Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICND110S01L08
Uploaded by
Rudi Firmansah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesCCNA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCCNA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesICND110S01L08
Uploaded by
Rudi FirmansahCCNA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Connecting to an
Ethernet LAN
Building a Simple Network
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-1
Network Interface Card
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-2
Comparing Ethernet Media
Requirements
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-3
Differentiating Between Connections
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-4
1000BASE-T GBIC
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-5
Cisco Fiber-Optic GBICs
Short wavelength (1000BASE-SX)
Long wavelength/long haul (1000BASE-LX/LH)
Extended distance (1000BASE-ZX)
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-6
Unshielded Twisted-Pair Cable
Speed and throughput: 10 to 1000 Mb/s
Average cost per node: Least expensive
Media and connector size: Small
Maximum cable length: Varies
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-7
RJ-45 Connector
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-8
RJ-45 Jack
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-9
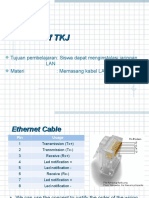
UTP Implementation (Straight-Through)
Cable 10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX Straight-Through Straight-Through Cable
Pin Label Pin Label
1 TX+ 1 TX+
2 TX- 2 TX-
3 RX+ 3 RX+
4 NC 4 NC
5 NC 5 NC
6 RX- 6 RX-
7 NC 7 NC Wires on cable ends
8 NC 8 NC are in same order.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-10
UTP Implementation (Crossover)
Cable 10BASE-T or
100BASE-TX Straight-Through Crossover Cable
EIA/TIA T568A EIA/TIA T568B
Pin Label Pin Label
1 TX+ 1 TX+
2 TX- 2 TX-
3 RX+ 3 RX+
4 NC 4 NC
5 NC 5 NC
6 RX- 6 RX-
7 NC 7 NC Some wires on cable
8 NC 8 NC ends are crossed.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-11
UTP Implementation: Straight-Through vs.
Crossover
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-12
Using Varieties of UTP
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-13
Summary
Also called a LAN adapter, the NIC plugs into a motherboard and
provides a port for connecting to the network.
The MAC address is burned onto each NIC by the manufacturer,
providing a unique, physical network address that permits the
device to participate in the network.
The cable and connector specifications used to support Ethernet
implementations are derived from the EIA/TIA standards body.
The categories of cabling defined for the Ethernet are derived
from the EIA/TIA-568 (SP-2840) Commercial Building
Telecommunications Wiring Standards.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-14
Summary (Cont.)
UTP cable is a four-pair wire. Each of the eight individual copper
wires in UTP cable is covered by an insulating material, and the
wires in each pair are twisted around each other.
A crossover cable is used to connect between similar devices
(such as switch to switch, router to router, PC to PC, and hub to
hub).
A straight-through cable is used to connect between dissimilar
devices (such as switch to router, switch to PC, hub to router, and
hub to PC).
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-15
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND1 v1.0—1-16
You might also like
- Connecting To An Ethernet LAN: Building A Simple NetworkDocument16 pagesConnecting To An Ethernet LAN: Building A Simple Networkธนวรรณ โภคาอนนต์No ratings yet
- Cabling in Internetwork: BSCI v3.0 - 2-1Document18 pagesCabling in Internetwork: BSCI v3.0 - 2-1Quân Lâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Cabling in Internetwork: BSCI v3.0 - 2-1Document18 pagesCabling in Internetwork: BSCI v3.0 - 2-1Quân Lâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer - Ethernet LAN - ARP - Physical PDFDocument58 pagesData Link Layer - Ethernet LAN - ARP - Physical PDFNguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Connecting To An Ethernet LAN: Building A Simple NetworkDocument17 pagesConnecting To An Ethernet LAN: Building A Simple NetworkKeepmoving NevergiveupNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document51 pagesLecture 7Mony JosephNo ratings yet
- Improving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDocument30 pagesImproving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionĐen Vs TrắngNo ratings yet
