Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Topic NI
Uploaded by
Abelle Ensui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThis document outlines the rules and guidelines for implementing the Philippine Health Information Exchange regarding the collection, use, and protection of patient health information. It discusses 12 rules that cover obtaining consent, limiting access, securing physical infrastructure, ensuring technical safeguards, using cloud services appropriately, social media guidelines, and research requirements. The overall goal is to prescribe procedures that ensure patient privacy within the national health information system.
Original Description:
Original Title
2nd-topic-NI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the rules and guidelines for implementing the Philippine Health Information Exchange regarding the collection, use, and protection of patient health information. It discusses 12 rules that cover obtaining consent, limiting access, securing physical infrastructure, ensuring technical safeguards, using cloud services appropriately, social media guidelines, and research requirements. The overall goal is to prescribe procedures that ensure patient privacy within the national health information system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pages2nd Topic NI
Uploaded by
Abelle EnsuiThis document outlines the rules and guidelines for implementing the Philippine Health Information Exchange regarding the collection, use, and protection of patient health information. It discusses 12 rules that cover obtaining consent, limiting access, securing physical infrastructure, ensuring technical safeguards, using cloud services appropriately, social media guidelines, and research requirements. The overall goal is to prescribe procedures that ensure patient privacy within the national health information system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
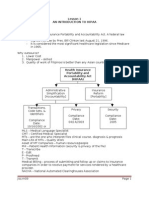
NURSING INFORMATICS
HEALTH PRIVACY CODE
SHELA BALUNSAT
DR. JOSEPHINE LORICA, DPA, RN
HEALTH PRIVACY CODE IMPLEMENTING THE JOINT
ADMINISTRATIVE ORDER NO. 2016-0002 “PRIVACY 7. Reportorial requirements
GUIDELINES FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE Ø RA # 3573 – Law on Reporting Communicable
PHILIPPINE HEALTH INFORMATION ECHANGE” Disease – immediately collected and reported to
local and national authorities
JOINT because it involved: RULE 2: Access of Health Information
• Department of Health (DOH), in cooperation with
the
Department of Science and Technology (DOST), 1. Access of Health Care Providers
Philippine Health Insurance Corporation - upon patient consent, only a health care provider and
(PhilHealth), authorized authorities shall have access to patient’s
• University of the Philippines-Manila (UPM) and the health information
Commission on Higher Education (CHED),
Established the the National eHealth Program (NeHP) that 2. Access of Third party
envisions widespread information-technology (IT)- - In cases required by law or authorized by the patient
enabled health services by 2020.
RULE 3: Use and Disclosure of Health Information
PURPOSE
- to prescribe the procedures and guidelines that 1.Use and disclosure
ensure the protection of the privacy of a patient. Ø Planning of quality services
SCOPE OF APPLICATION Ø Reporting of communicable, infectious and other
- shall apply to the Phil Health Information Exchange notifiable disease
(PHIE) system, Health Facilities, Health Care Ø Continuing care to patients
Providers, and any natural or juridical person Ø Reporting of physical injury
involved in the processing of health information Ø Reporting of interpersonal violence to proper
within the PHIE framework. authorities
RULE 1: Collection and Processing of Health Information Ø Mandatory reporting required by licensing and
accreditation bodies
1. Consent – valid and informed 2. Privilege Communication
Requirements: - Conversation or working relationship which takes place
a. Competence – sound mind , 18 years old between two parties within the context of a protective
b. Amount and accuracy of information relationship such as between healthcare provider and a
- relevant & factual data – procedure, treatments, benefits, patient.
