Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O18 C 7 R08 VEJZp YGJ963
Uploaded by
Netaji WaghmareOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O18 C 7 R08 VEJZp YGJ963
Uploaded by
Netaji WaghmareCopyright:
Available Formats
have a valrney or 2pplicaaons, ranging from storm water collection to industrial basic logic of Figure above holds true;
rue; wellbeing is maximized for society as a
#Explain EIA & CPCB?(U3)=EIA:Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is the
and commercial disposal. whole when.(a)Water is priced at its marginal cost and (b) Water is used up until
process of evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed project or
the marginal cost and marginal benefit are equal
development, taking into account both positive and negative inter-related
socioeconomic, cultural, and human-health impacts.EIA can provide both
environmental and economic benefits, such as reduced project implementation #Explain economic value of water?(U4)= Total economic value includes use #(National State, local) Current Water Laws?(U5)= *The area of law that deals
and design costs, avoided treatment/clean-up costs, and reduced impact of values and non-use values, with the basic idea to combine use values and with water ownership, access, and control is known as water law. *It also
laws and regulations.An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a well- nonuse values. Use values are concrete, such as the value we get from the addresses the Interstate and transnational aspects of water, the division of
established preventive policy tool around the world it is a process that aims to production of a good, and can be broken down into separate categories; direct authority among the states, local governments (such as municipalities in urban
provide early and adequate information about the likely environmental use, indirect use, and option values.Direct use value occurs when something is areas and panchayats in rural areas), public and private actors, and the problem
consequences of various plans and projects, as well as to propose alternatives directly used or consumed.Indirect use values are usually measures of benefits of water quality with its effects on the environment and human health.*The
and mitigation measures.EIA is one of the most important preventive tools for or services. Ecosystem services can be beneficial directly or indirectly whether term "laws" in common usage refers to the entire collection of regulations
describing and valuing the potential effects of activities that may harm water they are consumed or not. If water is taken out of rivers for irrigation or for pertaining to a single topic or deriving from a single source.* The term "law" in
resources. In terms of sustainable development, EIA is primarily regarded as a municipal uses that is a direct use. Indirect use could involve aesthetic values the context of Indian water legislation includes.(i)The Constitution of India.
project planning tool. People request that different alternatives be compared such as the beauty of the water. Uses that involve both direct and Indirect use (ii)Laws or acts.(iii)Decisions of the Supreme Court of India, High Courts, district
for each type of project and plan.*CPCB:The Central Pollution Control Board values include water for fisheries, wildlife, and ecosystems. Estimated values courts and nyay panchayats.(iv)Common law or law developed by English judges
(CPCB), statutory organisation, was constituted in September, 1974 under the and prices can be determined for such uses that are deferred, or the willingness through judicial decisions, as applied in India.(v)Customary norms or rules of
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. Further, CPCB was to pay to maintain a resource.Nonuse values include existence values and behaviour that may be unwritten but established by long practice or
entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control bequest values. A basic difference between option values and nonuse values is usage.*However, a bill passed by the Parliament may supersede them. The water
of Pollution) Act, 1981.It serves as a field formation and also provides technical the difference in time horizons. Bequest values, which are nonuse values, are legislation in India is composed of various parts. Federal and state laws are
services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests of the provisions of the technically the same as option values (use values); however, the bequest values included, as well as international treaties.* It also comprises a number of less
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.*Functions of the CPCB:Principal Functions have a longer time frame, such as being held for future generations. Existence formal agreements, such as policies relating to and water-related issues, as well
of the CPCB, as spelt out in the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, values (nonuse values) are pure benefits, such as the value of knowing that as traditional laws and rules.
1974: (1)To promote gleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the something exists for the value of its existence. It is the least tangible of the
States by prevention, control and abatement of water pollution.(2) To advise various types of values. #Explain water rights and types of water rights?(U5)= All civilizations have
the Central Government on any matter concerning restoration and maintaining their primary foundation in water. Many civilizations' rise and collapse have
#Water Scarcity and its Types and measures preventing it?(U4)= There is
the wholesomeness of aquatic resources and the prevention, control and been influenced by water. The interconnections in the environment and the
virtually any evidence of a global water deficit. Water is not always available in
abatement of water pollution.(3)To plan and cause to be executed a nation- necessity of ecologically based perspectives are lessons that water resources
the appropriate place at the right time, which is a challenge connected to its
wide programme for the prevention, control and abatement of water pollution. continuously impart to societies. People have always had a strong love
temporal and spatial distribution.*Types:1. Physical water scarcity: When a
(4)To provide technical assistance and guidance to the State Pollution Control towards water. The availability and quality of water are essential to the health
region's demand exceeds its available water supply, there is physical or
Board.(5)To lay down and annul standards for the quality of water in streams of every community. Global environmental movements continue to place a
absolute water shortage. Around 1.2 billion people, many of whom reside in
and wells. high priority on concerns relating to water.During this process, conventional
arid or semi-arid regions, according to the Food and Agricultural Organization
water saving measures are forsaken. Traditional communities, which serve the
#Explain water pollution,its effects?(U3)= water pollution is pollution that (FAO) of the United Nations, live in physically deficient areas. It is anticipated
main reservoirs of traditional knowledge, are also being displaced from their
occurs above ground in bodies of water such as oceans, streams, lakes, and that as populations rise and weather patterns become more erratic due to
neighborhoods. Tribal groups and other groups are the most impacted in India
rivers. These waters become polluted as a result of contaminated rainwater climate change, the number of people affected by this type of water scarcity
by the building of major dams and the vast deforestation that goes along with
runoff that enters nearby water sources.Runoff from farm fertilisers and would increase.2. Economic water scarcity: The main causes of this type of
it. Water rights may control how surface water or groundwater from a
homeowner lawn care, as well as salts and chemicals from city and highway water scarcity are either a widespread absence of water infrastructure or
particular source is used.*Types of Water Rights: The two primary categories
roads, is some of the leading causes of water contamination. Surface water can Inadequate management of water resources in areas where infrastructure is
present. More than 1.6 billion people, according to FAO estimates, have of water rights are riparian water rights and prior appropriation water rights
also become contaminated as a result of sewage leaks and animal factory However, because water rights vary greatly based on geography, some water
waste. These pollutants are extremely dangerous and can even be fatal for economic water shortages. Unrestricted water consumption for agriculture and
industry at the expense of the wider population can also lead to economic rights exist in some states but not others. In the United States, there are
human consumption because they contain high levels of pathogens and
water scarcity. numerous types of water rights, including the following : (1)Riparin water
waterborne diseases. Examples of what pollutant substances can cause in
rights.(2)Non-riparin water rights.(3)Hybrid water rights.(4)Absolute
surface water include: (i)A decrease in dissolved oxygen in water, due to the
*Measures for Preventing Water Scarcity:(1)Aquifer Recharging:A body of dominion.(5)Correlative rights.(6)Littoral rights.(7)Public trust.(8)Right to clean
presence of organic matter and nutrients.(ii)An increase in turbidity, or a darker
permeable soil or rock that holds or transports groundwater is known as an water.