- CCNAv7 Equipment List October 2019Document2 pagesCCNAv7 Equipment List October 2019Jefry Gutiérrez CelisNo ratings yet
- Spec PTP 810i July2012Document6 pagesSpec PTP 810i July2012longDiamond 14No ratings yet
- 2015 AIS VoIP 0504Document37 pages2015 AIS VoIP 0504MBIEDA NGOMEGNI FRANK GAETANNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument23 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolGeelyn Faye FerminNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document34 pagesLec 3Muhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Cabling in Internetwork: Building A Simple NetworkDocument18 pagesCabling in Internetwork: Building A Simple NetworkViet Thang NguyenNo ratings yet
- PCB Layout For The Ethernet PHY Interface: Chassis Ground System GroundDocument6 pagesPCB Layout For The Ethernet PHY Interface: Chassis Ground System GroundJay PinedaNo ratings yet
- Improving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDocument30 pagesImproving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDuyHuynhNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument31 pagesPhysical LayerManar AdelNo ratings yet
- Mgate Mb3170/Mb3270 Quick Installation Guide: Edition 7.1, February 2016Document6 pagesMgate Mb3170/Mb3270 Quick Installation Guide: Edition 7.1, February 2016heikelNo ratings yet
- 9Ch NMEA (Serial) Ethernet GatewayDocument16 pages9Ch NMEA (Serial) Ethernet GatewayEvgeny YudinNo ratings yet
- 10baset, 100baset - 45 Connectors: A TutorialDocument6 pages10baset, 100baset - 45 Connectors: A TutorialGiz999100% (1)
- Local Area NetworkingDocument55 pagesLocal Area NetworkingparatosayoNo ratings yet
- Gigabit Crossover CableDocument22 pagesGigabit Crossover Cablegdfotky1No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Network: Bits Techno Development Pvt. Ltd. KolhapurDocument33 pagesBasic Computer Network: Bits Techno Development Pvt. Ltd. KolhapursurajNo ratings yet
- Manual-De-Usuario OkDocument28 pagesManual-De-Usuario OkERIKA VELANDIANo ratings yet
- LAN Ethernet CableDocument16 pagesLAN Ethernet CableNusa PerkasaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Part 2 1959036Document76 pagesUser Manual Part 2 1959036lu1040sgNo ratings yet
- The RS-485 Design Guide: Application ReportDocument9 pagesThe RS-485 Design Guide: Application ReportraghuNo ratings yet
- AR-727iV3: Part NO. AR-727i V3 AR-727CM V3Document4 pagesAR-727iV3: Part NO. AR-727i V3 AR-727CM V3jorge franco HerreraNo ratings yet
- Cabling 2Document16 pagesCabling 2Samah ElshariefNo ratings yet
- Cables and Connectors Printed Circuit Boards (PCBS) Packaging of Components & Ics Electronic InterconnectionsDocument35 pagesCables and Connectors Printed Circuit Boards (PCBS) Packaging of Components & Ics Electronic InterconnectionsARAVINDNo ratings yet
- ALU Devices and ConfigurationDocument76 pagesALU Devices and ConfigurationRichard ThainkhaNo ratings yet
- Site Engineering Technical Solution-P5ycj - V1.1 - 20170609第二批Document82 pagesSite Engineering Technical Solution-P5ycj - V1.1 - 20170609第二批Toewin Zaw100% (1)
- Tester Lan LCT-400Document1 pageTester Lan LCT-400jakogriNo ratings yet
- Quickserver Fs-Qs-2Xx0-F: Msa Grid-Fieldserver Manager Registration Connects YourDocument3 pagesQuickserver Fs-Qs-2Xx0-F: Msa Grid-Fieldserver Manager Registration Connects Yourarf.infinixNo ratings yet
- Mgate Mb3170/Mb3270 Quick Installation Guide: Version 8.1, November 2019Document7 pagesMgate Mb3170/Mb3270 Quick Installation Guide: Version 8.1, November 2019Abd AbdallahNo ratings yet
- CN510 PDFDocument5 pagesCN510 PDFhenryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document56 pagesLecture 6Mony JosephNo ratings yet
- 9 E4010E-01 (NEO Training Manual 20jun)Document106 pages9 E4010E-01 (NEO Training Manual 20jun)JuanNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Introduction NETWORKINGDocument7 pages1 Basic Introduction NETWORKINGdev chauhanNo ratings yet
- Optical Network Terminals: Trident7™ Ieee 802.3 EfmDocument5 pagesOptical Network Terminals: Trident7™ Ieee 802.3 EfmHo Siauw TjengNo ratings yet
- Moxa Nport S9450i Series Datasheet v1.2Document7 pagesMoxa Nport S9450i Series Datasheet v1.2vinay moogiNo ratings yet
- Study The Physical Media of Connectivity: Practical No. 1Document40 pagesStudy The Physical Media of Connectivity: Practical No. 1Ram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Devices: What Is Network?Document9 pagesDevices: What Is Network?Sunny_chdNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Proposed DesignDocument9 pages2.1 Proposed DesignSisay DesalegnNo ratings yet