risks possible complications Ø Consent of both patient and health care provider
c. Patient understanding - language or dialect, education. must be secured prior to use
d. Voluntariness – autonomous- understand that can 3. Training Hospitals and Academic or Clinical
withdraw anytime Requirements
Ø Comply with Professional Regulation Commission
2. Point of Collection of Information (PRC) requirements
- start at the time of registration in the health facility, Ø Non-disclosure clause – included in the contract of
admission, different points of care a school affiliated
3. Processing of Information RULE 4: Organizational Security Measures
- May be through an Electronic Health Record (EMR) or
Health facility Information System 1. Policies and procedures
- Encoding and processing will be coordinated through the Ø Privacy and security
medical records section or health facility information 2. Contract with Third Party
management system Ø Document storage and disposal
Ø Data management processes – with tracking and
4. Patient Identifier controlling records, type of data sent and received
- Unique – Philhealth Personal Identification Number and individuals who have access to records
Ø Description of output reporting
Ø Periodic staff training
5. Point of de-identification Ø Communication requirements
- De identified health information – stored in PHIE data 3. The Information Technology personnel
warehouse Ø Support implementation of security guidelines –
- Patient’s consent – the health records as part of PHIE confidentiality of records
maybe processed without de-identification otherwise, Ø Charged with conduct of system-related functions
health information must be de-identified – leaving only including troubleshooting
those necessary for immediate statistical reference 4. Medical records Officer
Ø With privacy officer - authority to audit patient’s
6. Authorized persons to amend data if required shared health records
– authorized employee of the health facility
– when changing data: RULE 5: Physical Security
Ø Original entry must be visible
Ø Change must be dated and countersigned or logged 1. Inventory of Information technology Physical Devices
Ø Reason for change must be entered or specified 2. Access to Physical Infrastructure (IT)
NURSING INFORMATICS
HEALTH PRIVACY CODE
SHELA BALUNSAT
DR. JOSEPHINE LORICA, DPA, RN
Ø Server Access – in designated area and complies 4. Research Data
with ISO 27001 standards - de-identified or destroyed
Ø Computer Access – authorized personnel only
Ø Devices registered to the health facility – can not be RULE 11: Patient Registeries
brought outside health facility
Ø Bring your own device (BYOD) – allowed with strict
policies on access, processing, storage , 1. Registry Design – clear purpose, avoid ethical and
transmission and output of data compliance issues
3. Business continuity and Disaster recovery 2. Informed Consent
Ø Physical back up 3. Registry Data – conforms with standard definitions,
Ø Business continuity – even during disaster – terminologies and specifications
minimum data requirements identified by Data 4. Data Collection – close to place and time of care with
Protection officer trained data collectors
RULE 6: Technical Safeguards 5. Registry Data for research – appropriate design, data
element, operating procedures and documented
1. Access controls – only to persons or software programs methodologies
granted access rights
Ø Information Access management (required)
Ø User identification (required)
Ø Emergency Access Procedure (required)
Ø Automatic Log off (addressable)
Ø Encryption and Decryption (addressable)
Ø Multifactor authentication (addressable)
2. Audit controls – record who accessed, when and what
operations were performed
Ø Recording of Information (required)
Ø Audit data life span (addressable)
Ø Access to audit data (addressable)
3. Integrity controls – protection from improper alteration or
destruction
Ø Mechanism to authenticate Electronic health
Information (addressable)
Ø Digital Signature (required)
Ø Sum verification (required) – determine if input data
matches source data
Ø Anti-virus software (required)
Ø Data storage encryption (required)
Ø Transmission encryption (required)
Ø Proper handling of mechanical components
(Addressable)
Ø Offline modes and caching (addressable)
Ø Interface Integration of Information Systems
(Addressable) – for interoperability and data
compatibility
4. Transmission security
5. Identity authentication