color in water.(iii)Sedimentation of solid pollutants in the bottom of water
bodies.*Effects:(1)Ecosystems:Water pollution is a major global environmental aquifer. Usually, rain or melting snow refills them. According to UN statistics, #What are water allocation priorities?(U5)= While planning and operation of
issue because it can degrade aquatic ecosystems. Water pollution is caused by a groundwater withdrawal has increased thrice over the past 50 years; the water resource systems, water allocation priorities Follows: (A) Drinking
variety of contaminants, including chemicals, pathogens, and physical changes regions with the biggest withdrawals are parts of China, India, and the United water: Everybody should have access to adequate safe drinking water
such as increased temperature. (2)Public health and waterborne diseases:Due States. About 67% of it is put to agricultural use, 22% goes to residential facilities, including in urban and rural locations. Where there is no other
to polluted surface water use various water_borne diseases such consumption, and 11% goes to industry.(2) Water reuse and Zero-Liquid source of drinking water, irrigation and multipurpose projects should always
Gastrointestinal, cholera, diarrhea, etc. occurs. (3)Ocean acidification: Another Discharge Technology:This method can help municipalities and industries deal include a drinking water component. The first use of any accessible water
effect of water pollution is ocean acidification. The ongoing decrease in the pH with water scarcity. Water is used, treated, and reused in a closed-loop system should be for human and animal consumption.(B)Irrigation: Application of
value of the Earth's oceans caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from with no release or discharge in Zero Liquid Discharge technologies.(3)Coastal water to soll for crop production is known as irrigation. In order to the water
the atmosphere is known as ocean acidification. Reservoir Projects:Coastal reservoir projects in Singapore, Hong Kong, and Japan that is available from rainfall and groundwater, Irrigation water is given.
have been successfully operating and supplying people with drinking water. Rainfall quantity and timing are often insufficient in manyparts of the world to
#Explain Water Act 1979?(U3)= An Act to provide for the prevention and (4)Desalination Plants:This is a treatment method for saline or brackish water. provide crops with the moisture they need. (C) Hydropower: Hydropower is a
control of water pollution, and the maintaining or restoring of wholesomeness This method can be used to treat seawater or groundwater that has high salt safe, dependable, and renewable energy source that supports the goals of the
of water, for the establishment, with a view to carrying out the purposes concentrations and is therefore unfit for drinking. Salt concentration in highly country's environmental and energy policies. Hydropower uses the kinetic
aforesaid, of Boards for the prevention and control of water pollution, for saline water ranges from 10,000 to 35,000 parts per million (ppm). Freshwater energy of falling water to generateelectricity without using more water than
conferring on and assigning to such Boards powers and functions relating is defined as water with a salinity of less than 1,000 ppm. the environment naturally provides.(D)Ecology: The investigation of the
thereto and for matters connected therewith.WHEREAS it is expedient to elements Influencing species distribution and abundance.(E) Industrial
provide for the prevention and control of water pollution and the maintaining #Explain water resource projects and need of planning?(U4)= *The goals of demand of water: A variety of functions, such as air conditioning, sanitation,
or restoring of wholesomeness of water, for the establishment, with a view to water resources project planning may be by theuse of constructed facilities, or small-scale equipment cooling, and product processing make up industrial
carrying out the purposes aforesaid, of Boards for the prevention and control of structural measures or by management and legal techniques that do not water use. Water consumption is significantly influenced by the presence of
water pollution and for conferring on and assigning to such Boards powers and require constructedfacilities. The latter are called non- structural measures and industries in or near the city. Depending on the industry, a different amount of
functions relating there to. AND WHEREAS Parliament has no power to make may include rules to limit or control water and land use which complement or water is needed.(F)Navigation: When people and products are moved from
laws for the States with respect to any of the matters aforesaid except as substitute for constructed facilities.* Planning and management of water one location transported by water. From the perspective of energy
provided in articles 249 and 250 of the Constitution. AND WHEREAS in resources systems are essential due to following factors:(1) Severity of the conservation as well, the expansion of inland water to another via navigation,
pursuance of clause (1) of article 252 of the Constitution resolutions have been adverse consequences of droughts, floods and excessive pollution. These can they are transport or navigation is essential.