- QuickServer FS-QS-2X10Document3 pagesQuickServer FS-QS-2X10Pio Wilde Quispe GarciaNo ratings yet
- Review of Wired NetworkDocument6 pagesReview of Wired NetworkssprudhviNo ratings yet
- Ethernet SwitchDocument5 pagesEthernet Switchabdulbaset alselwiNo ratings yet
- 5000s Equipment IntroductionDocument76 pages5000s Equipment IntroductionmoazamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument128 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingKapil TanejaNo ratings yet
- Carver School DatabaseDocument5 pagesCarver School DatabaseLost ContactNo ratings yet
- FibeAir IP-20E DatasheetDocument4 pagesFibeAir IP-20E DatasheetrgualbertNo ratings yet
- n2k c2248tp e DatasheetDocument6 pagesn2k c2248tp e Datasheetbonsai todayNo ratings yet
- 505-DataConv ActiSense All Products - Training NMEA 2000 13-4-2018Document17 pages505-DataConv ActiSense All Products - Training NMEA 2000 13-4-2018Antonio ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- BRKSEC-3020 Troubleshooting ASA FirewallsDocument136 pagesBRKSEC-3020 Troubleshooting ASA FirewallsPiyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Twisted Pair CablesDocument11 pagesTwisted Pair CablesSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Moxa Nport 6100 6200 Series Datasheet v1.0Document6 pagesMoxa Nport 6100 6200 Series Datasheet v1.0Fernando RamirezNo ratings yet
- Product Features: The Industrial Network CompanyDocument4 pagesProduct Features: The Industrial Network CompanyLuiyi Lazcano MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Ads 8509Document34 pagesAds 8509KoldodeRostovNo ratings yet
- Nettap 100: High-End Gateway For Industrial Automation NetworksDocument2 pagesNettap 100: High-End Gateway For Industrial Automation NetworkseloymaasturNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledtestNo ratings yet
- ICND110S06L02Document14 pagesICND110S06L02Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S04L03Document22 pagesICND110S04L03Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S03L04Document2 pagesICND110S03L04Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Functions of Routing: LAN ConnectionsDocument12 pagesExploring The Functions of Routing: LAN Connectionsamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- ICND110S04L02Document8 pagesICND110S04L02Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Discovering Neighbors On The NetworkDocument11 pagesDiscovering Neighbors On The NetworkAlberto García ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Switch Issues: Ethernet LansDocument13 pagesTroubleshooting Switch Issues: Ethernet Lansamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- 6-3 Configuring Serial EncapsulationDocument24 pages6-3 Configuring Serial Encapsulationsandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- ICND110S03L01Document11 pagesICND110S03L01Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S00Document15 pagesICND110S00Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Wlan: Wireless LansDocument13 pagesImplementing A Wlan: Wireless LansAbdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Module Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0-5-1Document4 pagesModule Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0-5-1meno25sNo ratings yet
- Icnd110s05l05 RipDocument21 pagesIcnd110s05l05 RipAbdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Module Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0 - 2-1Document3 pagesModule Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0 - 2-1Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Managing Cisco Devices: Network Environment ManagementDocument16 pagesManaging Cisco Devices: Network Environment Managementamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Packet DeliveryDocument37 pagesExploring The Packet DeliveryDang KhueNo ratings yet
- Module Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0 - 4-1Document4 pagesModule Summary: © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ICND1 v1.0 - 4-1Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Accessing Remote Devices: LAN ConnectionsDocument9 pagesAccessing Remote Devices: LAN Connectionsamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- ICND110LGDocument26 pagesICND110LGRudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S05L01Document15 pagesICND110S05L01Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Enabling Static Routing: WAN ConnectionsDocument11 pagesEnabling Static Routing: WAN Connectionsamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- ICND110S04L09Document12 pagesICND110S04L09Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Using The Cisco SDM: LAN ConnectionsDocument10 pagesUsing The Cisco SDM: LAN Connectionsamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- Understanding Switch Security: Ethernet LansDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Switch Security: Ethernet LansAbdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- ICND110S02L02Document13 pagesICND110S02L02Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Securing The Network: Building A Simple NetworkDocument11 pagesSecuring The Network: Building A Simple Networkamapreet.scorpioNo ratings yet