6. Storage Security
RULE 7: Cloud Services
Ø Must not compromise privacy or security
Ø Contract – Health care provider and service
provider
RULE 8: Cloud Services
Ø Unauthorized posting – penalized in accordance to
Data Privacy Act
Ø Guidelines should be established
Ø Responsible social media use
Ø Health education and promotion – caution must be
observed
RULE 10: Research
1. Research Subject
2. Research protocol
3. Research projects
– 1,000 or more data sets – register with the National
Privacy Commission
You might also like
- Diesel Engines For Vehicles D2066 D2676Document6 pagesDiesel Engines For Vehicles D2066 D2676Branislava Savic63% (16)
- Medical Data: It S Only Sensitive If It Hurts When You Touch ItDocument58 pagesMedical Data: It S Only Sensitive If It Hurts When You Touch ItBerrezeg MahieddineNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) PDFDocument479 pagesPower System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) PDFAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Hipaa Lesson 1Document6 pagesHipaa Lesson 1Jepoy OlivoNo ratings yet
- The Future of FinanceDocument30 pagesThe Future of FinanceRenuka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Springs: All India Distributer of NienhuisDocument35 pagesSprings: All India Distributer of NienhuisIrina DroliaNo ratings yet
- Principles of The Data Privacy Act - Leandro Angelo Y AguirreDocument67 pagesPrinciples of The Data Privacy Act - Leandro Angelo Y AguirreVoltaire M. Bernal100% (1)
- Present Tenses ExercisesDocument4 pagesPresent Tenses Exercisesmonkeynotes100% (1)
- MT Laws FinalsDocument14 pagesMT Laws FinalsRyle PanesNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Ethical Issues in Health InformaticsDocument28 pagesUnit 5 Ethical Issues in Health InformaticsJenilyn Farnacio100% (1)
- Electronic Medical RecordDocument5 pagesElectronic Medical RecordSujatha J Jayabal100% (2)
- MODULE 2: Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesMODULE 2: Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticejuiceNo ratings yet
- Landscape ArchitectureDocument9 pagesLandscape Architecturelisan2053No ratings yet
- Electronic Health Record: 3.1 Application of Health Informatics in Clinical PracticeDocument3 pagesElectronic Health Record: 3.1 Application of Health Informatics in Clinical Practicepamela rasmoNo ratings yet
- Health Information Privacy in The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesHealth Information Privacy in The PhilippinesAhmad Rajiv AlaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare-Ethics-Module-5 Handout Ethical-Issues-related-to-TechnologyDocument6 pagesHealthcare-Ethics-Module-5 Handout Ethical-Issues-related-to-TechnologySheryhan Tahir Bayle100% (2)
- Deepscribe HIPAADocument25 pagesDeepscribe HIPAADwight Kristian CruzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oil Gas Accounting International Petroleum Accounting International Petroleum Operations MSC Postgraduate Diploma Intensive Full TimeDocument70 pagesAdvanced Oil Gas Accounting International Petroleum Accounting International Petroleum Operations MSC Postgraduate Diploma Intensive Full TimeMoheieldeen SamehNo ratings yet
- Patient Information and Confidentiality Assignment 1Document4 pagesPatient Information and Confidentiality Assignment 1api-383904539No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Overview of Health Information SystemDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Overview of Health Information SystemMr. PotatoheadNo ratings yet
- Heather Moore Policy 1Document5 pagesHeather Moore Policy 1api-358245933No ratings yet
- Ni FinalsDocument8 pagesNi FinalsKayobi BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Privacy Security and Confidentiality NCM 110Document32 pagesPrivacy Security and Confidentiality NCM 110YomeiNo ratings yet
- Caldicott PolicyDocument10 pagesCaldicott PolicyMuhammad Zahid FaridNo ratings yet
- His For Mls - Medical Laboratory Science It (Prelim Reviewer)Document3 pagesHis For Mls - Medical Laboratory Science It (Prelim Reviewer)Kyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- 2020-09-15-DOH Standard On Patient Healthcare Data Privacy For PublicationDocument18 pages2020-09-15-DOH Standard On Patient Healthcare Data Privacy For PublicationEd NurNo ratings yet
- His Lesson 5 and 6 LecDocument7 pagesHis Lesson 5 and 6 LecJean SicatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14: Ethics, Privacy and Security: Ethics in Health InformaticsDocument6 pagesLesson 14: Ethics, Privacy and Security: Ethics in Health InformaticsvivianschuylerNo ratings yet