passed by all the Houses of the Legislatures of the States of Assam, Bihar, lead to.(a) Too little water due to growing urbanization, additional water
Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, requirements, in stream flow requirements etc. Measures should be taken to #Explain CWC roles and functions?(U5)= *Roles: 1. The Central Water
Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Tripura and West Bengal to the effect that the reduce the demand during scarcity times.(b)Too much water due to increased Commission of India has the responsibility of initiation and coordination of
matters aforesaid should be regulated in those States by Parliament by law. flood frequencies and also increase in water requirements due to increased schemes introduced by the Ministry of Jal Shakti.2 They include schemes that
#What is the Polluters Pay Principle?(U3)= The 'polluter pays principle states economic development on river floodplains,(c)Polluted water due to both are founded to conserve as well as control the water resource usage in the
that those who cause pollution should bear the costs of managing it to prevent industrial and household discharges.(2) Degradation of aquatic and riparian country and the States.3.The schemes launched also help in the fields of flood
harm to human health or the environments for example, a factory that systems due to river training and reclamation of floodplains for urban and management, irrigation activities, drinking water supply. hydroelectricity
generates a potentially toxic substance as a byproduct of its operations is Industrial evelopment, poor water quality due to discharges of pesticides, generation, etc.4. The CWC will consult the state government and central
typically held liable for its safe disposal The polluter pays principle one of fertilizers and wastewater effluents etc.(3) While port development requires government where required.*Functions :The commission is also vested with
several guiding principles for global sustainable development.The polluter pays deeper rivers, narrowing the river for shipping purposes will increase the flood the responsibilities of:(1)Management And Control Of Floods.(2)Checking
principle is enacted in environmental law to hold the party responsible for level.(4) River bank erosion and degradation of river bed upstream of the Financial Feasibility And Economic Vlability Of Different Irrigation Projects.
pollution liable for the damage done to the natural environment. Because of reservoirs may increase the flooding risks (5) Sediment accumulation in the (3)Collecting Compiling And Publishing The Analysed Hydrological Data In The
the strong support it has received in most Organization for Economic reservoir due to poor water quality. Country. (4)Construction, Development, Examination, And Implementation Of
Cooperation and Development (OECD) and European Union countries, it is The Schemes Necessary.
regarded as a regional custom.The polluter pays' principle essentially holds the #Decision making?(U4)= In general, water resource projects are very large and
polluter responsible for environmental pollution The polluter is responsible for involve large sums of money, which are frequently public. They compete with #Inter basin Water transfer?(U5)= Water transfer is the phrase used to
all environmental damage. So, under the 'polluter pays principle,' the polluter other societal needs and have an impact on many other aspects of society's describe the movement of water via engineering structures, typically across
must not only compensate the victims of pollution, but also compensate for the structure. As a result, the decision-making process that leads to the river basins, for a useful purpose. Inter-basin Water Transfer (IBWT), one of the
restoration of environmental degradation caused by pollution implementation of a water resources project is lengthy, and final decisions are potential remedies for a lack of water, resembles other options like dams,
According to OECD Recommendation (1)(2) of 1972 and 1974, the made at political and socioeconomic rather than technical levels.The basis for a desalination, groundwater extraction, etc. Transporting excess waterfrom one
measures to be taken by the polluter to control pollution are decided by decision on a water resources project is a plan that outlines the project's basin to another that lacks water is known as inter-basin water transfer.Inter-
public authorities so that the environment is in an acceptable state after the objectives as well as the means by which they are to be accomplished, their basin water transfer begins with an unsustainable scenario in the receiving
industry operation. APPLICATION: 1 green house gas emission 2.drinking costs, and the project's consequences in terms of benefits and negative impacts. basin because of the ongoing water shortages there. This will need the
water suppliers 3.industrial pollution 4.urban waste water treatment Water resource planning encompasses all activities that lead to such a plan. The transfer of water over significant distances, sometimes on the order of
broader the scope of the planning process, the larger the project and the more thousands of kilometres, if the surplus and deficit basins are notclose to one
#Explain the need of training to water user?(U3 )= Water user training is an intensive use of water resources. There are few water resource projects that another, which is quite commonly the case.Water is typically transported
important tool for capacity building and is required by all water organisations. have only local implications, and the majority of them must be viewed in the between basins using canals; ridges are crossed via tunnels and pipelines. The
The necessary shift in approach can be accomplished through specially designed broader context of regional, national or international development. final decision is contingent on the area's geography, climate, nearby soil
courses, modifications to university courses, and on-the-job training characteristics, and amount of water present.When a mountain must be
programmes. Any training must be incorporated into the terms of reference for #Global & National Perspectives of water crises?(U5)= A global perspective on traversed and the construction of a tunnel is impractical, many inter-
including water professionals, and adequate funding must be allocated to this water management predominates in high- level policy discussions. This has the basin transfer projects use pumping water in some
end.Trainer training is a specialised field that necessitates an understanding of advantage that over-arching issues can be highlighted and international sections.