- ICND110S04L04Document16 pagesICND110S04L04Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S04L07Document7 pagesICND110S04L07Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- ICND110S02L03Document15 pagesICND110S02L03Rudi FirmansahNo ratings yet
- Lutron Integration ProtocolDocument136 pagesLutron Integration ProtocolAmy ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Network Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Document86 pagesNetwork Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Tariq EhsanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: - Non-Blocking Switching Fabric - Throughput Capacity 176 GbpsDocument5 pagesData Sheet: - Non-Blocking Switching Fabric - Throughput Capacity 176 GbpsHuy DoanNo ratings yet
- Understanding High Throughput Satellite (HTS) Technology: Sanjeev BhatiaDocument17 pagesUnderstanding High Throughput Satellite (HTS) Technology: Sanjeev BhatiasergioNo ratings yet
- Base Als1 CFGDocument7 pagesBase Als1 CFGJ Daniel FlorezNo ratings yet
- Multicast Live Video Broadcasting Using Real Time TransmissionDocument2 pagesMulticast Live Video Broadcasting Using Real Time Transmissionaruna2707No ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Chapter 3 - Transport LayerDocument11 pagesComputer Networks - Chapter 3 - Transport LayerNirzor LiveNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PDFDocument17 pagesCompany Profile PDFHari KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Major ProjectDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Major ProjectJAVAUGHN LEWISNo ratings yet
- F-R100 User Manual - Industrial Router - FourFaithDocument80 pagesF-R100 User Manual - Industrial Router - FourFaithmato3848No ratings yet
- Watchnet Bullet Mpix-40bivfDocument3 pagesWatchnet Bullet Mpix-40bivfSamastha Nair SamajamNo ratings yet
- Manual Usuario Grandstream GXP1405Document35 pagesManual Usuario Grandstream GXP1405alberto_03No ratings yet
- Beckhoff Training - 03 CX900x Comms & Hardware Setup 2011Document41 pagesBeckhoff Training - 03 CX900x Comms & Hardware Setup 2011marina890416100% (1)
- Reducing Ping-Pong Handovers in LTE by Using A1-Based MeasurementsDocument6 pagesReducing Ping-Pong Handovers in LTE by Using A1-Based Measurementssyed02No ratings yet
- Port SecurityDocument13 pagesPort SecurityharlanmaulanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Lecture Slide Switching IntroDocument46 pages1 Lecture Slide Switching IntroNebil AregaNo ratings yet
- P2CC Komunikator AngDocument2 pagesP2CC Komunikator Angsasahito100% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions PNPKIDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions PNPKIARNEL DE QUIROSNo ratings yet
- Salesforce - CRM Security Audit GuideDocument14 pagesSalesforce - CRM Security Audit GuideArthur EckleyNo ratings yet
- What Can We Do For Your Network?: SecureDocument6 pagesWhat Can We Do For Your Network?: SecureTV ZHNo ratings yet
- 175 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Chapter23Document3 pages175 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Chapter23saravkiruNo ratings yet
- SCR3310v2.0 USB Smart Card ReaderDocument2 pagesSCR3310v2.0 USB Smart Card ReaderDaniel DinisNo ratings yet
- Hadoop 2.0Document20 pagesHadoop 2.0krishan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Layer2 Network DesignDocument102 pagesLayer2 Network DesignAlex VillaNo ratings yet
- Wifi Hacking: Authentication Cracking MonitoringDocument1 pageWifi Hacking: Authentication Cracking Monitoringakunbuat yutubNo ratings yet
- OpenLDAP Admin GuideDocument264 pagesOpenLDAP Admin Guideindar.raajNo ratings yet
- 220 702Document164 pages220 702Vanina LorenaNo ratings yet
- DomiplexDocument2 pagesDomiplexbaskaranbNo ratings yet
- TerraDocument9 pagesTerrajamsuxNo ratings yet
- Load Balanced QuanggaDocument4 pagesLoad Balanced QuanggaAchmad MuzaqiNo ratings yet