- CCS113 EISP Grp4Document3 pagesCCS113 EISP Grp4CHOI HunterNo ratings yet
- Information Technology and Community Health: Chapter 15-Ehealth in The Community SettingDocument7 pagesInformation Technology and Community Health: Chapter 15-Ehealth in The Community SettingJullienne Ysabelle AngNo ratings yet
- WFP Guide To Personal Data Protection and PrivacyDocument129 pagesWFP Guide To Personal Data Protection and PrivacyMikiyas AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ICTM111Document4 pagesReviewer in ICTM111Angelie Marian100% (1)
- Ictm111 Week 16Document3 pagesIctm111 Week 16KATHREEN CRYSTALLE SALVADORNo ratings yet
- Overview of Health InformaticsDocument2 pagesOverview of Health InformaticsERESTALL SENNDI GRACE OLIVERASNo ratings yet
- HIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 12)Document5 pagesHIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 12)Cesmaine SanchezNo ratings yet
- Data Privacy Act: Charry Mae P. Romero, DMDDocument18 pagesData Privacy Act: Charry Mae P. Romero, DMDJoyce EbolNo ratings yet
- Health IT Policy CommitteeDocument19 pagesHealth IT Policy CommitteeRich ElmoreNo ratings yet
- AlicdanRoncales RecordKeepingDocument2 pagesAlicdanRoncales RecordKeepingJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Practical Approaches To Creating A Security CultureDocument7 pagesPractical Approaches To Creating A Security CultureEPNo ratings yet
- HIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 4)Document3 pagesHIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 4)Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Data-Privacy-Manual USPDocument40 pagesData-Privacy-Manual USPHiraeth WeltschmerzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics (MIDTERMS)Document8 pagesNursing Informatics (MIDTERMS)Lyza MateoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Information System Security PolicyDocument24 pagesClinical Information System Security Policywanya64No ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Health InformaticsDocument3 pagesEthical Issues in Health InformaticsjackieNo ratings yet
- The Unauthorized Disclosure of Medical InformationDocument2 pagesThe Unauthorized Disclosure of Medical Informationmeeray2216No ratings yet
- NIDocument6 pagesNIJanah PagayNo ratings yet
- The Culture of Healthcare: Privacy, Confidentiality, and SecurityDocument22 pagesThe Culture of Healthcare: Privacy, Confidentiality, and SecurityHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012No ratings yet
- Medical Record Division Policies and ProceduresDocument3 pagesMedical Record Division Policies and ProceduresdrsharathsgNo ratings yet
- Ethicolegal ConsiderationsDocument29 pagesEthicolegal ConsiderationsAlthea Ashley NequiotaNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Group 7 HandoutsDocument7 pagesBioethics Group 7 HandoutsKimverly NamuagNo ratings yet
- Ethics, Privacy, SecurityDocument20 pagesEthics, Privacy, Securityqwerty masterNo ratings yet
- Health Information Privacy in The Philippines: Trends and Challenges in Policy and PracticeDocument14 pagesHealth Information Privacy in The Philippines: Trends and Challenges in Policy and PracticeLunar WalkerNo ratings yet
- Common HIPAA Violations and Preventative Measures To Keep Your Practice in ComplianceDocument10 pagesCommon HIPAA Violations and Preventative Measures To Keep Your Practice in ComplianceReva stevanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: Preliminary Quiz 1 & 2Document12 pagesNursing Informatics: Preliminary Quiz 1 & 2Aubrey RosalesNo ratings yet
- Overview of Health InformaticsDocument2 pagesOverview of Health Informaticsjoy kristine morallosNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 (Informatics - Communication Technologies in The Critical Care Units)Document2 pagesTopic 2 (Informatics - Communication Technologies in The Critical Care Units)Ghianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- HB Information GovernanceDocument8 pagesHB Information Governancebalaioara16No ratings yet
- ConfidentialDocument22 pagesConfidentialRayzl GacayanNo ratings yet
- Tabel 1: Informasi Kesehatan PribadiDocument3 pagesTabel 1: Informasi Kesehatan PribadiGita R. RustanaNo ratings yet
- BasePaperDocument4 pagesBasePaperPurvaNo ratings yet