adult learning methods as well as the importance of the peer group (farming resources mobilized. But water issues arise from local conditions and can only be
community, professional water community) in creating learning opportunities. resolved by people and Institutions with local authority and responsibility. High- #Dublin Principles?(U5)= A meeting in Dublin in 1922 gave rise to four
Many information exchange facilitators (for example, extension officers, field level policies can only have meaningful impact if they are informed by and principles that have been the basis for much of the mo water sector
guides, and field agents) have backgrounds in biophysical science and responsive to local and regional contexts. In keeping with the principle of reform.*Principle 1: Fresh water is a finite and vulnerable resource, essential
engineering and require cross-disciplinary training in communication, group subsidiarity, high level policy-making should support local and regional to sustain life, development and the environment.The idea that freshwater is
interaction facilitation, accounting, programme management, and interests, efforts, and policies.Developing nations have severe infrastructure a finite resource arises from the fact that the hydrological cycle produces a
counselling.Water resource management agencies must invest significantly in gaps. Uncontrolled human waste release and poor sewage treatment pose fixed amount of water per time period on average. This total quantity cannot
education programmes to train trainers in information exchange and serious health concerns to an estimated 2.5 billion people, mostly in low- and yet be significantly altered by human actions, but it can and frequently is
communication. In-service courses, seminars, and workshops are examples of middle-income nations.Poorly treated domestic and industrial effluents are depleted by man-made pollution. The freshwater resource is a natural asset
methods. There is a growing emphasis on electronic means of disseminating discharged, which degrades water quality in countries that are quickly that must be preserved in order to provide the desired services. This principle
information and training techniques, particularlydistance learning. industrialising, Water, energy, and nutrients must be recovered through waste recognizes that water is required for a variety of purposes, functions, and
management that is acceptable for the local environment.The lack of access to services; therefore, management must be holistic (integrated) and take into
#Causes of groundwater pollution(U3)-3. Hazardous Waste Disposal clean water and sanitary facilities has received attention from international account both the demands placed on the resource and the threats to
Photographic chemicals, motor oil, cooking oil, paint thinners, medicines, policy- making. particularly with the introduction of the Millennium it.*Principle 2: Water development and management should be based on a
swimming pool chemicals. . 4. Petroleum Products Petroleum storage tanks can Development Goals (MDGs). However, the sanitation objective is still unmet, participatory approach, involving users, planners and policymakers at all
we underground or above ground. Furthermore, petroleum products a primarily and urgent problems (such faecal sludge management) that affect access have levels.Water is a subject in which everyone is a stakeholder. Stakeholder
transported underground via pipeline Water Contamination can occur if these not been fully addressed. participation in the decision-making process is the only way to achieve true
substances leak ... 5. Solid Waste estimated that 0.3 to 0.6 kg Waste realesed participation. Depending on the spatial scale important to certain water
into ground per person per day in development countries. In contrast developed #Explain water as an economic good?(U4)= The concept of water as a management and investment decisions, the type of participation will vary. It
countries release 0.7 to 1 kg/person/day. These substances' chemicals are commodity is basic. Water has a value to its consumers, who are prepared to will also be impacted by the political climate in which such decisions are made.
leached into ground water yia precitation and surface runo ..6 Surface pay for it, just like any other good. Like with any other good, customers will The best method for building enduring consensus and common ground is a
compoundments –are shallow lagoons here liquid waste is stored. For example, utilize water as long as the advantages of using an extra cubic meter outweigh participatory approach.*Principle 3: Women play a central part in the
the country has over 180,000 surface These prevent leaching. 7. Agricultural the expenses associated with doing so.The ideal consumption is X".If a provision, management and safeguarding of water.*Principle 4: Water has an
Chemicals Milions of tonnes of agricultural chemicals, such as fertilisers and consumer is charged a price Pl that differs from the marginal cost of supply, economic value in all its competing uses and should be recognised as an
pesticides, are production around the world These chemicals are also used by they will instead consume X¹ instead of X'. There is a corresponding loss of net economic good as well as a social
other institutions, such as golt courses used to boost crop Excessive use of these benefits, also known as deadweight loss, when the increase in expenses (the
chemicals may result in groundwater contamination. .8 and Injection wells They area under the cost curve) exceeds the growth in benefits (the area under the
benefit curve).In general, the
#Management of Flood Plains?(U6)= Floodplain management is a community-
based effort to prevent or reduce the risk of flooding, resulting in a more resilient
community.The land close to a river bed that is more or less regularly submerged in
water during periods of heavy water discharge from nearby rivers is known as a
floodplain One kind of floodplain is a wand Floodplains can mitigate the effects of
heavy rainfall by holding onto water, preventing flood damage to downstream
populations and economic activity.Rivers can rise and spread out in floodplains,
relieving pressure on infrastructure during trial downpours In order to reduce flood
damage, supply clean water, recharge groundwater, and create open places for
recreation, we are providing towns with the tools and regulations they need to
connect flood plain Major floodplains roles have thus been lost, due to land
drainage, Intensive urbanization and river channelization. The objective is to
restore them, their retention capacity and ecosystem functions, by reconnecting
them to the river.*Strategies for Smarter Floodplain Management:(1)Land Use
Planning , (2) Watershed restoration , (3) Structural and Nonstructural solution, (4)
Design standards, (5) Disaster relief , (6) Community awareness, (7) Ecosystem
conservation , (8) Agricultural uses. IMPORTANCE FLOODPLAINS.1. FLOOD
PROTECTION .2.better water quality 3.they create extremely fertile areas for
agriculture.4.general improvements to habits.5.recreational usage.6.refilling
aquifers
#QGIS for IWRM?(U6)= QGIS is a desktop geographic information system (QGIS)
that provides viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of grographical data. It is free
and open-source across platforms. Early in 2002, Gary Sherman started working on
Quantum GIS, and in 2007, the Open Source Geospatial Foundation selected it as one
of its incubator incubator January 2009 saw the release of version 1.0.Geographic
information system (GIS) software performs the function of allowing users to
create, edit, and export graphical maps as well as analyse and modify spatial data,
Raster, vector, and mesh layers are supported by QGIS. Features such as points,
lines, or polygons make up vector data. The software can georeference images and
supports a variety of raster image formats. GRASS can also be accessed visually
with QGIS. Since QGIS requires less RAM and processing power than commercial
QGISs and has a smaller install footprint on the host file system, it can be utilised
on older hardware or run alongside other programmes whose CPU power may be
constrained. QGIS Applications in Water Resources(U6): QGIS has countless uses
in the field of water resources, and the list is constantly expanding.2. The use of
this method in conjunction with remote sensing is very cominon. When used to
manage input data and provide output in distributed modelling, QGIS is especially
useful.3. For instance, the Universal Soil Loss Equation is used to calculate long-
term soil erosion from agricultural fields (USLE). 4.The erosion values are provided
for bare standard plots at various slopes and these are altered by a number of
variables.5. The mean-annual soil erosion rates are obtained by utilising a QGIS to
overlay geographic data of various components and soils.
