDR Spectrum MonitoringDocument14 pagesApplication Note Usrp and HDSDR Spectrum MonitoringcaraboyNo ratings yet
- Linux Kernel Troubleshooting PDFDocument14 pagesLinux Kernel Troubleshooting PDFjoojayceeNo ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio MP 161 SPFDocument4 pagesRicoh Aficio MP 161 SPFStar OfsunNo ratings yet
- Annex I List of Major Equipments 2019Document2 pagesAnnex I List of Major Equipments 2019Eunica April Catahan FloresNo ratings yet
- Fulmo GT: ECA1092 SeriesDocument2 pagesFulmo GT: ECA1092 SeriesFlorescu FlorinNo ratings yet
- BackupRecovery With RMANDocument26 pagesBackupRecovery With RMANabidouNo ratings yet
- Centaur UserGuide 17935R13Document229 pagesCentaur UserGuide 17935R13denismatonNo ratings yet
- GC27 8105 01Document418 pagesGC27 8105 01choraNo ratings yet
- Instruction Set of 8085 Compatibility ModeDocument82 pagesInstruction Set of 8085 Compatibility ModeParth MadanNo ratings yet
- Gip UNIT IDocument39 pagesGip UNIT IjesudosssNo ratings yet
- FDocument4 pagesFmohdtakrimiNo ratings yet