- NI Finals Reviewer PDFDocument12 pagesNI Finals Reviewer PDFGAYAP, ALGEN M.No ratings yet
- Teleorthodontics: Litigation and LegislationDocument3 pagesTeleorthodontics: Litigation and LegislationRaji MurthyNo ratings yet
- (W1) Health Information SystemsDocument2 pages(W1) Health Information Systemsreghin89No ratings yet
- Confidentiality of Personal Health Information: C P S ODocument8 pagesConfidentiality of Personal Health Information: C P S OMuslimah UtamiNo ratings yet
- Development of Embedded Personal Health Care Record System: Ruba Alawneh, Aism El Sheikh, Raid KanaanDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Embedded Personal Health Care Record System: Ruba Alawneh, Aism El Sheikh, Raid Kanaanكن صديقيNo ratings yet
- Ethics Privacy and SecurityDocument27 pagesEthics Privacy and SecurityGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- Summary Notes (Introduction To The Male Genitalia and Rectum)Document3 pagesSummary Notes (Introduction To The Male Genitalia and Rectum)Abelle EnsuiNo ratings yet
- Ethics 02 Moral DilemmasDocument32 pagesEthics 02 Moral DilemmasSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- Ethics 01 Moral and Nonmoral Standards 001Document67 pagesEthics 01 Moral and Nonmoral Standards 001Abelle EnsuiNo ratings yet
- Table FNCPDocument3 pagesTable FNCPAbelle EnsuiNo ratings yet
- MENOPAUSEDocument6 pagesMENOPAUSEAbelle EnsuiNo ratings yet
- PREGNANCYDocument5 pagesPREGNANCYAbelle EnsuiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Storage Tank Systems: Codes, Regulations, and DesignsDocument4 pagesHandbook of Storage Tank Systems: Codes, Regulations, and DesignsAndi RachmanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Study of Parabolic Cylindrical Shell A Parametric StudyDocument4 pagesDynamic Study of Parabolic Cylindrical Shell A Parametric StudyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Ubicomp PracticalDocument27 pagesUbicomp Practicalvikrant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions Markets and ServicesDocument2 pagesFinancial Institutions Markets and ServicesPavneet Kaur Bhatia100% (1)
- SHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Document15 pagesSHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Romeo Espinosa Carmona JrNo ratings yet
- Kortz Center GTA Wiki FandomDocument1 pageKortz Center GTA Wiki FandomsamNo ratings yet
- Fuentes v. Office of The Ombudsman - MindanaoDocument6 pagesFuentes v. Office of The Ombudsman - MindanaoJ. JimenezNo ratings yet
- Writ Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalDocument22 pagesWrit Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalNANDANI kumariNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: Rotary Lobe PumpDocument77 pagesOperating Instructions: Rotary Lobe PumpRuslan SlusarNo ratings yet
- Worked Solution Paper5 A LevelDocument8 pagesWorked Solution Paper5 A LevelBhoosan AncharazNo ratings yet
- PCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?Document14 pagesPCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?sidd_mgrNo ratings yet
- Communication Skill - Time ManagementDocument18 pagesCommunication Skill - Time ManagementChấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsDocument3 pagesThe Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsalexiouconNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Wiring Degradation StudyDocument275 pagesAircraft Wiring Degradation Study320338No ratings yet
- Sharat Babu Digumarti Vs State, Govt. of NCT of Delhi (Bazee - Com Case, Appeal) - Information Technology ActDocument17 pagesSharat Babu Digumarti Vs State, Govt. of NCT of Delhi (Bazee - Com Case, Appeal) - Information Technology ActRavish Rana100% (1)
- Sage TutorialDocument115 pagesSage TutorialChhakuli GiriNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Lecture 1Document53 pagesThermal Physics Lecture 1Swee Boon OngNo ratings yet
- Leather PuppetryDocument8 pagesLeather PuppetryAnushree BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Stratum CorneumDocument4 pagesStratum CorneumMuh Firdaus Ar-RappanyNo ratings yet
- Developpments in OTC MarketsDocument80 pagesDeveloppments in OTC MarketsRexTradeNo ratings yet
- ES Parent Bulletin Vol#19 2012 May 25Document13 pagesES Parent Bulletin Vol#19 2012 May 25International School ManilaNo ratings yet
- Pantone PDFDocument53 pagesPantone PDF2dlmediaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 AcousticsDocument14 pagesAssignment - 1 AcousticsSyeda SumayyaNo ratings yet