#Flood risk mapping and its advantage?(6U)= The process of determining the
geographic extent of danger is called mapping flood risk (combining information on
probability and consequences). Combining maps of risks and vulnerabilities is
necessary for risk mapping The outcomes of these studies are frequently displayed
as maps that illustrate the scope and makeup of the risk. These risk maps are an
important medium of communication in sustainable flood management. They may
help to transfer the risk information to the residents as they depict flood risk in a
colourful and easy understandable way. The most important resources for planning
land use in flood-prone locations are flood risk maps. Flood return times are
typically taken into account while selecting the fundamental mapping criteria.
Other times, the anticipated water depth or dynamic factors are utilised. Flood risk
maps are designed to increase awareness of the likelihood of flooding among the
public, local authorities and other organizations. They also encourage people living
and working in flood-prone areas to find out more about the local flood risk and to
take appropriate action. It is important to note, that climate change must be
carefully considered when implementing flood risk mapping Flood risk mapping
typically provides a 'snapshot' of flood risk at a given point in time. When
considering the effects of climate change however, it is important to consider the
dynamic nature of flood risks. For example, SLR and changes in storm intensity,
occurring as a result of climate change, will causes changes in the areas susceptible
to flooding.
*Advantages:Flood risk mapping will make it possible to estimate how many
homes or businesses are at risk of flooding. This will make it easier to gauge the
size of the response and cleanup efforts.Recognizes and preserves wetlands,
woods, and other habitats that might be useful for flood protection. Offers the
data required to put in place flood protection measures at locations with high
pollution risks (eg power plants, nuclear facilities, etc.).Offers the data required for
evaluations of vulnerability to flooding. Enhances planning for flood control and
response (prioritization of interventions).Enhances land-use planning by restricting
construction in flood-prone areas. Improves information basis for property, crop
and infrastructure insurance.
#State and explain Hydropower Generation and its components?(U6)= people
have used the force of falling water to poweruseful devices, such as water wheels
for the grinding of grains. The mechanical energy of falling water is transformed
into electrical energy by a turbine and generator to create hydroelectric energy.
One of the cleanest and most efficient ways to produce electricity is through the
use of hydropower, a renewable energy source that emits no pollution into the air
or water.In projects with multiple uses, the production of hydroelectric energy is
integrated with other purposes, such as Irrigation, water supply, etc., yielding in
significant cost and resource savings.Another advantage of hydropower over other
forms of electricity generation is that reservoirs can store water during times of low
demand and can quickly start generating during the peak hours of electricity use.
Thermal power plants take much longer to start up from cold than hydropower
plants.*components: The reservoir behind the dam serves as a storage facility for
the water utilised to produce electricity. Forebay refers to the area of the reservoir
that is directly upstream of the intake construction. Through an intake structure,
water is taken out of the forebay and transported via penstocks to the
powerhouse.Water is transported from the forebay to the turbines through a
penstock, which has gates and valves fitted to control the water flow. Alternatively,
open channels or tunnels may be employed, depending on the site conditions.To
solve the issues caused by water hammer, a surge tank is built. The power house
has the turbines and generators installed. The water comes out of turbines through
draft tube and joins the tail water.
#Short note on arbitration and importance?(U5)= *Defination:Arbitration is a
procedure in which a dispute is submitted, by agreement of the parties, to one or
more arbitrators who make a binding decision on the dispute.In choosing
arbitration, the parties opt for a private dispute resolution procedure instead of
going to court.*Its principal characteristics are: (1). Arbitration is consensual:Only
when both parties have consented to the arbitration process can begin. The parties
include an arbitration cause in the relevant contract for any potential future issues
emerging under it.(2).Abitration is neutral:In addition to their selection of neutrals
of appropriate nationality, parties are able to choose such important ments as the
applicable law, language and venue of the arbitration. This allows them to ensure
that no party enjoys home court advantage.(3).Arbitration is a confidential
procedure:The WIPO Rules specifically protect the confidentiality of the existence
of the arbitration, any disclosures made during that procedure, and the award. In
certain circumstances, the WIPO Rules allow a party to restrict access to trade
secrets.*Importance of Arbitration in IWRM:(1) Achieving Good Water
Governance(2) Securing Water for People , (3) Securing Water for food , (4) Water
for Ecosystems , (5) Managing Risks , (6) Valuing Water, (7) Water for industries
and cities.
#Soft computing techniques for flood forecasting?(U6)= One of the most recent
methods for creating systems with computational intelligence is called soft
computing. Artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, and genetic algorithms are just a
few of the several computing paradigms that soft computing tries to incorporate.
(1) Artificial Neural Networks (ANN):An artificial neural network is a form of
computing model that draws inspiration from biology and is loosely based on how
the human brain functions. It is more helpful to imagine a neural network as a
collection of straightforward processing nodes or neurons that performs an input-
output mapping.(2) Fuzzy Logic:The mathematics of fuzzy set theory, on which
fuzzy logic is founded, has changed the traditional idea of binary set membership to
accommodate partial membership ranging from 0 to
1. Fuzzy sets, as opposed to their crisp counterparts, contain ambiguous borders
and hence gradual transitions between defined sets, making it possible to directly
model the uncertainty related to these ideas.(3) Genetic Algorithms (GA):The
biological principles of natural selection and the survival of the fittest serve as the
inspiration for genetic algorithms (GAs), which are nonlinear search and
optimization techniques. Contrary to other approaches like hill climbing and
simulated annealing, a GA demonstrates implicit parallelism, taking into account a
large number of locations at once during the search process and lowering the
likelihood of convergent local optimum.
#Role of dams in flood control?(U6)= Dams are an important part of any city's
flood protection. They safeguard against the potential loss of life and property
caused by flooding. Dams prevent flooding by collecting and storing water when it
reaches a certain level A dam could be built to release water collected during the
monsoon season back into the river at a controlled rate or to divert the water
elsewhere for other purposes.A reservoir's water level should be kept below a
certain level before the monsoon season begins. This is done so that when the
monsoon rains arrive, there is enough space to store the excess rainwater and also
so that water can be released in a controlled manner, preventing floods
downstream when the dams are over flowing. A dam that is solely used for flood
control and has no conservation storage is referred to as a "dry dam" (e.g. Mount
Morris Dam, Seven Oaks Dam).
IMPORTANCE OF DAMS IN IWRM.1. Since the first great civilization emerged on
the major rivers in the third millennium BC, dams have been essential to growth.
Only modest dams were first constructed for irrigation and water supply.
2.According to a WCD research, 30-40% of the 271 million hectares of irrigated
areas worldwide depend on dams, and half of the world's big dams were
constructed completely or mostly for irrigation. 3. According to estimates, 12-16%
of the world's food output comes from dams. 4.A billion people or so rely on the
food that is produced by irrigation associated to reservoirs. No other method of
production could have been used to make this meal.
USE OF DAM. 1 WATER SUPPLY-- Dam reservoir water is used to provide adequate
amounts of quality freshwater to residential, industrial, and mining sites.
2.irrigation. In many countries, cropland irrigation is done using water stored
behind dams.3.electrial generation . Hydropower is considered clean because it
does not contribute to global warming, air pollution, acid rain, orozone depletion.4.
Flood Control. For centuries, people have built dams to help control devastating
floods. It helps to prevent the loss of life and property.5.WATER STORAGE. Dams
create reservoirs that supply water for uses, including industrial, municipal, and
agricultural.6.MINE TALLINDS. It allows the mining and processing of coal and other
vital minerals while protecting the environment.7.DEBRIS CONTROL. Dams provide
enhanced environmental protection, such as the retention of riskous materials and
detrimentalsedimentation.8.NAVIGATION.Dams and locks provide for a stable
system of Inland river transportation throughout the nation.
You might also like
- REVIEW OF AGRICULTURE: An Alternative Draft for ConsiderationDocument14 pagesREVIEW OF AGRICULTURE: An Alternative Draft for ConsiderationAsha ShivaramNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Water Resource ManagementDocument4 pagesA Review Paper On Water Resource ManagementIJNTR JournalNo ratings yet
- Community Participation in The ManagementDocument7 pagesCommunity Participation in The ManagementAbdulbady MandugayNo ratings yet
- Laguna University: Name of Students: 1. Tamban, Jonathan E. 2. Datay, Fernandez 3. Dizon, JayswarthDocument7 pagesLaguna University: Name of Students: 1. Tamban, Jonathan E. 2. Datay, Fernandez 3. Dizon, JayswarthJonathanE.TambanNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument31 pagesProposalElisante David100% (2)
- Chap 08. Water Supply and Sanitation 30nov06 UPFDocument7 pagesChap 08. Water Supply and Sanitation 30nov06 UPFWI Eys To SeNo ratings yet
- Intervention - MWWUG Resource Consent Application - Part 2 Substantive - Final - Blank Signoff - 22 Nov2017Document13 pagesIntervention - MWWUG Resource Consent Application - Part 2 Substantive - Final - Blank Signoff - 22 Nov2017Catherine Murupaenga-IkennNo ratings yet
- Cve 654 IwrmDocument10 pagesCve 654 IwrmAremu OluwafunmilayoNo ratings yet
- E-Handout For Water-Related LawsDocument10 pagesE-Handout For Water-Related LawsAlexandra EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument7 pagesWater ResourcesMohd GulzarNo ratings yet
- Water SupplyDocument21 pagesWater SupplyBrhane WeldegebrialNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management in IndiaDocument30 pagesWater Resource Management in IndiaY. DuttNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Water Resources Systems Planning and ManagementDocument67 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Water Resources Systems Planning and ManagementmelakuNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management: M O D U L E 3Document22 pagesWater Resource Management: M O D U L E 3Lavina Edward JosephNo ratings yet
- Improving sanitation and public health in coastal communitiesDocument60 pagesImproving sanitation and public health in coastal communitiesSasuki Uchiha Batuigas87% (15)
- Harrison Et Al-2016-Aquatic Conservation - Marine and Freshwater EcosystemsDocument19 pagesHarrison Et Al-2016-Aquatic Conservation - Marine and Freshwater Ecosystemsabdul saktiNo ratings yet
- Article Sustainable Use of Water ResourcesDocument7 pagesArticle Sustainable Use of Water Resourcesignacio.garcia11No ratings yet
- Environment PDFDocument35 pagesEnvironment PDF葉約翰No ratings yet
- M3.19-1 Nexus ReportDocument8 pagesM3.19-1 Nexus ReportJhampol Rosales MuñozNo ratings yet
- CWTS Handouts Water Sanitation and ConservationDocument8 pagesCWTS Handouts Water Sanitation and Conservationdaniel alexis rosalesNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Management Under Climate ChangeDocument17 pagesStormwater Management Under Climate ChangeJericho CulasteNo ratings yet
- S I W M S K: Ustainable Ntegrated Ater Anagement Tate of The NowledgeDocument19 pagesS I W M S K: Ustainable Ntegrated Ater Anagement Tate of The NowledgeMashaelNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Management in A Changing WorldDocument6 pagesWater Resources Management in A Changing Worldbolistipo717No ratings yet
- Mwingi Central Feasibility StudyDocument15 pagesMwingi Central Feasibility StudyBARET KAMUNZUNo ratings yet
- Saving Water For The Future Public Awareness of Water Usage and Water QualityDocument12 pagesSaving Water For The Future Public Awareness of Water Usage and Water QualityNURUL FARRAH LIEYANA BT SHAMSUL BAHARINo ratings yet
- Settings and IwrpmDocument17 pagesSettings and IwrpmShreeyashNo ratings yet
- I Nternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (Ijceronline - Com) Vol. 2 Issue. 7Document5 pagesI Nternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (Ijceronline - Com) Vol. 2 Issue. 7International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Hydro-Politics Edited by T. ADocument39 pagesHydro-Politics Edited by T. ATulu SenaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Perspective On Water Quality GoalsDocument14 pagesEcological Perspective On Water Quality GoalsJen CaceresNo ratings yet
- Status of Watershed Management in Brgy. Dolos, Bulan, Sorsogon As Perceived by LGU Officials, BWD Employees and Its Residents For C.Y 2017-2018.Document17 pagesStatus of Watershed Management in Brgy. Dolos, Bulan, Sorsogon As Perceived by LGU Officials, BWD Employees and Its Residents For C.Y 2017-2018.Bulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Ecologically Sustainable Water Management: Managing River Flows For Ecological IntegrityDocument19 pagesEcologically Sustainable Water Management: Managing River Flows For Ecological IntegrityilanatzubaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Water Resources Planning Managemen: Role ofDocument29 pagesHydrology Water Resources Planning Managemen: Role ofjonalyncabulloNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDocument17 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDany AguilarNo ratings yet
- Water Security and Related Issues in Sri LankaDocument13 pagesWater Security and Related Issues in Sri LankaErangaNo ratings yet
- National Water Policy - Govenment of India PDFDocument13 pagesNational Water Policy - Govenment of India PDFBalakrishna KNo ratings yet
- Law Environment and Development Journal: Indonesia - Law On Water Resources, 2004Document31 pagesLaw Environment and Development Journal: Indonesia - Law On Water Resources, 2004darusalaNo ratings yet
- Postel e Barthom JR, 2005Document11 pagesPostel e Barthom JR, 2005Elfany ReisNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Water Supply EngineeringDocument8 pagesChapter One Water Supply Engineeringحميد مجيدNo ratings yet
- Water: Water Security in A Changing Environment: Concept, Challenges and SolutionsDocument21 pagesWater: Water Security in A Changing Environment: Concept, Challenges and SolutionsNazirul CompNo ratings yet
- CHN - Water PollutionDocument2 pagesCHN - Water PollutionLemuel BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Integrated Water Resources Management: Dr. Ir - Anik Sarminingsih, MTDocument100 pagesIntegrated Water Resources Management: Dr. Ir - Anik Sarminingsih, MTVio Alma ClariscaNo ratings yet
- Pollution of Water Bodies - 1Document54 pagesPollution of Water Bodies - 1sk11983No ratings yet
- River Basins of Imo State For Sustainable Water Resources Management 2165 784X.1000134Document8 pagesRiver Basins of Imo State For Sustainable Water Resources Management 2165 784X.1000134Dozie OhaeriNo ratings yet
- Community Managed Water Hyacinth Control Pilot ProjectDocument8 pagesCommunity Managed Water Hyacinth Control Pilot ProjectRajithWNNo ratings yet
- 3.2. Too Much Water: Water Resources Systems Planning and ManagementDocument18 pages3.2. Too Much Water: Water Resources Systems Planning and Managementama kumarNo ratings yet
- Bij 04 00159Document7 pagesBij 04 00159Ezeckhiel Reese VillegasNo ratings yet
- Water Security For All: Reimagining WashDocument24 pagesWater Security For All: Reimagining WashKARL MARXNo ratings yet
- Journal Pwat 0000202Document4 pagesJournal Pwat 0000202Eduardo CohimNo ratings yet
- Water ShortageDocument34 pagesWater ShortageAllyiah100% (1)
- GIRHMeshesha-Khare2019 - RIEGO AGRICULTURA REVISARDocument12 pagesGIRHMeshesha-Khare2019 - RIEGO AGRICULTURA REVISARMILEIDY SABALA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Riverprotection PDFDocument7 pagesRiverprotection PDFMznalqadiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Water Resource Management - Principles and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesIntegrated Water Resource Management - Principles and Applicationsephrahimahadi2000No ratings yet
- Building Services: Semester FourDocument71 pagesBuilding Services: Semester FouraswathiNo ratings yet
- 2-4Document3 pages2-4SalehMSulaimanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Evolution of The Concept of IwrmDocument8 pages2.1 Evolution of The Concept of IwrmFred BamwineNo ratings yet
- Joy ProjectDocument46 pagesJoy ProjectMuhammadjamiu BelloNo ratings yet
- Introduction to IWRM - Integrated Water Resources ManagementDocument89 pagesIntroduction to IWRM - Integrated Water Resources Managementgebremeskel aregayNo ratings yet
- The Worth of Water: Designing Climate Resilient Rainwater Harvesting SystemsFrom EverandThe Worth of Water: Designing Climate Resilient Rainwater Harvesting SystemsNo ratings yet
- Global Water Security: Lessons Learnt and Long-Term ImplicationsFrom EverandGlobal Water Security: Lessons Learnt and Long-Term ImplicationsWorld Water CouncilNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- 12 - Determinations of Cut Off Vshale-Por-SwDocument26 pages12 - Determinations of Cut Off Vshale-Por-SwSyafrin Kultsum Naura AzzaNo ratings yet
- Brightwater Treatment ProcessDocument2 pagesBrightwater Treatment ProcessThierry RodriguesNo ratings yet
- National Green Tribunal Upholds Stricter Sewage Treatment StandardsDocument14 pagesNational Green Tribunal Upholds Stricter Sewage Treatment StandardsBhaskar Challa100% (1)
- BSC Summit Historical Trends in VS - CLVillanoyDocument14 pagesBSC Summit Historical Trends in VS - CLVillanoygerald hullezaNo ratings yet
- F12 Price Sheet Effective 1st October 2011Document84 pagesF12 Price Sheet Effective 1st October 2011Arunanshu MohantyNo ratings yet
- BY - SAURABH BARMAN (AWS Practical Lab Manual)Document16 pagesBY - SAURABH BARMAN (AWS Practical Lab Manual)SauRabh BaRmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Adopting Multi Use of Stormwater Management FacilitiesDocument24 pagesGuidelines For Adopting Multi Use of Stormwater Management FacilitiesMohamedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Contaminants and TestingDocument34 pagesChemical Contaminants and TestingMohammad Bahram MonibNo ratings yet
- LID Stormwater Guide Enhanced Grass SwaleDocument12 pagesLID Stormwater Guide Enhanced Grass SwaleMohamedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Soil Water EffectsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Soil Water EffectsNajeebullah MandokhailNo ratings yet
- Log Book 1Document4 pagesLog Book 1Shadman NowroseNo ratings yet
- CRESTHIL153Document59 pagesCRESTHIL153kurou hazamaNo ratings yet
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.1 Sanitary Piping SystemDocument6 pagesECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.1 Sanitary Piping SystemAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- Harden Properties of Concrete Using STP Treated Water & Untreated Wash WaterDocument5 pagesHarden Properties of Concrete Using STP Treated Water & Untreated Wash WaterChethan G V0% (1)
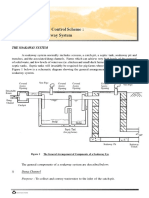
- UK Sub6 The Livestock Waste Control Scheme - Soakaway-SystemDocument5 pagesUK Sub6 The Livestock Waste Control Scheme - Soakaway-SystemLuiz AlvesNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures - 1Document5 pagesHydraulic Structures - 1ناهض عهد عبد المحسن ناهضNo ratings yet
- Handbook On RechargeDocument49 pagesHandbook On RechargeN.J. PatelNo ratings yet
- 40 KLD MBR QuoteDocument15 pages40 KLD MBR QuoteV Narasimha RajuNo ratings yet
- Pulsator TechnologyDocument2 pagesPulsator TechnologyDaniel Sanabria BarretoNo ratings yet
- 4a. PDC - 55 MLD MPS - Rev1Document6 pages4a. PDC - 55 MLD MPS - Rev1epe civil1No ratings yet
- Evaluating Septic Tank Systems at University of Port HarcourtDocument57 pagesEvaluating Septic Tank Systems at University of Port HarcourtNesru HamidNo ratings yet
- Aqualat® Anthracite Filter Media-19Document12 pagesAqualat® Anthracite Filter Media-19Dennis BoytsovNo ratings yet
- Review of Water and Wastewater TreatmentsDocument64 pagesReview of Water and Wastewater TreatmentsGelana ChulukeNo ratings yet
- 2009, Nalini S. RaoDocument11 pages2009, Nalini S. RaonataliaNo ratings yet
- Kulbhaskar Ashram PG College STP project presentationDocument16 pagesKulbhaskar Ashram PG College STP project presentationJuhi YadavNo ratings yet
- Manual For Precast Concrete Construction: by Ananda DevelopmentDocument1 pageManual For Precast Concrete Construction: by Ananda DevelopmentThanit ThanadirekNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDocument12 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Brunswick's ResolutionDocument2 pagesBrunswick's ResolutionJohanna Ferebee StillNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water Quality SDocument3 pagesDrinking Water Quality SDIOMER HERNAN ARISTIZABAL BUITRAGONo ratings yet
- Sanitary and Stormwater DrainageDocument15 pagesSanitary and Stormwater Drainagekrimchand1825No ratings yet